Superposition Of Sound Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
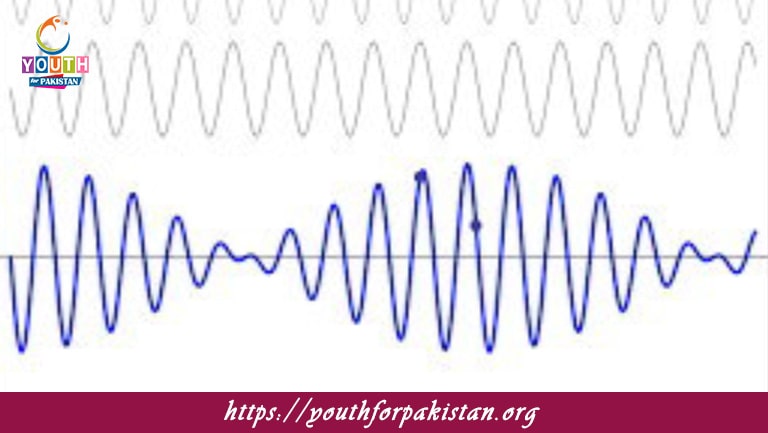
Superposition Of Sound Waves MDCAT Quiz refers to what happens when two or more sound waves meet at a point and combine to form a new wave. This is a basic principle in the theory of waves and applies not only to sound waves but to all kinds of waves, including light and water waves. When sound waves overlap, their displacements add up, resulting in either constructive or destructive interference. The principle of superposition is very important for MDCAT students in the interaction of sound waves and acoustics.
Applications of Superposition of Sound Waves
Interference Patterns: In environments like concert halls or auditoriums, the superposition of sound waves may result in interference patterns. In some areas, the sound is louder (because of constructive interference), while in others, the sound is softer or even silent (because of destructive interference). This is very important in acoustical design.
Noise-Canceling Technology: Noise-canceling headphones use destructive interference to cancel out unwanted background noise. They work by producing sound waves that are out of phase with the ambient noise, thus canceling it and providing a quieter listening experience.
Beats: When two sound waves of slightly different frequencies interfere, they produce what is known as beats. The periodic variation in loudness is due to constructive and destructive interference. The beat frequency is equal to the difference between the frequencies of the two sound waves. For example, if two tuning forks produce sound waves with frequencies of 440 Hz and 442 Hz, the resulting sound will vary in loudness with a frequency of 2 Hz, producing two beats per second.
Standing Waves: Superposition is also a necessary condition to create standing waves. When the reflected sound wave from any surface interfere with the incident or coming wave at that time, the phenomenon is a standing wave pattern. This happens in musical instruments such as the guitar and organ; the different standing wave patterns are related to different musical notes.
MDCAT Quiz: Superposition of Sound Waves
One can find questions on superposition of sound waves in the MDCAT, particularly questions on constructive and destructive interference, beats, and standing waves. The student may be asked to tell what the resultant intensity of sound would be if two waves interfere or may be asked to solve a problem in which beats are formed. One must understand the mathematical formulation and practical implications of wave superposition to successfully answer these kinds of questions.
- Test Name: Superposition Of Sound Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Superposition of Sound Waves
Free flashcards on the superposition of sound waves help MDCAT students visualize and reinforce key concepts such as interference, beat frequency, and standing waves. The flashcards can have examples of constructive and destructive interference, along with problems to practice calculating beat frequencies and resultant wave patterns. Regular use of these flashcards will deepen students’ understanding of wave behavior and enhance their performance on the MDCAT Quiz.

The principle of superposition of sound waves states that the displacement at a point is the ____ of the displacements of individual waves.

Destructive interference occurs when the displacement of one wave is ____ to the displacement of the other.

When two sound waves of different frequencies meet, they can produce a phenomenon called ____ interference.

If two sound waves of equal amplitude meet in such a way that they cancel each other out, it is an example of ____ interference.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.