Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Transverse Periodic Waves Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Transverse Periodic Waves MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
In a transverse wave, the particle motion is:
a) Parallel to the direction of wave propagation
b) Perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
c) Circular
d) Random
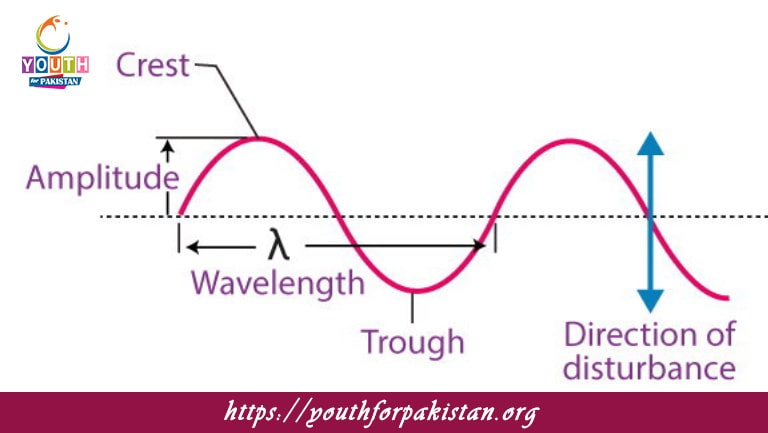
The highest point of a transverse wave is called the:
a) Trough
b) Crest
c) Node
d) Antinode
The lowest point of a transverse wave is known as the:
a) Crest
b) Node
c) Antinode
d) Trough
The distance between two consecutive crests in a transverse wave is called the:
a) Amplitude
b) Wavelength
c) Frequency
d) Period
The amplitude of a transverse wave is:
a) The distance between two consecutive crests
b) The maximum displacement of the particles from their equilibrium position
c) The time taken for one complete cycle
d) The number of waves passing a point per second
The period of a transverse wave is:
a) The distance between two consecutive crests
b) The time taken for one complete cycle to pass a point
c) The maximum height of the crest
d) The number of crests passing a point per second
The frequency of a transverse wave is:
a) The time taken for one complete cycle
b) The maximum displacement of the wave
c) The number of crests passing a point per second
d) The distance between two consecutive crests
The speed of a transverse wave is given by:
a)
=
×
v=λ×f
b)
=
v=
T
λ
c)
=
v=
λ
f
d)
=
÷
v=λ÷T
=
×
v=λ×f
In a transverse wave, nodes are:
a) Points of maximum displacement
b) Points of zero displacement
c) Points of minimum displacement
d) Points where amplitude is greatest
Antinodes in a transverse wave are:
a) Points of minimum displacement
b) Points where the wave has maximum displacement
c) Points of zero displacement
d) Points where frequency is highest
The wavelength of a transverse wave can be measured from:
a) Crest to crest
b) Trough to trough
c) Crest to trough
d) Both a and b
The speed of a transverse wave depends on:
a) The medium through which it travels
b) The amplitude of the wave
c) The frequency of the wave
d) The wavelength only
Which of the following is not a characteristic of transverse waves?
a) They have crests and troughs
b) Particle motion is parallel to wave propagation
c) They can travel through solids and on surfaces
d) They exhibit polarization
Transverse waves can be observed in:
a) Sound waves in air
b) Water waves on the surface of a pond
c) Seismic P-waves
d) Radio waves
The frequency of a transverse wave is:
a) Directly proportional to the wavelength
b) Inversely proportional to the period
c) Unrelated to the speed of the wave
d) The same as the amplitude
In a standing transverse wave, the nodes are:
a) Points of maximum displacement
b) Points where the wave is zero
c) Points where the wave travels fastest
d) Points of equal displacement
The amplitude of a transverse wave is related to:
a) The speed of the wave
b) The energy carried by the wave
c) The frequency of the wave
d) The wavelength of the wave
Transverse waves are characterized by:
a) Motion of particles parallel to the wave direction
b) Motion of particles perpendicular to the wave direction
c) Absence of nodes and antinodes
d) Non-periodic motion
The principle of superposition applies to:
a) Only transverse waves
b) Only longitudinal waves
c) Both transverse and longitudinal waves
d) Neither transverse nor longitudinal waves
The energy transported by a transverse wave is proportional to:
a) The square of its frequency
b) The square of its amplitude
c) The wavelength
d) The speed of the wave
The phase difference between two points on a transverse wave is:
a) The distance between them
b) The time difference between them
c) The fraction of a wavelength between them
d) The amplitude difference between them
A transverse wave traveling on a string is:
a) A longitudinal wave
b) A surface wave
c) A mechanical wave
d) An electromagnetic wave
The point of maximum displacement in a transverse wave is called the:
a) Node
b) Antinode
c) Crest
d) Trough
In which type of wave is polarization possible?
a) Longitudinal waves
b) Surface waves
c) Transverse waves
d) Both a and b
The wavelength of a transverse wave is the:
a) Distance between two consecutive nodes
b) Distance between two consecutive antinodes
c) Distance between two consecutive crests or troughs
d) Distance between two consecutive compressions
For a transverse wave traveling on a string, increasing the tension in the string will:
a) Decrease the wave speed
b) Increase the wave speed
c) Decrease the wavelength
d) Not affect the wave speed
If the frequency of a transverse wave increases while the speed remains constant, the wavelength will:
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Remain the same
d) Become zero
The speed of a transverse wave in a medium is determined by:
a) The medium’s density and elasticity
b) The frequency of the wave
c) The amplitude of the wave
d) The wavelength of the wave
The interaction of two transverse waves traveling in opposite directions can result in:
a) Destructive interference
b) Constructive interference
c) A standing wave pattern
d) All of the above
The unit of frequency for a transverse wave is:
a) Meters
b) Seconds
c) Hertz
d) Joules
The relationship between the speed, frequency, and wavelength of a transverse wave is:
a)
=
×
v=λ×f
b)
=
v=
λ
f
c)
=
÷
v=λ÷f
d)
=
×
v=f×λ
=
×
v=λ×f
When two transverse waves meet in phase, they will:
a) Cancel each other out
b) Reinforce each other
c) Create a longitudinal wave
d) Change direction
The energy carried by a transverse wave is directly proportional to its:
a) Frequency
b) Amplitude squared
c) Wavelength
d) Speed
A transverse wave with a longer wavelength has a:
a) Higher frequency
b) Lower frequency
c) Higher amplitude
d) Higher speed
The speed of a transverse wave on a string depends on:
a) The string’s mass per unit length
b) The tension in the string
c) Both a and b
d) The wave’s amplitude
The frequency of a transverse wave is the reciprocal of its:
a) Amplitude
b) Period
c) Wavelength
d) Speed
The velocity of a transverse wave in a medium is affected by:
a) The medium’s elasticity
b) The medium’s density
c) Both a and b
d) The wave’s frequency
In a standing transverse wave, the distance between two consecutive nodes or antinodes is:
a) Half the wavelength
b) One wavelength
c) Twice the wavelength
d) A quarter of the wavelength
The phenomenon where a transverse wave bends around an obstacle is called:
a) Reflection
b) Refraction
c) Diffraction
d) Absorption
If the wavelength of a transverse wave increases, while the speed remains constant, the frequency will:
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Remain the same
d) Become zero
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.





