Reflexes And Reflex Arc MDCAT MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Reflexes And Reflex Arc MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Reflexes And Reflex Arc Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Biology offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Reflexes And Reflex Arc MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
What is a reflex action?
a) A voluntary action
b) An involuntary, automatic response
c) A conscious reaction
d) A learned behavior
Which of the following is part of the reflex arc?
a) Motor neuron
b) Cerebrum
c) Spinal cord only
d) Sensory receptors
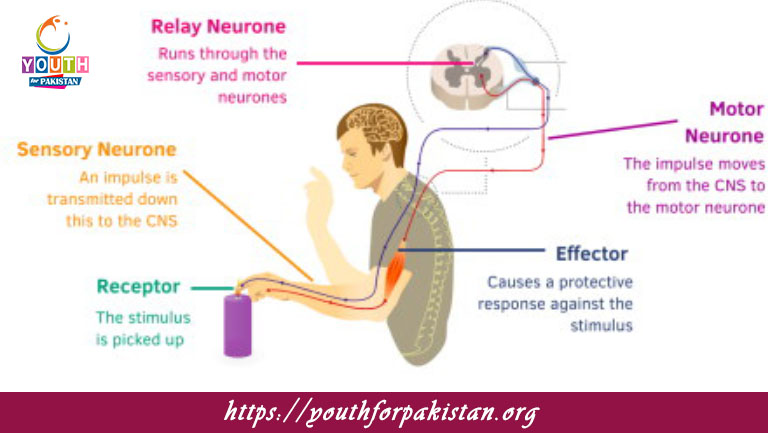
What is the role of sensory neurons in a reflex arc?
a) Transmit impulses to muscles
b) Carry impulses to the spinal cord
c) Inhibit reflex actions
d) Increase voluntary control
Which part of the nervous system controls reflex actions?
a) Brain
b) Spinal cord
c) Cerebellum
d) Hypothalamus
A reflex arc bypasses which part of the nervous system?
a) Cerebrum
b) Cerebellum
c) Spinal cord
d) Peripheral nervous system
In a reflex arc, the effector organ is usually a:
a) Muscle or gland
b) Brain
c) Sensory receptor
d) Interneuron
The patellar reflex is an example of a:
a) Conditional reflex
b) Stretch reflex
c) Withdrawal reflex
d) Learned reflex
Which type of neuron carries the signal from the spinal cord to the effector in a reflex arc?
a) Sensory neuron
b) Motor neuron
c) Relay neuron
d) Interneuron
What is the purpose of a reflex action?
a) To perform voluntary tasks
b) To respond rapidly to stimuli
c) To inhibit muscle movement
d) To increase brain activity
The simplest type of reflex arc involves how many neurons?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
What role do interneurons play in a reflex arc?
a) They detect stimuli
b) They connect sensory and motor neurons
c) They respond to the environment
d) They inhibit reflexes
Which of the following is an example of a conditioned reflex?
a) Blinking when something approaches the eye
b) Salivating at the smell of food
c) Withdrawal of hand from a hot object
d) Knee-jerk reflex
The withdrawal reflex is an example of a:
a) Monosynaptic reflex
b) Polysynaptic reflex
c) Conditioned reflex
d) Stretch reflex
Which type of reflex does not require input from the brain?
a) Simple reflex
b) Conditioned reflex
c) Voluntary action
d) Conscious response
What is the function of motor neurons in a reflex arc?
a) To receive stimuli
b) To transmit impulses to muscles or glands
c) To connect sensory neurons
d) To block involuntary actions
Which reflex action helps to maintain posture?
a) Stretch reflex
b) Withdrawal reflex
c) Crossed extensor reflex
d) Conditioned reflex
Which reflex is tested by striking the Achilles tendon?
a) Patellar reflex
b) Plantar reflex
c) Biceps reflex
d) Ankle jerk reflex
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for automatic reflexes?
a) Somatic nervous system
b) Autonomic nervous system
c) Central nervous system
d) Peripheral nervous system
Which reflex is responsible for maintaining balance when one foot is lifted?
a) Withdrawal reflex
b) Stretch reflex
c) Crossed extensor reflex
d) Plantar reflex
Which reflex action involves the spinal cord but not the brain?
a) Reflex arc
b) Voluntary movement
c) Conscious reaction
d) Cerebral reflex
Which reflex causes the pupil to constrict in response to bright light?
a) Patellar reflex
b) Pupillary light reflex
c) Withdrawal reflex
d) Crossed extensor reflex
The term “reflex arc” refers to:
a) The pathway of nerve impulses during a reflex action
b) The voluntary control of movement
c) The action of the cerebrum
d) The inhibition of a reflex
The receptor in a reflex arc is responsible for:
a) Detecting the stimulus
b) Transmitting impulses to the brain
c) Producing a response
d) Blocking sensory signals
What type of reflex is a knee-jerk reflex?
a) Conditional reflex
b) Monosynaptic reflex
c) Polysynaptic reflex
d) Involuntary reflex
The effector in a reflex arc is usually a:
a) Muscle or gland
b) Sensory neuron
c) Relay neuron
d) Receptor
Which part of the nervous system processes reflexes?
a) Cerebral cortex
b) Brainstem
c) Spinal cord
d) Cerebellum
Which reflex is often used to test neurological function in a clinical setting?
a) Plantar reflex
b) Crossed extensor reflex
c) Stretch reflex
d) Pupillary reflex
The reflex that allows a person to withdraw their hand from a hot object is known as the:
a) Patellar reflex
b) Withdrawal reflex
c) Stretch reflex
d) Crossed extensor reflex
Which reflex helps to prevent muscle overstretching?
a) Stretch reflex
b) Withdrawal reflex
c) Crossed extensor reflex
d) Pupillary reflex
In a reflex arc, what is the correct sequence of events?
a) Sensory receptor → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Effector
b) Motor neuron → Sensory neuron → Sensory receptor → Effector
c) Effector → Motor neuron → Sensory neuron → Sensory receptor
d) Sensory receptor → Effector → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron
Which type of reflex is considered a simple reflex?
a) Polysynaptic reflex
b) Conditioned reflex
c) Monosynaptic reflex
d) Crossed extensor reflex
Which of the following is not part of a reflex arc?
a) Receptor
b) Spinal cord
c) Brainstem
d) Motor neuron
The blink reflex helps protect the:
a) Ears
b) Skin
c) Eyes
d) Nose
Which of the following is a polysynaptic reflex?
a) Knee-jerk reflex
b) Withdrawal reflex
c) Plantar reflex
d) Patellar reflex
What happens to the reflex speed if the reflex arc involves more neurons?
a) Reflex speed increases
b) Reflex speed decreases
c) Reflex speed remains the same
d) Reflex does not occur
Which reflex allows an infant to turn its head when its cheek is touched?
a) Rooting reflex
b) Sucking reflex
c) Grasp reflex
d) Moro reflex
Which of the following is an example of an involuntary reflex?
a) Raising your hand
b) Walking
c) Pulling your hand away from a hot object
d) Talking
Which nerve impulse pathway is involved in the patellar reflex?
a) Reflex arc
b) Voluntary control
c) Sensory feedback loop
d) Autonomous response
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.