Electric Potential MDCAT Quiz with Answers
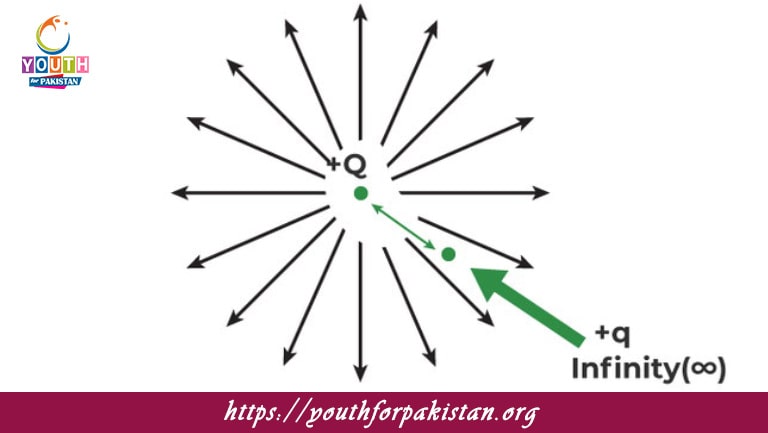
The Electric Potential MDCAT Quiz is a basic concept of electrostatics and can be described as the potential energy per unit charge at a given point in the electric field. It is work performed in transferring a unit positive charge from infinity to some point in the field without acceleration. The concept is crucial for MDCAT students because it provides the basis upon which electric charges are considered in the fields, relations of potential and electric field, and energy storage in electrostatic systems.
Properties of Electric Potential
Scalar Quantity: The electric potential, unlike the electric field, is a scalar quantity, hence it has only magnitude but no direction.
Equipotential Surfaces: The surfaces of constant electric potential are called equipotential surfaces. No work is done in moving a charge along an equipotential surface since the potential is the same at every point on the surface.
Superposition Principle: The total electric potential due to multiple charges is the algebraic sum of the potentials due to each charge.
Applications of Electric Potential
Energy Storage in Capacitors: Capacitors store energy in the form of electric potential energy between two conductive plates, and the potential difference across the plates determines the stored energy.
Electric Circuits: It is electric potential difference, or voltage, which drives current in electrical circuits. Understanding potential is key to analyzing and solving circuit problems.
Electrostatic Devices: Devices such as electron guns, cathode ray tubes, and electrostatic precipitators work on the principle of electric potential that controls and manipulates electric fields and charges.
MDCAT Quiz: Electric Potential
The MDCAT Quiz on Electric Potential tests students’ understanding of potential energy, electric potential due to point charges, and the relationship between electric field and potential. The questions may involve calculating potential at specific points in electric fields or understanding concepts like equipotential surfaces.
- Test Name: Electric Potential MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards about Electric Potential
Free flashcards for electric potential can help students quickly revise key concepts and formulas,
Applications of electric potential in capacitors and circuits.
With these flashcards, MDCAT students can grasp the concepts of and improve in problem-solving tasks in electrostatics.

The potential difference between two points is:
The work done per unit charge to move a test charge between the points

In a uniform electric field, the potential difference between two points is:
Directly proportional to the distance between them

The potential energy of a charge in an electric field is:
The product of the charge and the electric potential

The electric potential due to a uniformly charged spherical shell is:
Zero inside the shell and constant outside

The electric potential due to a point charge is:
Inversely proportional to the distance from the charge

The potential energy of a system of charges is:
The sum of the potential energies of the individual charges

The electric potential due to a charge distribution is:
The sum of potentials due to individual charges

The potential difference between two points in an electric field is related to:
The electric field strength and the distance between the points

The electric potential at a point in an electric field depends on:
The charge causing the field and the distance from it

The electric potential energy of a system of charges can be positive, negative, or zero depending on:
The relative positions of the charges

The potential difference between two points in a conductor is proportional to:
The resistance and the current
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.





