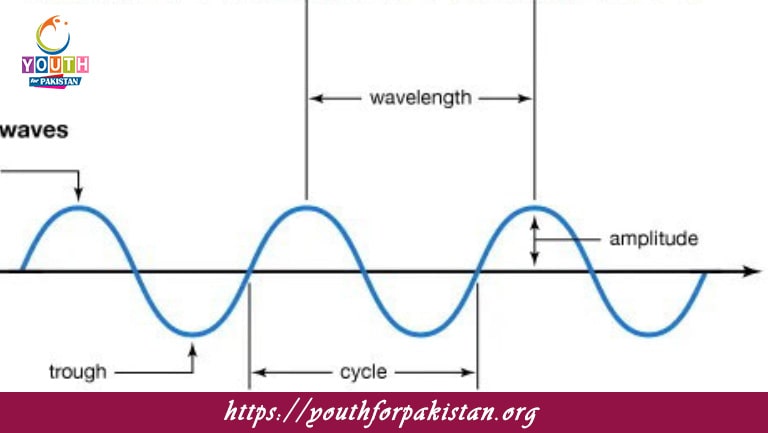
Welcome to the Longitudinal Waves MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Longitudinal Waves Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Longitudinal Waves MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Longitudinal Waves MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
Longitudinal waves are characterized by particle displacement that is:
A) Perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
B) Parallel to the direction of wave propagation
C) Circular to the direction of wave propagation
D) Random to the direction of wave propagation
In a longitudinal wave, compressions are regions of:
A) High pressure
B) Low pressure
C) Zero pressure
D) Constant pressure
Rarefactions in longitudinal waves are regions of:
A) High density
B) Low density
C) Zero density
D) Constant density
The speed of sound in air primarily depends on:
A) Temperature
B) Humidity
C) Pressure
D) Altitude
Which of the following is not an example of a longitudinal wave?
A) Sound wave
B) Seismic P-wave
C) Light wave
D) Pressure wave
The distance between two consecutive compressions in a longitudinal wave is called the:
A) Wavelength
B) Amplitude
C) Frequency
D) Period
What type of wave is used in ultrasound imaging?
A) Transverse wave
B) Longitudinal wave
C) Electromagnetic wave
D) Surface wave
The frequency of a longitudinal wave can be determined by:
A) The speed of the wave and its wavelength
B) The amplitude of the wave
C) The density of the medium
D) The pressure changes in the wave
In which medium does sound travel the fastest?
A) Air
B) Water
C) Steel
D) Wood
When the frequency of a longitudinal wave is increased, its wavelength:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains the same
D) Doubles
The term “phase” in a longitudinal wave refers to:
A) The position of a wave crest
B) The distance between rarefactions
C) The particle’s displacement from equilibrium
D) The specific location in the wave cycle
What phenomenon causes a change in the frequency of sound due to the relative motion of the source and observer?
A) Reflection
B) Refraction
C) Doppler effect
D) Diffraction
The unit of frequency is:
A) Hertz (Hz)
B) Meter (m)
C) Second (s)
D) Newton (N)
In longitudinal waves, the amplitude refers to:
A) The distance between two consecutive rarefactions
B) The maximum displacement of particles from their equilibrium position
C) The time period of one complete cycle
D) The speed of wave propagation
A sound wave traveling through water will have a wavelength that is:
A) Longer than in air
B) Shorter than in air
C) The same as in air
D) Independent of the medium
The speed of sound in a medium increases with:
A) Decreasing temperature
B) Increasing temperature
C) Increasing density
D) Decreasing density
The term “compression” in a longitudinal wave refers to:
A) The region where particles are farthest apart
B) The region where particles are closest together
C) The point of equilibrium
D) The maximum displacement in the opposite direction
Which of the following factors does not affect the speed of sound?
A) Medium
B) Temperature
C) Frequency
D) Humidity
The phenomenon of sound bending around obstacles is known as:
A) Reflection
B) Refraction
C) Diffraction
D) Absorption
In a longitudinal wave, the regions of maximum particle displacement occur at:
A) Compressions and rarefactions
B) Only compressions
C) Only rarefactions
D) Equidistant points
The relationship between the speed of sound, its frequency, and wavelength is given by the formula:
A) v = f * λ
B) v = λ / f
C) v = f / λ
D) v = λ + f
In which of the following media does sound travel slowest?
A) Air
B) Water
C) Steel
D) Mercury
A wave with a higher frequency will have:
A) A longer wavelength
B) A shorter wavelength
C) The same wavelength
D) A constant speed
The phenomenon where sound waves bounce back after hitting a surface is called:
A) Refraction
B) Reflection
C) Diffraction
D) Absorption
The part of a longitudinal wave where particles are furthest apart is called:
A) Compression
B) Rarefaction
C) Crest
D) Trough
The Doppler effect is most commonly observed with:
A) Light waves
B) Water waves
C) Sound waves
D) Seismic waves
What happens to the speed of sound as you go from a solid to a liquid and then to a gas?
A) It increases
B) It decreases
C) It remains constant
D) It first increases and then decreases
The principle behind a stethoscope is based on:
A) Reflection of sound waves
B) Diffraction of sound waves
C) Compression and rarefaction
D) The Doppler effect
Sound waves travel through which of the following best?
A) A vacuum
B) Air
C) Water
D) None of the above
The frequency of a wave is defined as:
A) The distance traveled in one second
B) The number of waves passing a point per second
C) The speed at which the wave travels
D) The distance between two consecutive crests
A medium that supports longitudinal waves must be:
A) Rigid and incompressible
B) Elastic and compressible
C) Elastic and incompressible
D) Rigid and compressible
When two sound waves of slightly different frequencies interfere, the phenomenon observed is called:
A) Constructive interference
B) Destructive interference
C) Beats
D) Diffraction
The wavelength of a longitudinal wave is measured from:
A) Peak to peak
B) Crest to crest
C) Compression to compression
D) Rarefaction to rarefaction
The property of a medium that affects how fast sound travels through it is:
A) Its density and elasticity
B) Its color
C) Its temperature
D) Its shape
In a longitudinal wave, the term “frequency” refers to:
A) The distance between two consecutive compressions
B) The number of waves passing a point per second
C) The amplitude of the wave
D) The speed of the wave
The region where particles are closer together in a longitudinal wave is called:
A) Rarefaction
B) Trough
C) Compression
D) Crest
Which of the following is a correct statement about longitudinal waves?
A) They require a medium to travel through
B) They travel faster in a vacuum than in a medium
C) They have no amplitude
D) They only travel through solids
The sound of a jet plane increases in pitch as it approaches and decreases as it moves away due to:
A) Reflection
B) Absorption
C) The Doppler effect
D) Diffraction
If a longitudinal wave is traveling through a medium and the frequency of the wave is doubled, the wavelength will:
A) Double
B) Halve
C) Stay the same
D) Be quadrupled
The speed of sound in a medium is directly proportional to the:
A) Density of the medium
B) Temperature of the medium
C) Frequency of the sound
D) Amplitude of the sound
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.