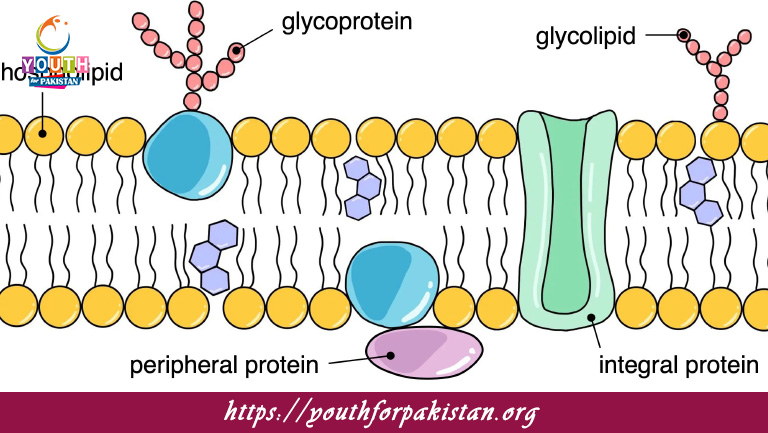
Welcome to the Fluid Mosaic Model MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Fluid Mosaic Model Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Biology offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Fluid Mosaic Model MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Who proposed the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane?
a) Watson and Crick
b) Singer and Nicolson
c) Schleiden and Schwann
d) Hooke and Leeuwenhoek
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the:
a) Nucleus
b) Cell Membrane
c) Mitochondria
d) Golgi Apparatus
The “fluid” part of the fluid mosaic model refers to the movement of which component?
a) Proteins
b) Lipids
c) Carbohydrates
d) Nucleic Acids
Which type of lipid is most abundant in the cell membrane?
a) Triglycerides
b) Phospholipids
c) Cholesterol
d) Glycolipids
The phospholipid bilayer has hydrophobic tails made of:
a) Fatty Acids
b) Proteins
c) Water Molecules
d) Carbohydrates
In the fluid mosaic model, what forms the “mosaic” part of the membrane?
a) Lipids
b) Proteins
c) Carbohydrates
d) Nucleic Acids
Which component of the cell membrane helps to maintain its fluidity?
a) Cholesterol
b) Phospholipids
c) Carbohydrates
d) Proteins
What type of proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer?
a) Integral Proteins
b) Peripheral Proteins
c) Glycoproteins
d) Enzymatic Proteins
Peripheral proteins are found:
a) Embedded within the membrane
b) Attached to the membrane surface
c) Inside the cytoplasm
d) Within the nucleus
Which of the following is a function of membrane proteins?
a) Energy Storage
b) Transport of Molecules
c) DNA Replication
d) Protein Synthesis
In the fluid mosaic model, how do proteins typically move?
a) They are fixed in place
b) They move laterally along the membrane
c) They move vertically in the membrane
d) They move outside the cell
The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face:
a) Toward the outside of the membrane
b) Toward the inside of the membrane
c) Toward the water
d) Both outside and inside the membrane
Which type of molecules can easily pass through the cell membrane without assistance?
a) Large Polar Molecules
b) Small Nonpolar Molecules
c) Ions
d) Proteins
The cell membrane is selectively permeable due to the presence of:
a) Cholesterol
b) Carbohydrates
c) Phospholipids
d) Proteins
Which of the following increases the fluidity of the cell membrane?
a) Saturated Fatty Acids
b) Cholesterol at low temperatures
c) Cholesterol at high temperatures
d) More Integral Proteins
Glycoproteins in the cell membrane function primarily as:
a) Transport Channels
b) Enzymes
c) Cell Recognition Markers
d) Structural Support
Which of the following best describes the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
a) Provides energy to the cell
b) Increases membrane permeability
c) Stabilizes membrane fluidity
d) Acts as a receptor
The asymmetric distribution of lipids in the cell membrane is important for:
a) Membrane Stability
b) Energy Storage
c) Membrane Flexibility
d) Cell Signaling
Which molecule is not found in the cell membrane?
a) DNA
b) Phospholipids
c) Cholesterol
d) Proteins
The fluidity of the membrane is influenced by the presence of:
a) Ribosomes
b) ATP
c) Phospholipids and Cholesterol
d) mRNA
What is the role of glycolipids in the cell membrane?
a) Transport of ions
b) Cell Recognition
c) DNA Replication
d) ATP Production
The cell membrane is described as “fluid” because:
a) Lipids and proteins can move laterally within the layer
b) It has a rigid structure
c) It dissolves in water
d) It contains only proteins
Which of the following molecules acts as a receptor in the cell membrane?
a) Glycolipids
b) Cholesterol
c) Glycoproteins
d) Phospholipids
Cholesterol in the cell membrane reduces fluidity at:
a) High temperatures
b) Low temperatures
c) Room temperature
d) All temperatures
What makes the cell membrane impermeable to water-soluble substances?
a) The hydrophilic phosphate heads
b) The hydrophobic fatty acid tails
c) The cholesterol molecules
d) The protein channels
The fluid mosaic model of the membrane allows for:
a) Rigid and stable structure
b) Flexibility and movement
c) DNA Replication
d) No permeability
Which type of molecules cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer without assistance?
a) Gases like O₂ and CO₂
b) Small Nonpolar Molecules
c) Ions and Large Polar Molecules
d) Water
What is the role of protein channels in the cell membrane?
a) Synthesize DNA
b) Control what enters and exits the cell
c) Stabilize membrane fluidity
d) Store genetic information
The fluid mosaic model is described as “mosaic” because of the:
a) Embedded cholesterol
b) Patchwork of proteins in the membrane
c) Double layer of phospholipids
d) Presence of enzymes
Integral proteins span the:
a) Cytoplasm
b) Entire membrane
c) Outside of the cell
d) Cell wall
Which of the following statements about the fluid mosaic model is true?
a) Membranes are rigid structures
b) Phospholipids can move laterally within the membrane
c) Proteins are only found on the surface
d) Cholesterol is absent
What is the major function of glycoproteins in the membrane?
a) Energy storage
b) Protein synthesis
c) Cell-cell recognition
d) DNA replication
Which of the following is NOT a component of the fluid mosaic model?
a) Phospholipids
b) Proteins
c) DNA
d) Cholesterol
The hydrophilic regions of the phospholipids in the cell membrane face:
a) Each other
b) The cytoplasm and the extracellular fluid
c) Only the cytoplasm
d) Only the extracellular fluid
Which molecules are responsible for the structural integrity of the cell membrane?
a) Proteins and Cholesterol
b) Nucleic Acids
c) Carbohydrates
d) Lipids and ATP
Which of the following increases the permeability of the membrane to small molecules?
a) Cholesterol
b) Saturated fatty acids
c) Unsaturated fatty acids
d) Integral proteins
Phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged in a:
a) Single layer
b) Triple layer
c) Bilayer
d) None of the above
Which of the following statements is true about cell membranes?
a) Membranes are impermeable to gases
b) Cholesterol increases membrane fluidity at low temperatures
c) All membrane proteins are peripheral
d) Phospholipids are hydrophobic molecules
Which of the following best describes the structure of the cell membrane?
a) Solid and rigid
b) Flexible and fluid
c) Static and immobile
d) Water-soluble
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.