Sn1 Sn2 E1 And E2 Reaction MDCAT Quiz with Answers
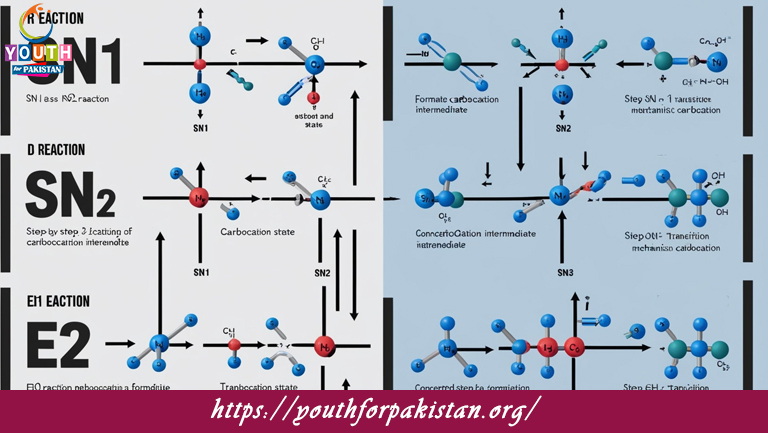
Sn1 Sn2 E1 And E2 Reaction MDCAT Quiz reactions are among the basic kinds of organic reactions that MDCAT students must learn very well. The mechanisms involved here are nucleophilic substitution (SN1 and SN2) and elimination (E1 and E2), with each having different characteristics and conditions.
SN1 (Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution): In this reaction, the rate-determining step is the formation of a carbocation intermediate after the leaving group departs. This reaction usually occurs with tertiary alkyl halides in polar protic solvents. The rate depends only on the substrate concentration.
SN2 (Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution): In this case, the nucleophile attacks the carbon center at the same time as the leaving group departs, forming a transition state. This reaction occurs predominantly with primary alkyl halides and in polar aprotic solvents. The reaction is stereospecific, meaning it inverts the configuration of the carbon center.
E1 (Unimolecular Elimination): Like SN1, this reaction proceeds through the formation of a carbocation intermediate, followed by the elimination of a proton (H⁺) and a leaving group. E1 reactions are usually in competition with SN1 reactions and take place with tertiary alkyl halides in polar protic solvents.
E2 (Bimolecular Elimination): During this reaction, the base abstracts a proton from the carbon adjacent to the one bearing the leaving group; simultaneously, the leaving group is eliminated, and an alkene is formed. This reaction occurs in a single step and is favored with strong bases and secondary/tertiary alkyl halides in polar aprotic solvents.
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 Reactions
Our MDCAT Quiz on SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions will help you solidify your understanding of these important mechanisms. The quiz includes questions on identifying the conditions that favor each reaction type, understanding their mechanisms, and predicting the products. Practicing this quiz will have you well-prepared for any related questions in the MDCAT exam.
Free Flashcard: Important Facts about SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 reactions
Our Free Flashcard set on SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions summarizes the key points about each reaction mechanism. These flashcards include information on the reaction steps, factors affecting the reaction rates, and the type of products formed. They are an excellent tool for quick review and reinforcement of your knowledge before the MDCAT exam.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.






