Welcome to the Types Of Progressive Waves MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Types Of Progressive Waves Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Types Of Progressive Waves MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Types Of Progressive Waves MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
A progressive wave is defined as:
a) A wave that travels through a medium without any disturbance
b) A wave that travels from one point to another
c) A wave that remains stationary
d) A wave that oscillates around a fixed point
In a transverse wave, the oscillations are:
a) Parallel to the direction of wave travel
b) Perpendicular to the direction of wave travel
c) Randomly oriented
d) In phase with the wave source
Longitudinal waves are characterized by:
a) Oscillations perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
b) Oscillations parallel to the direction of wave propagation
c) Oscillations that do not propagate
d) Oscillations that are stationary
An example of a transverse wave is:
a) Sound wave
b) Light wave
c) Seismic P-wave
d) Pressure wave
An example of a longitudinal wave is:
a) Radio wave
b) Light wave
c) Sound wave
d) Electromagnetic wave
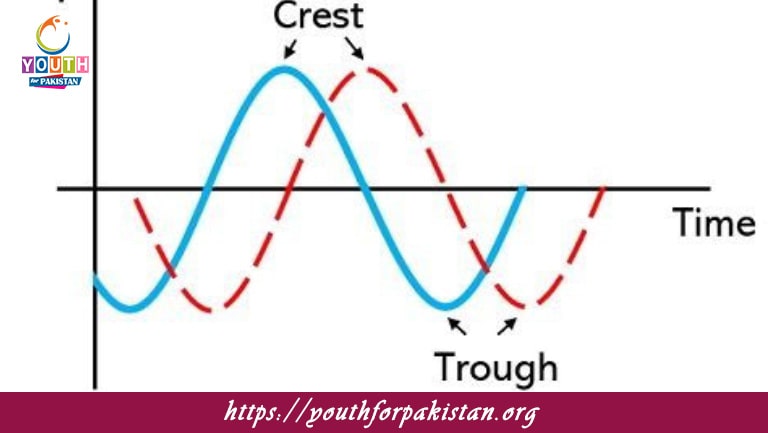
In a longitudinal wave, the regions where the particles are closest together are called:
a) Crests
b) Troughs
c) Compressions
d) Rarefactions
In a longitudinal wave, the regions where the particles are furthest apart are called:
a) Crests
b) Troughs
c) Compressions
d) Rarefactions
The speed of a wave is given by:
a) Frequency × Wavelength
b) Wavelength × Amplitude
c) Frequency / Wavelength
d) Amplitude / Frequency
The distance between two consecutive crests of a transverse wave is known as:
a) Amplitude
b) Wavelength
c) Frequency
d) Velocity
The maximum displacement of a particle from its mean position in a wave is called:
a) Wavelength
b) Frequency
c) Amplitude
d) Velocity
The number of oscillations or vibrations per unit time in a wave is referred to as:
a) Wavelength
b) Frequency
c) Amplitude
d) Velocity
If the frequency of a wave is doubled, its period:
a) Doubles
b) Halves
c) Stays the same
d) Quadruples
The time taken for one complete cycle of a wave is known as:
a) Frequency
b) Wavelength
c) Period
d) Amplitude
The phase difference between two waves is:
a) The difference in their frequencies
b) The difference in their amplitudes
c) The difference in their wavelengths
d) The difference in their phase angles
When two waves are in phase, they have:
a) A phase difference of 180 degrees
b) A phase difference of 90 degrees
c) A phase difference of 0 degrees
d) A phase difference of 360 degrees
When two waves are out of phase by 180 degrees, they:
a) Constructively interfere
b) Disperse
c) Destructively interfere
d) Are in resonance
The principle of superposition states that:
a) The total displacement is the algebraic sum of displacements from individual waves
b) The total energy is the sum of energies of individual waves
c) Waves combine to form a single wave
d) Waves never interfere with each other
The speed of a wave on a string depends on:
a) The tension in the string and the mass per unit length
b) The frequency and amplitude
c) The phase difference between waves
d) The wavelength and period
When a wave is reflected from a fixed boundary, it:
a) Inverts
b) Does not invert
c) Changes speed
d) Changes frequency
In a progressive wave, the energy transported is proportional to:
a) The square of the amplitude
b) The amplitude
c) The wavelength
d) The frequency
A standing wave is formed by:
a) The superposition of two traveling waves moving in opposite directions
b) The reflection of a wave from a boundary
c) The interference of waves moving in the same direction
d) A single wave traveling through a medium
The points of maximum displacement in a standing wave are called:
a) Nodes
b) Antinodes
c) Crests
d) Troughs
The points of minimum displacement in a standing wave are called:
a) Nodes
b) Antinodes
c) Crests
d) Troughs
The distance between two consecutive nodes in a standing wave is:
a) Half of the wavelength
b) One wavelength
c) Twice the wavelength
d) One-fourth of the wavelength
In a standing wave, the distance between two consecutive antinodes is:
a) Half of the wavelength
b) One wavelength
c) Twice the wavelength
d) One-fourth of the wavelength
The Doppler effect is observed when:
a) There is a change in the frequency of a wave due to relative motion between the source and the observer
b) Two waves combine to form a standing wave
c) Waves reflect from a boundary
d) Waves pass through a medium without interference
The phenomenon where waves pass through a small opening and spread out is called:
a) Reflection
b) Refraction
c) Diffraction
d) Interference
The phenomenon where two waves combine to form a resultant wave is known as:
a) Reflection
b) Refraction
c) Interference
d) Diffraction
When a wave travels from one medium to another, it changes:
a) Frequency
b) Wavelength
c) Speed
d) Both b and c
The bending of waves around obstacles or openings is known as:
a) Reflection
b) Refraction
c) Diffraction
d) Absorption
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of:
a) Refraction
b) Reflection
c) Diffraction
d) Absorption
The change in direction of a wave as it passes from one medium to another is called:
a) Reflection
b) Refraction
c) Diffraction
d) Interference
The principle of superposition can be used to explain:
a) The formation of standing waves
b) The reflection of waves
c) The Doppler effect
d) The dispersion of light
The speed of a wave depends on:
a) The properties of the medium
b) The frequency of the wave
c) The amplitude of the wave
d) The phase of the wave
The speed of sound in air is:
a) Greater than the speed of light
b) Less than the speed of light
c) Equal to the speed of light
d) Independent of the medium
A wave that oscillates in a single plane is called:
a) Longitudinal wave
b) Transverse wave
c) Polarized wave
d) Standing wave
In a polarized light wave, the electric field oscillates in:
a) Random directions
b) A single plane
c) Multiple planes
d) A circular path
The phenomenon where the amplitude of a wave varies with time is called:
a) Interference
b) Doppler effect
c) Modulation
d) Diffraction
The energy carried by a wave is proportional to:
a) The square of the frequency
b) The amplitude of the wave
c) The wavelength of the wave
d) The phase of the wave
The distance traveled by a wave in one period is equal to:
a) Its wavelength
b) Twice its wavelength
c) Its amplitude
d) Its frequency
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.