Projectile Motion Horizontal Range MDCAT Quiz with Answers
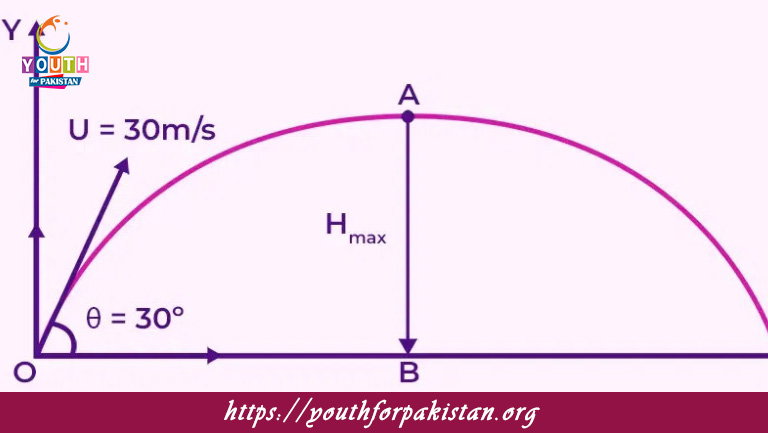
Projectile Motion Horizontal Range MDCAT Quiz is the distance traveled horizontally by a projectile before it returns to the ground. An essential aspect of projectile motion, calculation of horizontal range is something that MDCAT students need to master for the physics section of their exam. It depends upon the initial velocity, angle of launching, and acceleration due to gravity. By mastering this, MDCAT students can answer practical problems relating to motion and forces easily in the MDCAT Quiz.
Calculating Horizontal Range in Projectile Motion
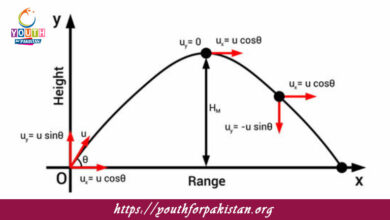
The horizontal range is the total distance a projectile covers in the horizontal direction before hitting the ground. It is determined by factors such as initial velocity, angle of projection, and acceleration due to gravity. MDCAT students must understand the derivation of the formula R=v2sin2θgR = \frac{v^2 \sin 2\theta}{g} and know how to apply it to different problem types. This foundational knowledge is crucial for solving physics questions accurately and efficiently during the exam.
MDCAT Quiz: Horizontal Range Questions
In the MDCAT Quiz, questions involving horizontal range often require students to calculate the distance traveled by a projectile based on its initial velocity and launch angle. For example, a problem might give the initial velocity and ask for the horizontal range of a projectile launched at a specific angle. Solving these problems requires students to break the motion into horizontal and vertical components, apply the appropriate kinematic equations, and ensure that the correct formula for range is used. Practicing these types of questions improves students’ ability to solve projectile motion problems quickly and accurately during the MDCAT exam.
- Test Name: Projectile Motion Horizontal Range MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Horizontal Range in Projectile Motion
We provide free flashcards designed to help MDCAT students master the concept of horizontal range. These flashcards include formula breakdowns, step-by-step problem-solving techniques, and key tips for identifying the best approach to range-related questions. Using these tools can significantly improve your grasp of this vital topic and support your MDCAT Quiz preparation.

The horizontal range of a projectile depends on __________.
the initial velocity and the angle of projection

The horizontal range of a projectile is maximum when the angle of projection is __________.
45∘45^circ45∘

The horizontal range of a projectile is proportional to __________.
the square of the initial velocity

The horizontal range of a projectile can be calculated using the formula __________.
R=v2sin2θgR = frac{v^2 sin 2theta}{g}R=gv2sin2θ

The horizontal range of a projectile launched at 60∘60^circ60∘ is __________ than when launched at 30∘30^circ30∘.
greater

For a given initial velocity, the horizontal range __________ as the angle of projection increases from 0∘0^circ0∘ to 90∘90^circ90∘.
increases

The horizontal range is __________ proportional to the height from which the projectile is launched.
directly

When two projectiles are launched with the same initial velocity but at different angles, their horizontal ranges are __________.
equal if the angles are complementary

The horizontal range of a projectile is inversely proportional to __________.
gravitational acceleration

A projectile launched at 45∘45^circ45∘ and 60∘60^circ60∘ with the same initial velocity will have __________ horizontal range.
equal

The horizontal range of a projectile is calculated by __________.
considering both horizontal and vertical velocities

The horizontal range of a projectile depends on __________.
the initial horizontal velocity and the angle of projection

The horizontal range of a projectile is doubled when the initial velocity is __________.
increased by a factor of 2sqrt{2}2

For the same initial velocity, the projectile launched at 60∘60^circ60∘ will travel __________ horizontal distance than one launched at 30∘30^circ30∘.
greater

The horizontal range of a projectile launched at an angle 45∘45^circ45∘ depends on __________.
the initial velocity
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.