Types Of Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
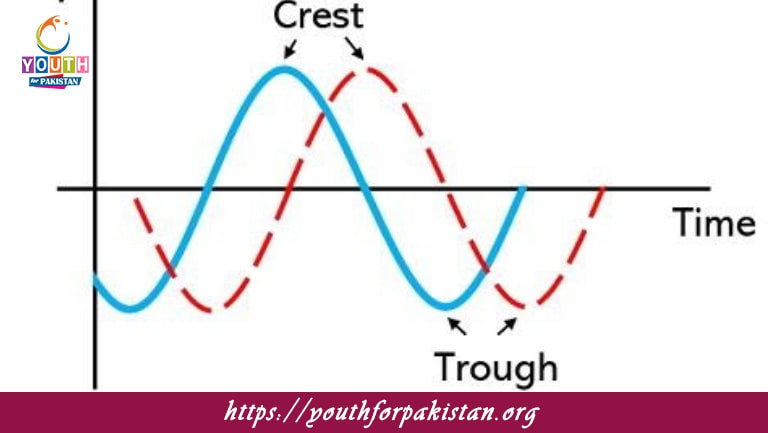
Types Of Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz are those waves that transfer energy from one place to another without any material displacement of the medium itself. Two main types can be classified: transverse and longitudinal waves. Both forms exhibit wave-like properties such as amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and speed, but they differ in how the particles of the medium move relative to the direction of wave propagation. MDCAT students must realize the differences that exist between these two types of waves, as both are very important and necessary for solving wave-related questions in the exam.
MDCAT Quiz: Types of Progressive Waves Questions
In the MDCAT Quiz, questions related to types of progressive waves may be about distinguishing between transverse and longitudinal waves. One may ask the student to describe the type of wave given its characteristics—say, the motion of the particles—or provide examples of each type in some real applications. Moreover, application in questions that require students to solve wave-related problems using concepts such as wavelength, amplitude, and frequency with respect to either transverse or longitudinal waves might be asked.
- Test Name: Types Of Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Types of Progressive Waves
Free flashcards focused on the types of progressive waves can be a useful study tool for MDCAT students. These flashcards can include diagrams comparing transverse and longitudinal waves, along with definitions and examples for each type. Students can review the differences in particle motion, energy transfer, and wave behavior, which will aid in solving questions related to wave properties in the MDCAT Quiz. Regularly reviewing these flashcards will strengthen students’ ability to identify and apply the concepts of both wave types efficiently.

A type of progressive wave where particles move perpendicular to the wave’s direction is called ____.

The main feature of a transverse wave is that the particles move ____ to the direction of propagation.

A wave that travels in a medium and displaces the particles in the direction of the wave is a ____ wave.

The direction of particle displacement in a transverse wave is ____ to the direction of energy transfer.

The main difference between transverse and longitudinal waves is that in transverse waves, particles move ____ to the wave’s motion.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.