Projectile Motion MDCAT Quiz with Answers
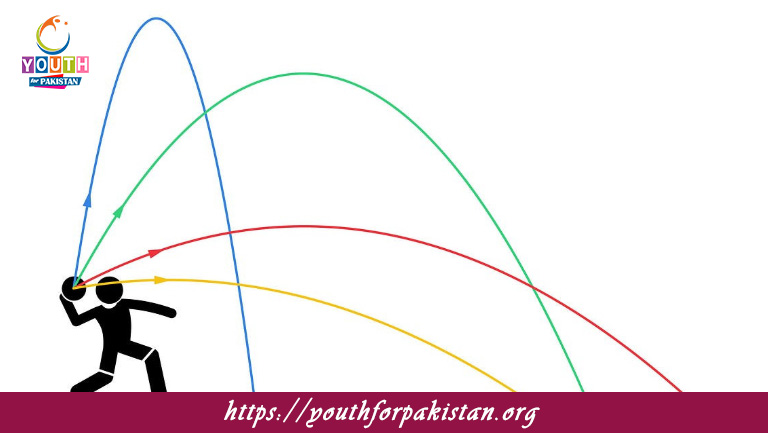
Projectile Motion MDCAT Quiz is an important concept in physics and a very crucial topic for MDCAT students. It is the motion of an object that is projected into the air and moves under the influence of gravity, following a curved path known as a parabolic trajectory. This motion is two-dimensional, with horizontal and vertical components acting independently. Understanding the principles of projectile motion is imperative to solve questions relating to trajectories, velocity, and time in the MDCAT Quiz.
Understanding the Components of Projectile Motion
Projectile motion can be separated into two independent components: horizontal and vertical. The horizontal motion is at a constant velocity because there are no forces acting in that direction externally (ignoring air resistance). On the other hand, the vertical motion is under the influence of gravity, where the object accelerates downward at a rate of 9.8m/s2. By analyzing these components, MDCAT students can calculate the range, maximum height, and time of flight of a projectile, which are common problem areas in the exam.
MDCAT Quiz: Projectile Motion Questions
The MDCAT Quiz often includes problems requiring students to analyze projectile motion. These questions may involve calculating the maximum height of a projectile, the total time it spends in the air, or the horizontal range it covers. For instance, a typical question might ask students to determine the range of a ball launched at a specific angle with a given initial velocity. To solve such problems, students must decompose the initial velocity into horizontal and vertical components using trigonometric functions and apply the equations of motion systematically. Practicing these problems improves understanding and prepares students for high-scoring performance in the MDCAT physics section.
- Test Name: Projectile Motion MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Projectile Motion
Free flashcards pertaining to projectile motion can greatly facilitate a student’s comprehension and retention of fundamental concepts. Examples of such flashcards include formulae for horizontal and vertical motion, derivation of key formulae, and examples of solving trajectory-related problems. Going through these flashcards on a daily basis ensures that students are able to recall important concepts quickly and correctly apply them during the MDCAT Quiz. This type of focused preparation builds confidence and efficiency in tackling questions on projectile motion, an important unit in the physics syllabus.

The horizontal range of a projectile depends on its __________.
initial velocity and angle of projection

If a projectile is launched with a velocity vvv at an angle θthetaθ, its horizontal range is __________.
v2sin2θgfrac{v^2 sin 2theta}{g}gv2sin2θ

The horizontal component of velocity for a projectile is calculated as __________.
vcosθv cos thetavcosθ

The vertical component of velocity for a projectile is calculated as __________.
vsinθv sin thetavsinθ

The time taken to reach maximum height by a projectile is __________.
vsinθgfrac{v sin theta}{g}gvsinθ

The vertical displacement of a projectile at time ttt is calculated using __________.
h=vsinθt−12gt2h = v sin theta t - frac{1}{2}gt^2h=vsinθt−21gt2

The horizontal displacement of a projectile at time ttt is calculated using __________.
x=vcosθtx = v cos theta tx=vcosθt

For the same initial velocity, the range of a projectile depends on the __________.
angle of projection
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.