Elastic Collision MDCAT Quiz with Answers
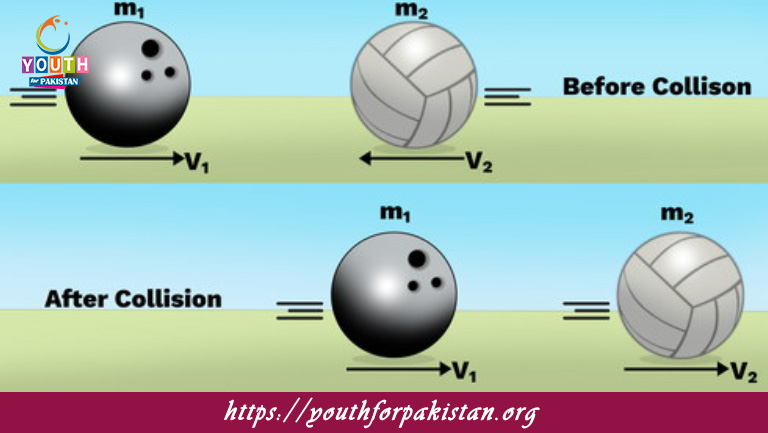
Elastic Collision MDCAT Quiz is a fundamental concept in physics, critical for MDCAT students preparing for the medical and dental entrance exams. It is a type of collision in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. These interactions occur in systems where objects collide without any loss of energy to heat, sound, or deformation. Examples of elastic collisions include collisions between billiard balls or gas molecules in ideal conditions. Understanding the principles and equations governing elastic collisions is essential for solving motion and force-related problems in the MDCAT Quiz.
Understanding Elastic Collisions
In an elastic collision, the total momentum of the system before and after the collision remains constant, as described by the Law of Conservation of Momentum. Additionally, the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved, making it unique compared to inelastic collisions where energy is partially dissipated. The students of MDCAT have to learn these principles in order to apply them correctly in problem-solving situations.
MDCAT Quiz: Elastic Collision Questions
The MDCAT Quiz gets questions from the concept of elastic collisions that test students’ analytical skills on both motion and energy. Some such questions in a quiz might ask about calculating final velocities in an elastic collision when masses and initial velocities of all objects are provided. One question might be related to determining the velocity of a given object after it undergoes an elastic collision with another. These types of exercises allow students to clearly understand how the concepts of momentum and energy conservation actually apply in practical scenarios. Mastery in this subdomain of physics is necessary if a student wishes to pass the physics section in the MDCAT exam with flying colors.
- Test Name: Elastic Collision MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Elastic Collision
The use of free flashcards is one of the best ways that MDCAT students can easily memorize and revise the concept of an elastic collision. The flashcards can help them retain formulas like momentum and energy conservation equations and understand common examples and applications. Regular review of flashcards improves recall and speeds up problem-solving for students to be adequately prepared to handle elastic collision questions in the MDCAT Quiz. This, therefore, becomes a tool that gives an added advantage when incorporated into the daily study routine in mastering physics topics for the exam.

In an elastic collision between two objects, the total __________ before and after the collision is the same.
velocity

If two objects collide elastically, the relative velocity of approach is __________ to the relative velocity of separation.
equal

In a head-on elastic collision, the velocities of two objects after the collision depend on their __________.
initial velocities

The relative velocity of approach equals the relative velocity of separation in __________ collisions.
perfectly elastic collisions

For two objects colliding elastically, the initial momentum is equal to __________ momentum after the collision.
final

In an elastic collision between two bodies, the total __________ remains constant.
momentum and energy

For an elastic collision between two objects, if the first object is at rest, the second object’s velocity changes __________.
only slightly

During a perfectly elastic collision, the objects will have the same __________ after the collision.
velocity

The total __________ after a perfectly elastic collision is equal to the total before the collision.
momentum

The velocities of two objects after a perfectly elastic collision depend on their __________.
masses and initial velocities

A collision where both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved is called __________.
elastic collision

If the relative speed of approach is greater than the relative speed of separation, the collision is __________.
inelastic
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.