Longitudinal Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Longitudinal Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz is a wave in which the particles of the medium oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave. Regions of compression and rarefaction are formed where the wave goes through the medium. These waves repeat themselves at regular intervals, hence they are called periodic waves. Longitudinal periodic waves are very important for sound waves, seismic waves, and other phenomena of this nature. This is an important topic for MDCAT students while solving physics problems involving wave motion and energy flow.
Characteristics Longitudinal Periodic Waves
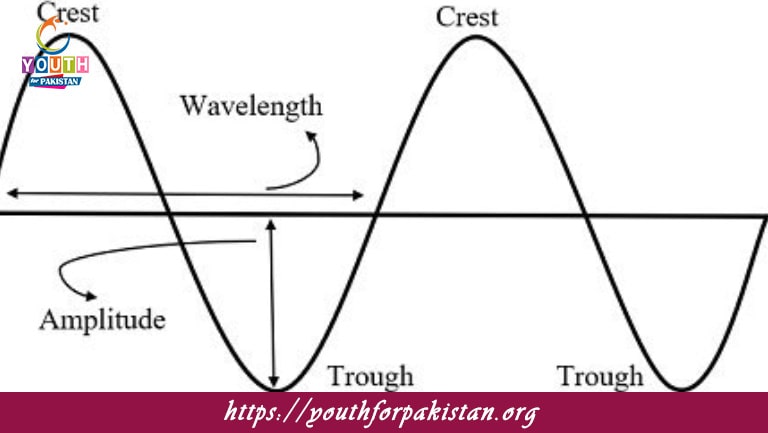
Particle Motion: In a longitudinal wave, the particles constituting the wave move back and forth parallel to the direction the wave travels. Thus, it results in regions of compression and rarefaction, or particles tightly packed in compressions and widely spaced in rarefactions. The back-and-forth motion transfers energy in such media.
Compression: That region of the wave, where particles are closely packed, yielding higher pressure.
Rarefaction: A region of the wave where particles are spread apart, leading to lower pressure.
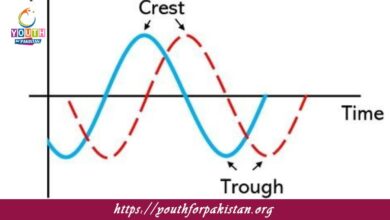
Amplitude: The amplitude of a longitudinal wave refers to the maximum displacement of particles from their equilibrium position during oscillation. For longitudinal waves, amplitude is related to the density of compressions and rarefactions—the greater the amplitude, the more pronounced these regions are.
Examples of Longitudinal Periodic Waves
Sound Waves: Sound is a classic example of a longitudinal periodic wave. In sound waves, particles in a medium such as air oscillate back and forth, creating regions of compression and rarefaction that propagate through the medium. Sound requires a medium to travel, and its speed varies depending on the density and elasticity of the medium.
Seismic Waves: Some seismic waves, such as P-waves (primary waves), are longitudinal waves that travel through the Earth’s interior. These waves cause particles in the Earth’s crust to move in the direction of wave propagation, creating regions of compression and rarefaction. P-waves are faster than other types of seismic waves and can travel through both solids and liquids.
Pressure Waves in Fluids: Longitudinal waves also occur in fluids, where pressure waves move through liquids and gases. These waves transfer energy through compressions and rarefactions, similar to sound waves, and they are often observed in the movement of fluids in pipes or during water sloshing in a tank.
Energy Transfer: In longitudinal waves, energy is transferred through the medium via the oscillation of particles. As particles compress and rarefy, they pass the energy on to adjacent particles, allowing the wave to propagate through the medium. The larger the amplitude, the more energy is transferred.
Reflection and Refraction: When longitudinal waves encounter boundaries, such as the surface of the Earth or the walls of a container, they can be reflected back into the medium. Refraction can occur when the wave passes from one medium into another (for example, from air to water), causing changes in wave speed and wavelength.
MDCAT Quiz: Longitudinal Periodic Waves Questions
Understanding longitudinal periodic waves enables MDCAT students to answer questions related to sound waves, seismic waves, and other types of mechanical waves. In the MDCAT Quiz, students may be asked to calculate wave speed, frequency, or wavelength or analyze the behavior of longitudinal waves in different media. Application of concepts like amplitude, compression, rarefaction, and wave speed is a must for takers to succeed in the physics sections of this exam.
- Test Name: Longitudinal Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Longitudinal Periodic Waves
Free flashcards on longitudinal periodic waves will enable MDCAT students to ace the main ideas related to these waves. Such flashcards may contain diagrams of compressions and rarefactions, explain wave properties such as amplitude and wavelength, or even contain sample problems to practice the wave equation. The regular use of flashcards will strengthen the understanding of longitudinal waves and improve performance in the MDCAT Quiz.

How does the amplitude of a longitudinal wave relate to its energy?
Energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude

What is the relationship between the speed, frequency, and wavelength of a longitudinal wave?
Speed = Frequency × Wavelength

What happens to the sound intensity when the amplitude of a longitudinal wave is increased?
The intensity increases

How is the velocity of a longitudinal wave related to the medium through which it travels?
The velocity depends on the medium’s properties

What is the phase relationship between compressions in a longitudinal wave?
Compressions occur at regular intervals

How does the frequency of a longitudinal wave affect its pitch?
Higher frequency results in higher pitch

What happens to the wavelength of a longitudinal wave if the frequency is increased?
The wavelength decreases

What is the relationship between the time period and frequency of a longitudinal wave?
Frequency is the reciprocal of the time period

In a longitudinal wave, what happens when particles are in compression?
Particles are pushed together

What is the main characteristic of a longitudinal wave?
Particles move parallel to the direction of wave propagation

In a longitudinal wave, what happens to the medium as the wave propagates?
The medium undergoes periodic compressions and rarefactions

How is the frequency of a longitudinal wave measured?
By counting the number of compressions or rarefactions per second

In a longitudinal wave, what is the relationship between compressions and rarefactions?
They alternate regularly

What happens when a longitudinal wave passes from one medium to another?
The speed of the wave changes

In a longitudinal wave, how do particles in the medium move relative to the direction of wave propagation?
They move back and forth along the same direction

How does the amplitude of a longitudinal wave affect its intensity?
Greater amplitude results in greater intensity

What is the time period of a longitudinal wave?
The time it takes for one complete cycle of compression and rarefaction

What is the primary cause of longitudinal waves in a medium?
A disturbance that pushes or pulls particles along the wave direction
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.