Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers

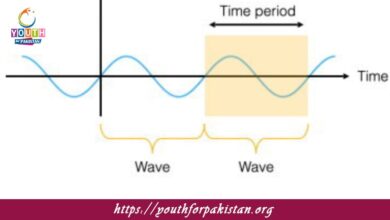
Waves MDCAT Quiz are oscillations or disturbances that transfer energy from one point to another without the physical transfer of matter. They are ubiquitous in many areas of physics and are integral to understanding a range of phenomena, such as sound, light, and electromagnetic radiation. In the context of the MDCAT exam, waves form a very important topic, and students need to understand the different types of waves, their properties, and their mathematical descriptions.
MDCAT Quiz: Waves Questions
In the MDCAT Quiz, students may be asked to calculate the properties of waves or solve problems involving the behavior of waves. For example, students might need to calculate the wavelength of a wave given its speed and frequency or determine the frequency of a wave when its wavelength and speed are known. Students might also be asked to distinguish between different types of waves, such as mechanical and electromagnetic waves, and understand the properties that characterize them.
- Test Name: Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Waves
Free flashcards on the topic of waves can thus be a very useful tool for MDCAT students to revise all the key concepts, such as properties of waves, differences between transverse and longitudinal waves, and formulas for wave speed, frequency, and wavelength. These flashcards may have examples, definitions, and practice problems on them—thereby becoming the best tool to ace the topic of waves and to definitely succeed in the MDCAT Quiz. Reviewing these flashcards will allow students to gain confidence in solving wave-related questions efficiently.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.