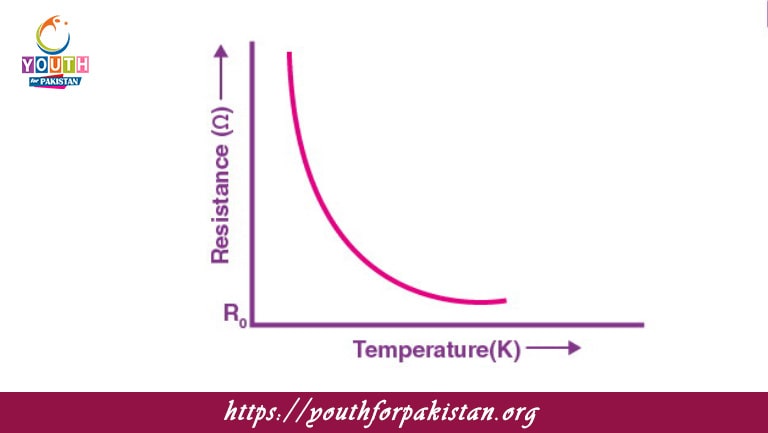
The Effect Of Temperature On Resistance MDCAT Quiz is one of the most vital topics in the study of electrical properties of materials. When temperature increases, the resistance of most conductors also increases due to increased collisions of electrons with atoms in the material. For conductors like metals.
Test Your Knowledge with an MDCAT Quiz
An MDCAT Quiz on the effect of temperature on resistance will help you solidify your understanding of how temperature changes influence the behavior of materials in electrical circuits. These quizzes feature questions on the temperature coefficient of resistance and how to calculate resistance at different temperatures. Practicing these questions will enhance your ability to solve both conceptual and numerical problems, ensuring better performance in the MDCAT exam.
- Test Name: Effect Of Temperature On Resistance MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
0Get Your Username and Password for MDCAT Tests
Sign Up Now
Free Flashcards for Quick Revision
Strengthen your preparation by using Free Flashcards that address how temperature affects resistance. These flashcards provide quick access to main formulas, definitions, and concepts, such as the difference between metallic conductors and semiconductors, which behave differently with temperature changes. Flashcards are an effective tool for reviewing key points and guaranteeing that you don’t forget critical information when it comes to the MDCAT exam.

The resistance of a conductor increases with:

When temperature increases, the resistance of metals generally:

The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to:

The temperature coefficient of resistance is:
A measure of how resistance changes with temperature

The resistance of an ideal conductor is:

For metals, the resistance increases with:

In semiconductors, the resistance usually:
Decreases with increasing temperature

The relationship between resistance and temperature for a metal can be expressed as:

The resistance of a conductor at a given temperature depends on:
The material and temperature

The temperature coefficient of resistance is:

The resistance of insulators changes significantly with:

The resistance of an object at a higher temperature is usually:

In conductors, the increase in resistance with temperature is due to:
Increased atomic vibrations

The resistance of a conductor at 0°C is:

The formula for the temperature dependence of resistance is R = R₀(1 + αT). In this equation, α is:
The temperature coefficient of resistance

For a material with a positive temperature coefficient, resistance will:
Increase with increasing temperature

For an ideal conductor, the resistance is:

The temperature coefficient of resistance is greater in:

The resistance of a conductor at room temperature is:
Directly related to its temperature

In semiconductors, resistance decreases as temperature:

The effect of temperature on resistance is negligible for:

The resistance of a conductor is directly related to:
The temperature and material

The temperature coefficient of resistance for metals is typically:

The resistance of a metallic conductor increases with:

For a given temperature increase, a material with a higher temperature coefficient of resistance will show:
A greater increase in resistance

The resistance of a conductor can be calculated using the formula R = R₀(1 + αT). In this formula, R₀ represents:

The effect of temperature on resistance is more significant in:
High-resistance materials

The change in resistance of a conductor with temperature is due to:
The increase in atomic vibrations

The resistance of a wire increases as the temperature increases because:
The atoms vibrate more and scatter electrons

For a metal conductor, the resistance increases with:
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.
View Your Dashboard