First Law Of Thermodynamics MDCAT Quiz with Answers
First Law Of Thermodynamics MDCAT Quiz: Energy conservation and its application to chemical and physical processes: This law is the basis for understanding energy transfers within a system and how work, heat, and internal energy are interrelated. MDCAT Quiz section often asks questions regarding energy conservation, so one has to understand this law in order to solve the associated problems.
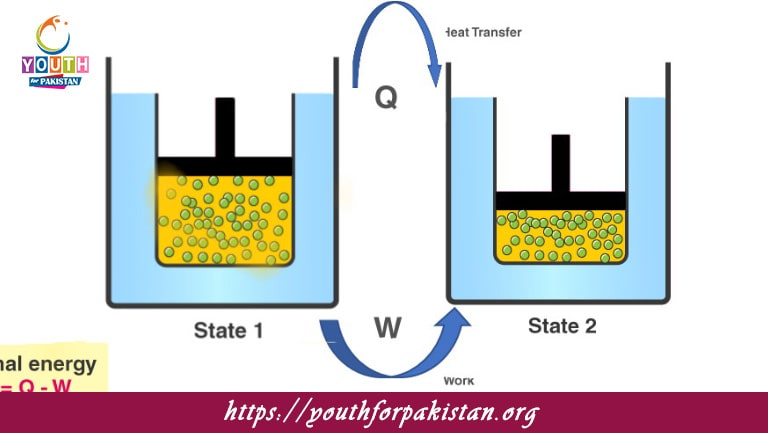
The first law of thermodynamics, otherwise known as the law of conservation of energy, is a principle in physics and chemistry that postulates that no energy can be created or destroyed, only converted or transferred. This principle forms a very essential foundation for the understanding of dynamics of energy in biological and chemical systems for the MDCAT students. Our all-inclusive MDCAT Quiz on the subject ensures you grasp the central themes of the law, be it energy transfer processes or their applications in a thermodynamic system.
Master First Law with MDCAT Quiz
Energy transformations, including work and heat, are vital for living organisms and medical science. The MDCAT Quiz on the First Law of Thermodynamics includes detailed questions to test your understanding of the principles of internal energy, enthalpy, and energy conservation. On performing such preparation for your MDCAT exam, you will come across the relevance of this law within open and closed systems, examples of which range from chemical reactions to biological procedures. This is a valuable study tool that sets your knowledge free and helps strengthen your confidence against real exam challenges.
- Test Name: First Law Of Thermodynamics MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Thermodynamics
Use our free flashcards on the First Law of Thermodynamics to further your preparation. The flashcards have short definitions, key formulas, and examples of how energy conservation is applied in everyday life. Use these flashcards to brush up quickly on some of the important concepts in thermodynamics, such as heat and work relationship, thermodynamic equilibrium, and how the first law is practically applied in medicine. By integrating these study tools into your routine, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of thermodynamic principles critical for MDCAT success.

In the first law of thermodynamics, the change in internal energy (ΔU) is:
The heat added to the system minus work done by the system

The heat capacity of a substance is defined as:
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature by one degree
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.