Oxidative Phosphorylation MDCAT Quiz with Answers
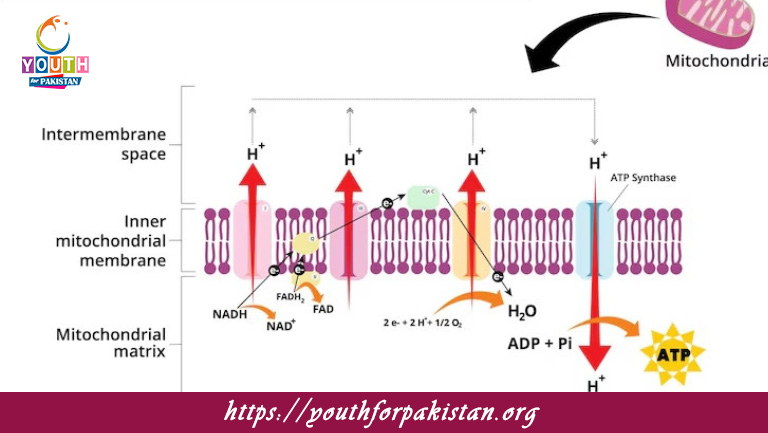
Oxidative Phosphorylation MDCAT Quiz: Oxidative phosphorylation is the last step of cellular respiration, in which energy from high-energy electrons is used to drive the synthesis of ATP. It takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane and depends on the electron transport chain (ETC) and chemiosmosis. This is the most efficient method for the production of ATP; as many as 32-34 ATPs are produced per glucose molecule. In the process of oxidative phosphorylation, electrons carried by NADH and FADH₂ are passed through the ETC, a series of protein complexes and mobile carriers located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The flow of electrons causes pumping of protons (H⁺) across the inner membrane, resulting in a proton gradient. This gradient drives the enzyme ATP synthase, which catalyzes the synthesis of ATP as protons flow back into the mitochondrial matrix. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor, and it combines with electrons and protons to form water. The MDCAT students have to learn the detail about oxidative phosphorylation in the bioenergetic and metabolic pathway.
Test Your Knowledge with an MDCAT Quiz
An MDCAT Quiz on Oxidative Phosphorylation will help you assess your understanding of the electron transport chain, ATP synthesis, and the role of oxygen in this process. The quiz will include topics such as proton gradients, ATP synthase function, and the energy yield of NADH and FADH₂. Regular practice with these quizzes will ensure you are prepared for related MDCAT questions on energy production in cells.
Free Flashcards for Quick Revision
Free Flashcards on Oxidative Phosphorylation summarizes the critical steps and components involved in ATP production. These flashcards cover the role of the electron transport chain, the proton motive force, and, most importantly, the importance of oxygen acting as the final electron acceptor. They provide a very nice way to rapidly review and reinforce the important details for the MDCAT exam.
Oxidative phosphorylation is crucial to understanding efficient energy production within cells via the process of aerobic respiration. Use our resources, including quizzes and flashcards, to help you master this portion of your exam prep for MDCAT.

Which molecule donates electrons to the electron transport chain during oxidative phosphorylation?
NADH

What is the main purpose of the proton gradient generated during oxidative phosphorylation?
To drive ATP synthesis

What is the name of the process that uses the proton gradient to synthesize ATP in oxidative phosphorylation?
Chemiosmosis

What is the energy source that drives ATP synthesis during oxidative phosphorylation?
Proton gradient

In which part of the mitochondrion does the electron transport chain take place?
Inner mitochondrial membrane

How does the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane contribute to ATP production?
It drives ATP synthase

What is the main function of oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation?
To act as the final electron acceptor
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.