Longitudinal Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Longitudinal Waves MDCAT Quiz is a progressive wave in which the particles of the medium oscillate in the same direction as that in which the wave is propagated. In other words, the particles move back and forth parallel to the direction of the energy flow. The waves have compressions and rarefactions that move through the medium. Longitudinal waves are common in mechanical waves such as sound waves and seismic waves. MDCAT students must know the important properties and behavior of longitudinal waves in order to solve physics problems related to wave motion.
Characteristics of Longitudinal Waves
Particle Motion: The particles in a longitudinal wave oscillate back and forth parallel to the direction of wave travel. In so doing, it creates areas of compression—where particles are close together—and rarefaction—where particles are spread apart. For instance, in a sound wave, air molecules vibrate in the same direction as the wave, creating compressions and rarefactions as it moves through the air.
Compressions and Rarefactions:
Compression: A region where the particles of the medium are closest together and the pressure is highest.
Rarefaction: A area where the particles are most spread out, creating low pressure.
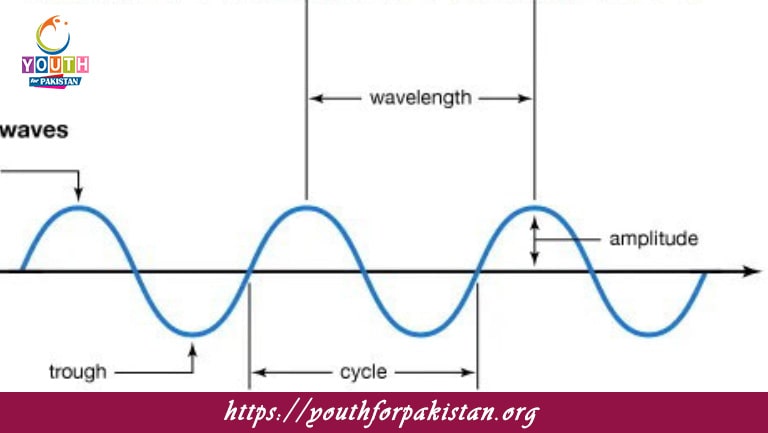
Amplitude: The amplitude of a longitudinal wave refers to the greatest displacement of the particles from their equilibrium or rest position. In sound waves, greater amplitude means louder and smaller amplitude, quieter.
Wavelength: The wavelength in longitudinal waves is the distance between two successive compressions (or rarefactions). It is an important factor in determining the wave’s frequency and speed.
Wave Speed: The speed of a longitudinal wave depends upon the properties of the medium, like density and elasticity. The speed of sound, for instance, varies in different media: it is faster in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases.
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
Sound Waves: Sound is one of the best examples of a longitudinal wave. When sound is produced—for example, by a vibrating guitar string—it creates compressions and rarefactions in the air, which travel through the medium to our ears. Sound waves require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to propagate.
Seismic Waves: Some seismic waves, namely P-waves or primary waves, are longitudinal in nature. The waves move through the interior of the Earth and cause particles to move in the same direction as that in which the wave is propagating, thereby causing compressions and rarefactions in the Earth’s crust.
Waves in Springs: When the spring is compressed and then released, longitudinal waves travel through the coils. Each coil moves back and forth along the direction of wave propagation.
Pressure Waves in Fluids: When a disturbance occurs in a fluid (like water), longitudinal waves can form, where the particles of the fluid move in the direction of the wave’s travel, creating areas of compression and rarefaction.
MDCAT Quiz: Questions on Longitudinal Waves
In the MDCAT Quiz, there might be questions in which students have to distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves. For longitudinal waves, the questions could be on concepts such as compression, rarefaction, amplitude, and wave speed. Students may also need to apply the wave equation v=fλ to solve problems involving sound waves, seismic waves, or other examples of longitudinal waves.
- Test Name: Longitudinal Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Longitudinal Waves
Free flashcards focused on longitudinal waves can help MDCAT students understand critical aspects of these waves. Flashcards may include definitions, diagrams showing compressions and rarefactions of the waves, and real examples of longitudinal waves. These resources are helpful in revisiting the concepts of wave motion and preparing one for questions related to longitudinal waves in the MDCAT Quiz. Regular review of these flashcards by the student is going to help in mastering the topic for effective application in their studies.

A longitudinal wave is one in which the particles move ____ to the direction of wave propagation.
parallel

In a longitudinal wave, the direction of vibration is ____ to the direction of energy transfer.
parallel
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.