Specific Heat Capacity MDCAT MCQs with Answers
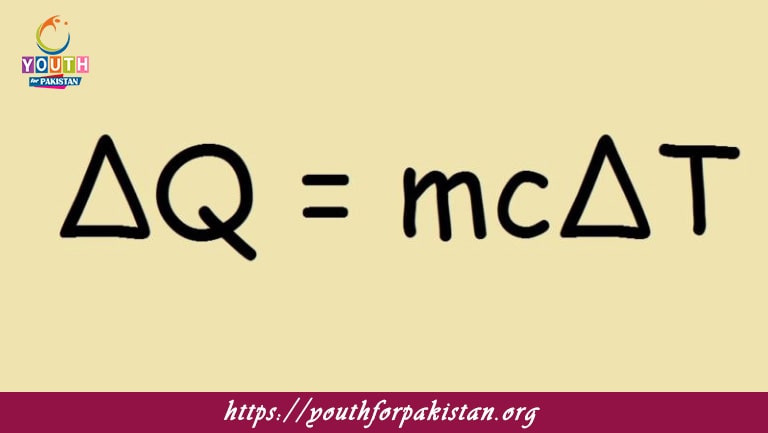
Welcome to the Specific Heat Capacity MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Specific Heat Capacity Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Specific Heat Capacity MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Specific Heat Capacity MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
Which of the following has the highest specific heat capacity?
A) Water
B) Iron
C) Copper
D) Aluminum
The SI unit of specific heat capacity is:
A) J/kg
B) J/kg°C
C) J/mol
D) J/mol°C
If the specific heat capacity of a substance is high, it means that the substance:
A) Heats up quickly
B) Cools down quickly
C) Heats up slowly
D) Cools down slowly
Which of the following substances would require the most heat to raise its temperature by 1°C?
A) Water
B) Sand
C) Iron
D) Mercury
The specific heat capacity of a substance is dependent on:
A) The mass of the substance
B) The volume of the substance
C) The temperature of the substance
D) The nature of the substance
Which of the following materials has a specific heat capacity of approximately 0.385 J/g°C?
A) Water
B) Copper
C) Iron
D) Lead
When a substance with a high specific heat capacity is heated, it:
A) Absorbs a lot of heat energy
B) Absorbs very little heat energy
C) Does not absorb any heat energy
D) Loses heat energy
Which of the following has a specific heat capacity of approximately 4.18 J/g°C?
A) Copper
B) Aluminum
C) Iron
D) Water
If 2000 J of heat is added to 2 kg of a substance, causing its temperature to rise by 5°C, what is its specific heat capacity?
A) 50 J/kg°C
B) 200 J/kg°C
C) 400 J/kg°C
D) 1000 J/kg°C
Which substance has a higher specific heat capacity, implying it can store more heat for a given mass and temperature change?
A) Water
B) Iron
C) Copper
D) Lead
The specific heat capacity of a substance can be affected by:
A) Its mass
B) Its temperature
C) Its phase (solid, liquid, gas)
D) All of the above
What is the specific heat capacity of ice?
A) 2.09 J/g°C
B) 4.18 J/g°C
C) 1.00 J/g°C
D) 0.90 J/g°C
If a material has a specific heat capacity of 0.9 J/g°C, how much heat is needed to raise the temperature of 100 g of the material by 10°C?
A) 90 J
B) 900 J
C) 9 J
D) 1000 J
Which has the lowest specific heat capacity?
A) Water
B) Lead
C) Aluminum
D) Iron
The specific heat capacity of a substance is directly related to:
A) The amount of energy required to change its temperature
B) The amount of energy required to change its mass
C) The amount of energy required to change its volume
D) The amount of energy required to change its density
What is the specific heat capacity of aluminum?
A) 0.897 J/g°C
B) 4.18 J/g°C
C) 2.09 J/g°C
D) 0.385 J/g°C
A substance with low specific heat capacity will:
A) Change temperature quickly
B) Change temperature slowly
C) Not change temperature
D) Maintain its temperature
What happens to the temperature of a substance when it absorbs heat but its specific heat capacity remains the same?
A) The temperature decreases
B) The temperature remains the same
C) The temperature increases
D) The temperature fluctuates
If 500 J of heat is added to 5 kg of a substance, causing its temperature to rise by 2°C, what is its specific heat capacity?
A) 20 J/kg°C
B) 50 J/kg°C
C) 100 J/kg°C
D) 200 J/kg°C
Which substance would require the least heat to raise its temperature by 1°C?
A) Water
B) Lead
C) Iron
D) Aluminum
If the specific heat capacity of a substance is 0.5 J/g°C, how much heat is required to raise the temperature of 200 g of the substance by 10°C?
A) 1000 J
B) 500 J
C) 50 J
D) 100 J
Which of the following is true for a substance with a high specific heat capacity?
A) It heats up quickly
B) It heats up slowly
C) It cools down quickly
D) It does not change temperature
The specific heat capacity of iron is approximately:
A) 0.45 J/g°C
B) 0.90 J/g°C
C) 1.00 J/g°C
D) 2.09 J/g°C
What does the specific heat capacity of a substance depend on?
A) The type of material
B) The mass of the substance
C) The temperature of the substance
D) The volume of the substance
If two substances have the same mass but different specific heat capacities, which will heat up faster?
A) The one with higher specific heat capacity
B) The one with lower specific heat capacity
C) Both will heat up at the same rate
D) It depends on the initial temperature
What is the specific heat capacity of lead?
A) 0.128 J/g°C
B) 0.900 J/g°C
C) 4.18 J/g°C
D) 0.385 J/g°C
The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance is directly proportional to:
A) Its specific heat capacity
B) Its mass
C) The temperature change
D) All of the above
A substance with a low specific heat capacity will:
A) Retain heat for a long time
B) Quickly change temperature
C) Have high thermal conductivity
D) Be a good insulator
If a metal has a specific heat capacity of 0.9 J/g°C, how much energy is required to raise the temperature of 50 g of this metal from 20°C to 30°C?
A) 450 J
B) 900 J
C) 90 J
D) 0.9 J
Which of the following statements about specific heat capacity is true?
A) It is the same for all substances
B) It varies depending on the state of the substance
C) It is independent of the mass of the substance
D) It depends on the external pressure
If 100 J of heat is required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C, what is the specific heat capacity of water?
A) 100 J/kg°C
B) 1000 J/kg°C
C) 4.18 J/g°C
D) 1 J/g°C
Which substance has the highest specific heat capacity?
A) Water
B) Iron
C) Copper
D) Lead
The specific heat capacity of a substance is 0.2 J/g°C. If the temperature of a 5 g sample of this substance is raised by 10°C, how much heat energy has been absorbed?
A) 1 J
B) 10 J
C) 20 J
D) 100 J
If a substance with a specific heat capacity of 1 J/g°C absorbs 200 J of energy, causing its temperature to rise by 20°C, what is the mass of the substance?
A) 2 g
B) 10 g
C) 100 g
D) 200 g
Which has a lower specific heat capacity, implying it heats up quickly?
A) Water
B) Sand
C) Air
D) Oil
In calorimetry, the concept of specific heat capacity is used to:
A) Measure the density of a substance
B) Determine the change in temperature of a substance
C) Calculate the energy required for a phase change
D) Measure the thermal conductivity of a substance
A higher specific heat capacity means that a substance will:
A) Change temperature quickly
B) Require more energy to change its temperature
C) Absorb less heat for a given temperature change
D) Have a lower boiling point
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.