Electrostatics MDCAT Quiz with Answers
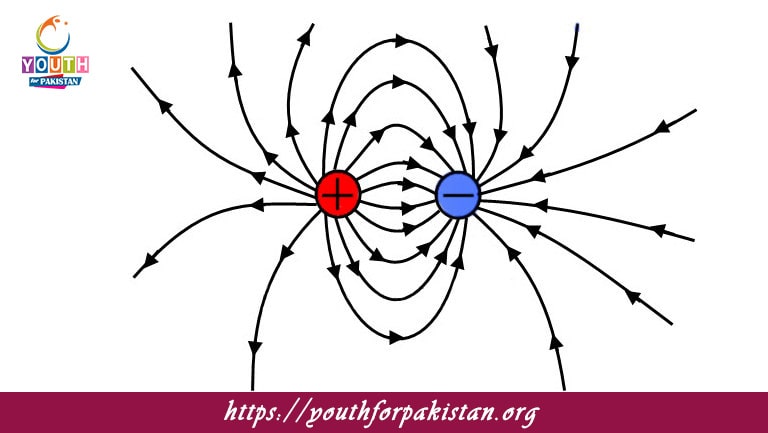
Electrostatics MDCAT Quiz is the branch of physics that deals with the study of electric charges at rest. It discusses the forces, fields, and potentials created by stationary charges and how they interact with each other. Understanding electrostatics is crucial for MDCAT students because it lays the foundation for advanced topics like electromagnetism, electric circuits, and modern physics.
Applications of Electrostatics
Capacitors: These store electric energy based on electrostatic principles. They are extensively used in electronic circuits.
Precipitators: Electrostatic precipitators remove dust and pollutants from industrial exhaust gases.
Medical Imaging: Electrostatic principles are applied in technologies such as X-rays and CT scans.
Electric Field Control: Lightning rods and shielding devices use electrostatics to control high-voltage discharges.
MDCAT Quiz: Electrostatics
The MDCAT Quiz on Electrostatics challenges students on Coulomb’s law, electric fields, electric potential, and related concepts. Students may encounter numerical problems, conceptual questions, and applications of electrostatic principles in real-world scenarios.
- Test Name: Forces Causing Centripetal Acceleration MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards on Electrostatics
Free flashcards on electrostatics are invaluable in reviewing formulas, key definitions, and problem-solving strategies. Examples include charge interactions, electric field calculations, and energy stored in capacitors. Practice regularly with these flashcards to gain a firm hold on the concepts of electrostatics so that MDCAT students will not have problems in this crucial topic.

The principle of superposition in electrostatics states that:
The net electric field is the vector sum of individual fields

The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depends on:
The area of the plates and the distance between them

The electric field between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is:
Uniform and directed perpendicular to the plates

Gauss's law states that:
The electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed

The force between two point charges is inversely proportional to:
The square of the distance between them

The electric field at a point due to a charge depends on:
The magnitude of the charge and the distance from the charge

The work done in moving a charge in an electric field is:
Equal to the change in electric potential energy
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.