Enzymes MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Enzymes MDCAT Quiz: Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They play a vital role in nearly all physiological processes, such as digestion, metabolism, and cellular signaling. Enzymes are proteins, though some RNA molecules also have catalytic activity. The concept of enzymes is very essential for MDCAT students in the subject areas of biochemistry and physiology.
Structure of Enzymes:
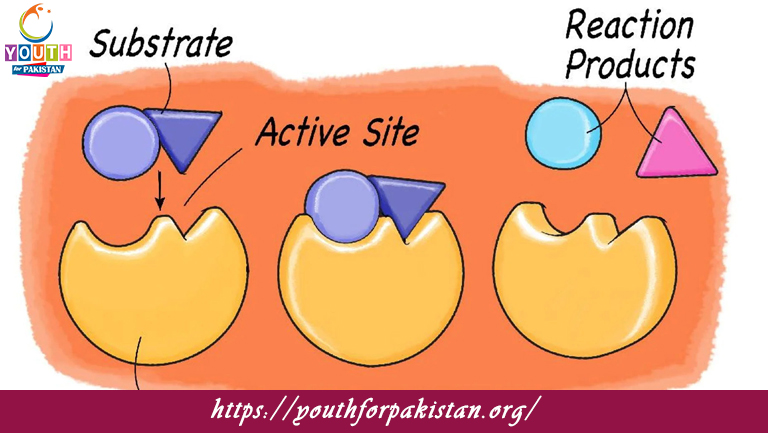
Enzymes are usually large proteins, consisting of amino acid chains folded into specific three-dimensional shapes. The active site is the region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate, which is the molecule upon which the enzyme acts. The structure of the enzyme is highly specific to the substrate, and this specificity is important for the proper functioning of the enzyme. Activity of the enzyme may be influenced by temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors or activators.
Examples:
The enzyme amylase has an active site that specifically binds to the starch molecules, helping in their breakdown to simpler sugars.
Mechanism of Action:
Enzymes catalyze reactions by reducing the activation energy required for the reaction to take place. They form an enzyme-substrate complex, wherein the enzyme temporarily binds to the substrate, and this facilitates the conversion of the substrate into products. There exist two major models to explain enzyme action: the lock and key model and the induced fit model. In the lock and key model, the enzyme’s active site perfectly fits the substrate just like a key fitting into a lock. In the induced fit model, the enzyme’s active site undergoes a slight conformational change upon substrate binding.
Example:
Zinc is a cofactor for the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which participates in the regulation of blood pH.
Enzyme Kinetics:
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates of enzyme-catalysed reactions. The Michaelis-Menten equation relates the rate of the reaction with the concentration of the substrate. The Km value, or Michaelis constant, is a substrate concentration when the rate of reaction reaches half of its maximal value (Vmax). Lower Km values indicate higher affinity between the enzyme and substrate.
Free Flashcard: Key Insights on Enzymes
The free Flashcard set on enzymes covers important aspects, including structure, classification, and kinetics. Use these flashcards to better prepare and be confident in dealing with questions related to the topic during the MDCAT exam.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.






