Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz are waves that transfer energy through a medium with no permanent displacement of the medium itself. In such waves, the disturbance moves from one place to another, and hence, the energy is transferred through the medium. Progressive waves play a vital role in several divisions of physics, such as sound waves, light waves, and seismic waves. MDCAT students should properly understand the characteristics, behavior, and mathematical relationships controlling progressive waves in order to solve related problems in their exams.
MDCAT Quiz
In the MDCAT Quiz, students may be asked to solve problems regarding the properties of progressive waves, such as calculating the speed of a wave given its frequency and wavelength or determining the amplitude or frequency of a wave based on given data. Also, students may find problems that require them to distinguish between transverse and longitudinal progressive waves and describe how waves behave in different media. The ability to apply equations related to waves and knowledge of wave properties is very important in attempting these kinds of problems.
- Test Name: Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Progressive Waves
Free flashcards for progressive waves are very important to MDCAT students. They can include the important characteristics of progressive waves, types of progressive waves, which include transverse and longitudinal waves, and the important formulae that give wave speed, frequency, and wavelength. They may also contain practice questions that illustrate the behavior of waves in different situations. Periodic review of these flashcards will consolidate the knowledge of progressive waves by the students, thus enabling them to tackle wave-related questions with increased speed in the MDCAT Quiz.

What is the main characteristic of a progressive wave?
It continuously transfers energy through a medium

In a progressive wave, how does the displacement of particles change as the wave passes?
The displacement oscillates around the equilibrium position

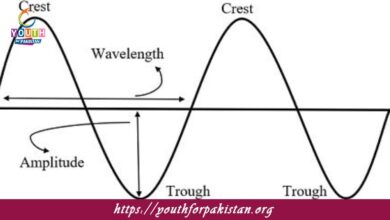
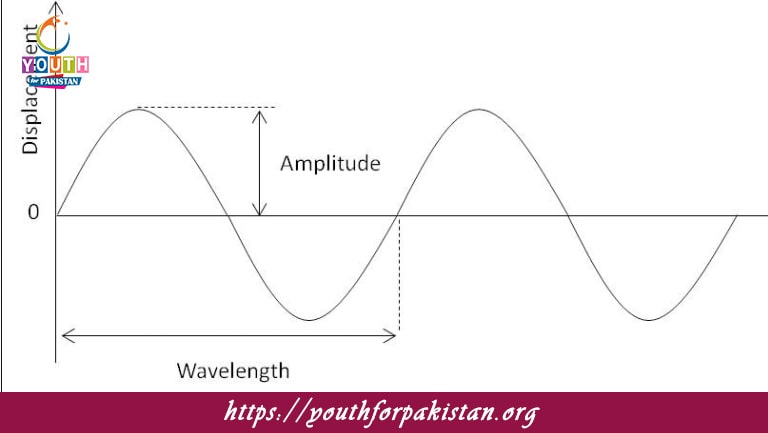
What is the amplitude of a progressive wave?
The maximum displacement of particles from the equilibrium position

In a progressive wave, the wavelength is defined as:
The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs

What is the main difference between a progressive wave and a stationary wave?
A progressive wave transfers energy; a stationary wave does not

What does the phase difference between two points in a progressive wave determine?
The type of interference

What is the phase difference between two points on a progressive wave at the same time?
It depends on their relative position

How is the energy of a progressive wave related to its amplitude?
Energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude

In a progressive wave, what happens to the frequency as the wavelength increases?
The frequency decreases

What happens to the speed of a progressive wave as the frequency increases?
The speed remains constant

What is the effect of changing the medium on the speed of a progressive wave?
The speed changes depending on the medium's properties

What is the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and wave speed?
Wave speed = frequency × wavelength
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.