Structure Of Skeletal Muscles MDCAT Quiz with Answers
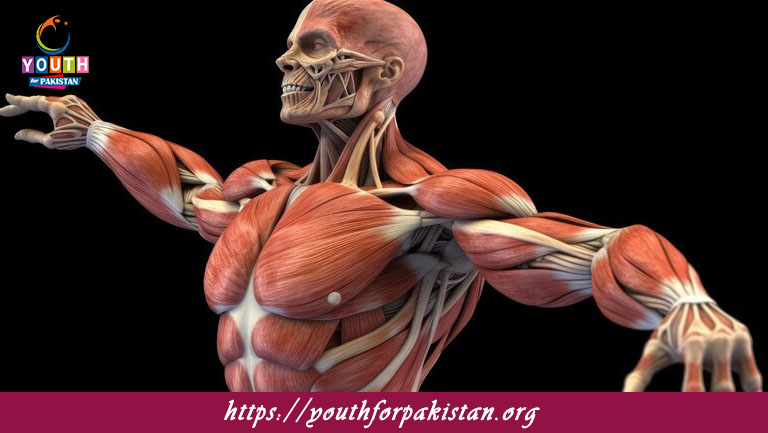

Structure Of Skeletal Muscles MDCAT Quiz: Skeletal muscles are the most common type of muscle tissue found in the human body, responsible for voluntary movement and providing support and stability. These muscles are attached to bones by tendons and play a key role in body movement, posture, and maintaining equilibrium. MDCAT students must understand the structure of skeletal muscles, as it forms the basis needed to understand how muscles function and their physiology. The MDCAT Quiz on the structure of skeletal muscles will test your knowledge of muscle anatomy and the components that contribute to muscle contraction and movement.
Components of Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles are composed of muscle fibers (cells) grouped into fascicles. Each muscle fiber is a multinucleated, cylindrical cell that contains many myofibrils, which are the contractile elements of the muscle. These myofibrils consist of repeating units called sarcomeres, which contain the proteins actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments). The arrangement of these filaments allows skeletal muscles to contract and produce force. The MDCAT Quiz will test your understanding of the organization of muscle fibers, fascicles, and myofibrils, and how these components work together to generate muscle movement.
Connective Tissue in Skeletal Muscle
The skeletal muscle is surrounded and supported by several layers of connective tissue. The most superficial is the epimysium, which envelops the entire muscle. The perimysium surrounds each fascicle, a bundle of muscle fibers, and the endomysium surrounds individual muscle fibers. These connective tissues help transmit the force generated by the muscle fibers to the tendons, which in turn move the bones. Blood vessels and nerves also run through the connective tissue layers, bringing the muscle nutrients and control. A Free Flashcard on the connective tissue layers in skeletal muscles will help you remember the roles of the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium.
Neuromuscular Junction and Muscle Contraction
The neuromuscular junction is the synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fibre. When a motor neuron fires, the neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft, thereby exciting the muscle fibre and causing it to contract. This process is mediated by the interaction of actin and myosin within the sarcomeres. The MDCAT Quiz will test your knowledge of the neuromuscular junction and how nerve impulses lead to skeletal muscle contraction, allowing for coordinated body movements.
Quiz on the Structure of Skeletal Muscles
Taking a sample MDCAT Quiz on the structure of skeletal muscles will ensure that you understand the organization and components of skeletal muscles, including muscle fibers, myofibrils, and connective tissues. You will be quizzed on aspects such as the structure of sarcomeres, actin and myosin in muscle contraction, and the neuromuscular junction. Using Free Flashcards will also reinforce key concepts concerning the structure and physiology of skeletal muscles to ensure that you are well-prepared for your MDCAT exam.

The individual skeletal muscle fibers are surrounded by a connective tissue called ________.
Endomysium

The structure that transmits action potentials into the muscle fiber is called the ________.
T-tubule

The organelles responsible for storing and releasing calcium in skeletal muscles are the ________.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum

The ________ regulates the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Terminal cisternae

The filament proteins that regulate muscle contraction are called _________.
Tropomyosin and troponin
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.