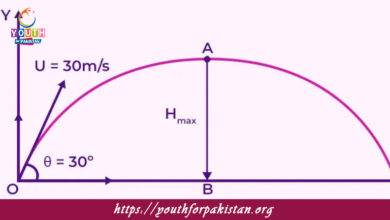
Ohm’s Law MDCAT Quiz is one of the most basic laws in physics, relating voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit; it says that the current V=IR is the foundation of circuit analysis and a must-know for MDCAT students looking to ace the physics section.
Test Your Knowledge with an MDCAT Quiz
An MDCAT Quiz on Ohm’s Law is a fantastic way to reinforce your understanding. These quizzes include practical problems such as calculating resistance, voltage, or current in various circuit configurations. Practicing these questions helps students understand the real-world applications of Ohm’s Law, such as in resistors and electrical devices, and boosts their exam confidence.
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
0Get Your Username and Password for MDCAT Tests
Sign Up Now
Free Flashcards for Fast Learning
Strengthen your preparation with Free Flashcards dedicated to Ohm’s Law. These flashcards underline critical aspects, including units of measurement (ohms, volts, and amperes), key formulas, and problem-solving techniques. Using these flashcards makes the memorization and recall of this relationship easier, so you are well-prepared for any question related to the topic.

Ohm's Law relates the voltage, current, and resistance as:

The SI unit of voltage is:

The resistance of a conductor depends on:
Its material, length, and temperature

If the resistance in a circuit is constant, the current is:
Directly proportional to voltage

The relationship between voltage and current in an ideal conductor is:

If the current in a circuit is doubled, while the resistance remains the same, the voltage will:

The formula for current using Ohm’s law is:

In Ohm’s law, the resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to:

The unit of resistance is:

If the voltage across a resistor is increased, the current will:

The power dissipated in a resistor can be calculated using:

The current in a conductor is directly proportional to the:

If the resistance of a conductor is halved, the current will:

If the voltage is constant, the current in a circuit is inversely proportional to:

In a circuit, if the voltage is tripled, the current will:

The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is:

The power dissipated by a resistor is:

For a fixed resistance, the current is:
Directly proportional to the voltage

The voltage across a conductor is proportional to the current

If the resistance in a circuit is tripled, the current will:
Decrease by a factor of 3

Ohm’s law is used to determine:
Current, voltage, or resistance

The power consumed by a resistor is the product of:

In an ideal conductor, the resistance is:

The voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to:

The unit of electric power is:

If the resistance is increased and the voltage remains constant, the current will:

In Ohm’s law, voltage is directly proportional to:

The current in a circuit with constant resistance is:
Directly proportional to voltage

In a simple circuit, if the voltage is doubled, the current will:
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.
View Your Dashboard