Specific Heat Capacity MDCAT Quiz with Answers
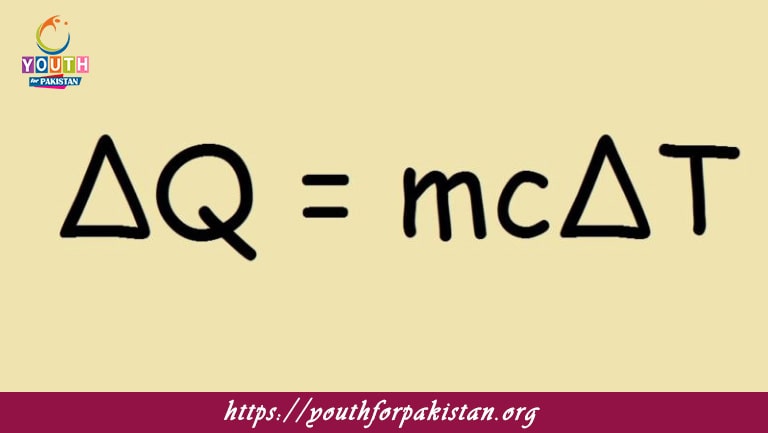
Specific Heat Capacity MDCAT Quiz refers to the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of any substance by one degree Celsius, or Kelvin. The concept becomes essentially important in thermodynamics, since it explains how various materials respond to heat. Most MDCAT students need an understanding of the topic of specific heat capacity in order to solve problems associated with heat transfer, energy conservation, and temperature changes.
Importance of Specific Heat Capacity
Heat Storage and Transfer: Materials possessing high specific heat capacities, such as water, can absorb extensive quantities of heat energy with small changes in temperature. This characteristic is utilized in climate regulation, cooking, and thermal storage systems.
Practical Applications:
Engineering: Specific heat is crucial in designing cooling and heating systems, such as radiators and heat exchangers.
Medicine: It explains how the human body maintains temperature by means such as sweating.
Astronomy: Helps in understanding planetary heat dynamics and atmospheric behavior.
Role in Phase Transitions: During phase changes, such as melting or boiling, the heat energy is used to overcome intermolecular forces rather than changing temperature, which is explained using specific heat capacity.
- Test Name: Specific Heat Capacity MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Specific Heat Capacity
Free flashcards for specific heat capacity are a very good way to reinforce this concept. The flashcards may include important formulas, units, example problems, and comparative values of specific heat capacities of common substances. Regular practice with these flashcards will surely help the student strengthen their concepts and problem-solving skills, ensuring success in MDCAT physics topics.

The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of:
1 kg of the substance by 1°C

If the mass of a substance increases, the heat required to increase the temperature by 1°C will:
Increase

In a calorimeter, the heat required to raise the temperature of water depends on its:
Mass and specific heat capacity

The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C is:
Its specific heat capacity

The heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance is proportional to:
Its specific heat capacity

The heat required to increase the temperature of a substance depends on:
Its specific heat capacity and mass

The specific heat capacity of a material can be used to calculate:
The amount of heat required to change its temperature

The heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C is known as:
Its specific heat capacity
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.