Welcome to the Time Period MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Time Period Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Time Period MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Time Period MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
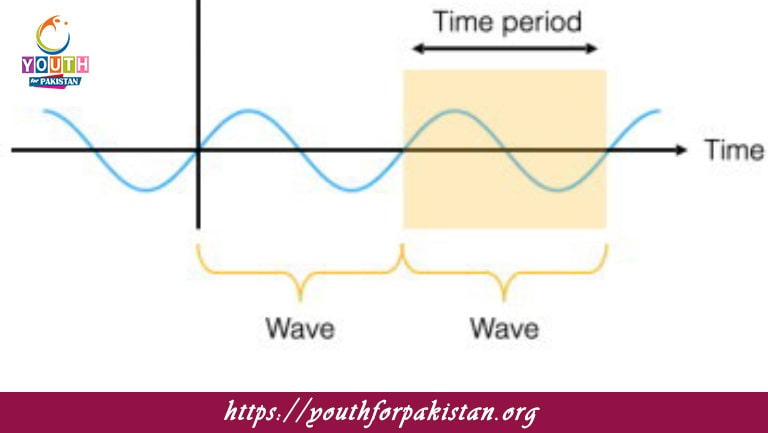
The time period of a wave is defined as:
a) The number of waves passing a point per second
b) The distance between successive wave crests
c) The time taken for one wave to pass a point
d) The speed at which the wave travels
The unit of the time period is:
a) Hertz (Hz)
b) Seconds (s)
c) Meters (m)
d) Joules (J)
The time period of a wave is the reciprocal of its:
a) Speed
b) Frequency
c) Wavelength
d) Amplitude
If the frequency of a wave is 20 Hz, its time period is:
a) 0.02 s
b) 0.05 s
c) 0.1 s
d) 5 s
The time period of a pendulum depends on:
a) The mass of the pendulum bob
b) The length of the pendulum
c) The amplitude of the swing
d) The density of the pendulum bob
The time period of a simple harmonic oscillator is proportional to:
a) The square root of its mass
b) The square root of the spring constant
c) The square of its amplitude
d) The inverse of the spring constant
For a pendulum, the time period is independent of:
a) Length of the pendulum
b) Acceleration due to gravity
c) Mass of the pendulum bob
d) Amplitude of oscillation
The time period of a wave can be found using the formula:
a) T = 1/f
b) T = f/λ
c) T = v/λ
d) T = λ/v
In a simple pendulum, doubling the length of the pendulum will:
a) Double the time period
b) Halve the time period
c) Increase the time period by a factor of 4
d) Decrease the time period by a factor of 4
The time period of a vibration in a string is affected by:
a) The tension in the string
b) The density of the medium
c) The length of the string
d) The amplitude of vibration
The time period of a pendulum is given by:
a) T = 2π√(L/g)
b) T = 2π√(g/L)
c) T = 1/√(L/g)
d) T = 1/√(g/L)
The time period of a mass-spring system is given by:
a) T = 2π√(m/k)
b) T = 2π√(k/m)
c) T = m/2π√(k)
d) T = k/2π√(m)
The time period of a vibrating tuning fork is related to its:
a) Material
b) Length
c) Frequency
d) Temperature
The time period of a wave in a string is determined by:
a) The tension in the string
b) The speed of the wave
c) The mass of the string
d) The length of the string
If a pendulum takes 2 seconds to complete one oscillation, its frequency is:
a) 0.5 Hz
b) 1 Hz
c) 2 Hz
d) 4 Hz
The time period of a wave is measured in:
a) Hertz
b) Joules
c) Seconds
d) Meters
For a mass-spring system, increasing the mass will:
a) Increase the time period
b) Decrease the time period
c) Have no effect on the time period
d) Double the time period
The time period of a simple harmonic oscillator is independent of:
a) The amplitude of oscillation
b) The mass of the oscillator
c) The spring constant
d) The frequency of oscillation
If the time period of a wave is 0.1 seconds, its frequency is:
a) 10 Hz
b) 100 Hz
c) 1 Hz
d) 0.1 Hz
The time period of an oscillation in a mass-spring system is affected by:
a) The amplitude of oscillation
b) The temperature
c) The mass of the object
d) The initial velocity
The time period of a wave traveling in a medium with increased density will:
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Remain unchanged
d) Depend on the frequency
The time period of a vibrating guitar string depends on:
a) The tension in the string
b) The thickness of the string
c) The length of the string
d) All of the above
The time period of a pendulum is given by:
a) T = 2π√(L/g)
b) T = 2π√(g/L)
c) T = L/g
d) T = √(L/g)
The time period of a wave is inversely related to:
a) The amplitude
b) The speed of the wave
c) The wavelength
d) The frequency
The time period of a vibrating object can be measured using:
a) A stopwatch
b) A thermometer
c) A voltmeter
d) A barometer
The time period of a harmonic oscillator is affected by:
a) The amplitude of oscillation
b) The mass of the oscillating body
c) The damping force
d) The frequency of oscillation
The time period of a mass-spring system can be calculated using:
a) T = 2π√(k/m)
b) T = 2π√(m/k)
c) T = m/2π√(k)
d) T = k/2π√(m)
In a vibrating string, the time period depends on:
a) The tension in the string
b) The mass per unit length of the string
c) The length of the string
d) All of the above
The time period of an oscillation can be found using:
a) The frequency and its reciprocal
b) The wavelength and speed
c) The amplitude and frequency
d) The temperature and pressure
The time period of a pendulum increases with:
a) The decrease in length
b) The increase in mass
c) The increase in length
d) The decrease in gravitational acceleration
The time period of a wave in a medium depends on:
a) The medium’s properties
b) The wave’s speed
c) The frequency of the wave
d) The wave’s amplitude
The time period of a mass-spring system increases if:
a) The mass is decreased
b) The spring constant is increased
c) The mass is increased
d) The amplitude is increased
The time period of a simple pendulum in a vacuum is:
a) Independent of the medium
b) Affected by air resistance
c) Directly proportional to air density
d) Directly proportional to temperature
The time period of a harmonic oscillator with a higher spring constant is:
a) Longer
b) Shorter
c) Unchanged
d) Zero
The time period of a wave in water is determined by:
a) The wave’s frequency
b) The water’s density
c) The wavelength of the wave
d) The wave’s speed
The time period of a wave in a rope is affected by:
a) The tension in the rope
b) The length of the rope
c) The mass of the rope
d) All of the above
The time period of a wave can be found by:
a) Measuring the time for multiple wavelengths
b) Measuring the speed of the wave
c) Measuring the amplitude
d) Measuring the wavelength
For a vibrating string, increasing the tension will:
a) Increase the time period
b) Decrease the time period
c) Have no effect on the time period
d) Double the time period
The time period of a pendulum is approximately given by:
a) 2π√(L/g)
b) 2π√(g/L)
c) π√(L/g)
d) π√(g/L)
The time period of an oscillating system with greater damping:
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remains unchanged
d) Becomes zero
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.