Frequency MDCAT MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Frequency MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Frequency Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Frequency MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Frequency MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
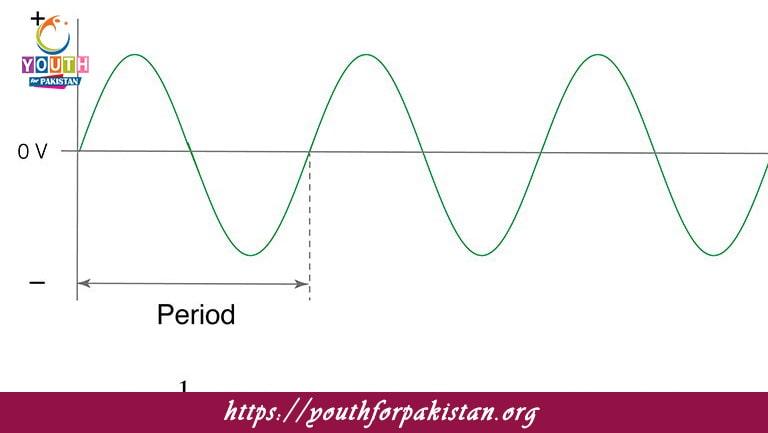
The frequency of a wave is defined as:
a) The number of waves passing a point per second
b) The distance between successive wave crests
c) The time taken for one wave to pass a point
d) The speed at which the wave travels
The unit of frequency is:
a) Hertz (Hz)
b) Joule (J)
c) Newton (N)
d) Pascal (Pa)
If the time period of a wave is 0.01 seconds, its frequency is:
a) 10 Hz
b) 100 Hz
c) 1000 Hz
d) 0.1 Hz
The frequency of a sound wave determines its:
a) Loudness
b) Pitch
c) Quality
d) Speed
The frequency of electromagnetic waves increases as:
a) Wavelength increases
b) Wavelength decreases
c) Speed increases
d) Amplitude increases
The frequency of the sound wave produced by a tuning fork depends on:
a) The length of the fork
b) The temperature of the surroundings
c) The amplitude of vibration
d) The density of the material of the fork
A wave with a frequency of 50 Hz has a period of:
a) 0.02 s
b) 0.2 s
c) 2 s
d) 0.5 s
The audible range of frequencies for humans is approximately:
a) 0 to 20 Hz
b) 20 to 2000 Hz
c) 20 to 20,000 Hz
d) 2000 to 200,000 Hz
The frequency of a wave does not change when it passes from one medium to another because:
a) The speed of the wave changes
b) The wavelength changes
c) The energy of the wave changes
d) The source frequency remains constant
In a standing wave, nodes are points where:
a) The displacement is maximum
b) The displacement is zero
c) The frequency is maximum
d) The amplitude is maximum
The frequency of the fundamental note produced by a stretched string is inversely proportional to:
a) The length of the string
b) The tension in the string
c) The mass per unit length of the string
d) The square root of the tension in the string
The Doppler effect occurs when:
a) A source of sound moves towards or away from an observer
b) A source of sound is stationary
c) An observer moves towards or away from a source of sound
d) Both a and c
The frequency of electromagnetic waves is directly proportional to:
a) The amplitude
b) The speed of light
c) The wavelength
d) The energy of the waves
The frequency of a photon is related to its energy by:
a) E = mc²
b) E = hν
c) E = 1/2 mv²
d) E = kT
The resonant frequency of an LC circuit depends on:
a) The resistance
b) The capacitance
c) The inductance
d) Both b and c
The frequency of a wave is doubled, the wavelength:
a) Doubles
b) Halves
c) Remains the same
d) Quadruples
The highest frequency of sound that can be heard by the average human ear is about:
a) 2,000 Hz
b) 10,000 Hz
c) 20,000 Hz
d) 50,000 Hz
The natural frequency of a system is the frequency at which the system:
a) Absorbs maximum energy
b) Emits maximum energy
c) Resonates
d) None of the above
The beat frequency produced by two waves of frequencies 100 Hz and 104 Hz is:
a) 4 Hz
b) 104 Hz
c) 202 Hz
d) 200 Hz
The frequency of the third harmonic of a string fixed at both ends is:
a) The same as the fundamental frequency
b) Twice the fundamental frequency
c) Three times the fundamental frequency
d) Half the fundamental frequency
The change in frequency due to the motion of a source or observer is called:
a) Interference
b) Resonance
c) Diffraction
d) Doppler effect
The frequency of the radio waves used in mobile communication is in the range of:
a) 3 Hz to 3 kHz
b) 3 kHz to 300 kHz
c) 300 MHz to 3 GHz
d) 3 GHz to 30 GHz
The frequency of a pendulum is inversely proportional to:
a) The square of its length
b) The square root of its length
c) The length
d) The mass
When the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength:
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remains constant
d) Depends on the medium
The fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe is:
a) Equal to that of an open pipe of the same length
b) Half that of an open pipe of the same length
c) Double that of an open pipe of the same length
d) Independent of the length of the pipe
The frequency of a wave is related to its wavelength by the equation:
a) f = λv
b) f = v/λ
c) f = λ/v
d) f = vλ²
The frequency of a sound wave can be determined using:
a) An oscilloscope
b) A barometer
c) A spectrometer
d) A thermometer
In the electromagnetic spectrum, the frequency range of visible light is:
a) 300 GHz to 3 THz
b) 3 THz to 30 THz
c) 430 THz to 770 THz
d) 300 THz to 3 PHz
The frequency of the electromagnetic radiation used in microwave ovens is typically:
a) 300 Hz
b) 3 kHz
c) 3 MHz
d) 2.45 GHz
The frequency of a wave is measured in:
a) Joules
b) Watts
c) Hertz
d) Decibels
In a sound wave, the frequency is related to:
a) The pitch
b) The volume
c) The speed
d) The intensity
The frequency of ultrasound waves used in medical imaging is typically:
a) 20 Hz to 20 kHz
b) 2 MHz to 18 MHz
c) 20 kHz to 100 kHz
d) 100 MHz to 1 GHz
The frequency of alternating current (AC) in most countries is:
a) 10 Hz
b) 50 Hz
c) 100 Hz
d) 200 Hz
The natural frequency of a simple pendulum is determined by:
a) The mass of the pendulum bob
b) The length of the string
c) The amplitude of the swing
d) The gravitational acceleration
The frequency range of AM radio broadcasting is:
a) 535 kHz to 1705 kHz
b) 88 MHz to 108 MHz
c) 54 MHz to 88 MHz
d) 2 MHz to 18 MHz
The frequency of a wave increases, and the speed of the wave remains constant. The wavelength:
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remains constant
d) Becomes zero
The frequency of a wave in a vacuum is determined by:
a) The medium
b) The energy of the wave
c) The wavelength
d) The speed of light
In a string instrument, the frequency of the sound produced can be altered by:
a) Changing the tension in the string
b) Changing the length of the vibrating part of the string
c) Changing the thickness of the string
d) All of the above
The frequency range for VHF (Very High Frequency) is:
a) 30 MHz to 300 MHz
b) 300 MHz to 3 GHz
c) 3 GHz to 30 GHz
d) 3 MHz to 30 MHz
The frequency of the fundamental note in a closed organ pipe is determined by:
a) The length of the pipe
b) The temperature of the air
c) The speed of sound in the pipe
d) All of the above
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.