Effect Of Temperature On Resistance MDCAT MCQs with Answers
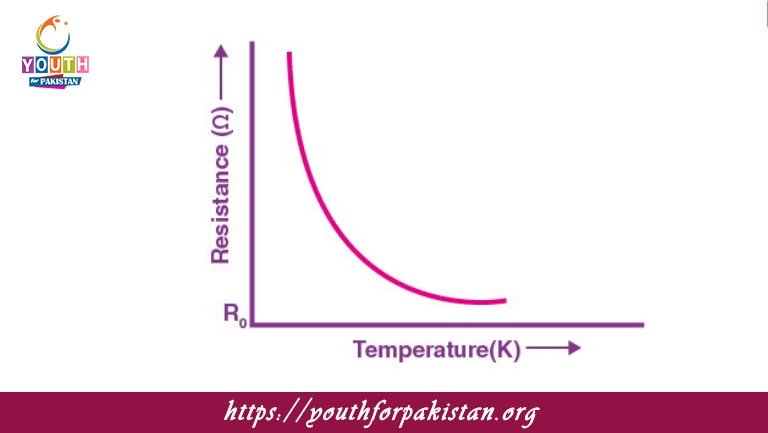
Welcome to the Effect Of Temperature On Resistance MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Effect Of Temperature On Resistance Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Effect Of Temperature On Resistance MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Effect Of Temperature On Resistance MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
As the temperature of a metallic conductor increases, its resistance generally:
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remains constant
d) Becomes zero
The temperature coefficient of resistance for most metals is:
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Zero
d) Undefined
For a semiconductor, as temperature increases, the resistance generally:
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Remains constant
d) Becomes zero
Which of the following materials has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance?
a) Carbon
b) Copper
c) Silver
d) Aluminum
The resistance of a thermistor decreases with:
a) Increasing temperature
b) Decreasing temperature
c) Increasing current
d) Increasing voltage
What happens to the resistance of an insulator as temperature increases?
a) It increases
b) It decreases
c) It remains constant
d) It becomes zero
The resistance of a metal wire at 100°C compared to its resistance at 20°C is likely to be:
a) Higher
b) Lower
c) The same
d) Zero
In a material with a high positive temperature coefficient of resistance, a small temperature change will:
a) Significantly change the resistance
b) Have little effect on the resistance
c) Cause the resistance to become negative
d) Keep the resistance constant
Which of the following is true for a negative temperature coefficient of resistance?
a) The resistance decreases with increasing temperature
b) The resistance increases with increasing temperature
c) The resistance remains constant with temperature
d) The resistance becomes zero with increasing temperature
The temperature coefficient of resistance is a measure of:
a) How resistance changes with temperature
b) How voltage changes with temperature
c) How current changes with temperature
d) How power changes with temperature
In semiconductors, increasing temperature typically:
a) Increases the number of charge carriers
b) Decreases the number of charge carriers
c) Keeps the number of charge carriers constant
d) Increases the resistance of the material
The resistance of an alloy generally:
a) Increases with temperature
b) Decreases with temperature
c) Remains constant with temperature
d) Is unpredictable with temperature changes
In metals, the rate of change of resistance with temperature is due to:
a) Increased atomic vibrations
b) Decreased atomic vibrations
c) Increased electron mobility
d) Decreased electron mobility
What is the effect of cooling a thermistor?
a) The resistance increases
b) The resistance decreases
c) The resistance remains constant
d) The resistance becomes negative
The resistance of an electrical component with a positive temperature coefficient will:
a) Increase as the component heats up
b) Decrease as the component heats up
c) Remain constant as the component heats up
d) Become zero as the component heats up
In a conductor, increasing temperature affects the electron collisions in which way?
a) It increases the number of collisions
b) It decreases the number of collisions
c) It has no effect on the collisions
d) It changes the type of collisions
For a metal wire, if the temperature is decreased, the resistance will:
a) Decrease
b) Increase
c) Remain constant
d) Become zero
Which of the following has a resistance that increases with temperature?
a) Metallic conductor
b) Thermistor
c) Superconductor
d) Carbon resistor
A positive temperature coefficient of resistance in a material indicates that:
a) The resistance increases with temperature
b) The resistance decreases with temperature
c) The resistance remains constant with temperature
d) The resistance becomes negative with temperature
The resistance of a typical metal at very low temperatures approaches:
a) Zero
b) Infinite
c) A constant high value
d) A variable value
In most metals, resistance is directly proportional to:
a) Temperature
b) Voltage
c) Current
d) Cross-sectional area
For a thermistor, a decrease in temperature will result in:
a) An increase in resistance
b) A decrease in resistance
c) No change in resistance
d) The resistance becoming zero
In semiconductors, as temperature increases, the resistance generally:
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Remains constant
d) Becomes zero
If the temperature of a resistor is increased, the rate of change of resistance can be calculated using:
a) The temperature coefficient of resistance
b) The power dissipation
c) The voltage drop
d) The current flowing through it
A negative temperature coefficient of resistance is characteristic of:
a) Thermistors
b) Metallic wires
c) Superconductors
d) Standard resistors
Which material’s resistance decreases as temperature increases?
a) Carbon
b) Gold
c) Silver
d) Copper
For most metals, the resistance-temperature relationship is:
a) Linear
b) Exponential
c) Logarithmic
d) Constant
The resistance of an alloy is typically more sensitive to temperature changes than that of:
a) Pure metals
b) Insulators
c) Superconductors
d) Semiconductors
Which of the following is true for the resistance of a thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient?
a) It decreases as temperature increases
b) It increases as temperature increases
c) It remains constant with temperature changes
d) It becomes zero at higher temperatures
The resistance of a material with a high positive temperature coefficient will:
a) Increase rapidly with temperature
b) Decrease rapidly with temperature
c) Remain nearly unchanged with temperature
d) Become negative with temperature
Which of the following factors does not affect the temperature coefficient of resistance?
a) Material composition
b) Temperature
c) Physical dimensions of the material
d) Pressure
For an ideal conductor, the resistance at different temperatures:
a) Remains zero
b) Is directly proportional to temperature
c) Is inversely proportional to temperature
d) Varies unpredictably
The resistance of a superconductor at temperatures above its critical temperature:
a) Increases dramatically
b) Decreases
c) Remains constant
d) Becomes zero
As the temperature of a resistor increases, the increase in resistance is primarily due to:
a) Increased lattice vibrations
b) Decreased lattice vibrations
c) Increased electron mobility
d) Decreased electron mobility
The resistance of an electrical wire at very high temperatures can become:
a) Very high
b) Very low
c) Zero
d) Constant
In materials with a high negative temperature coefficient, a rise in temperature leads to:
a) A decrease in resistance
b) An increase in resistance
c) No change in resistance
d) Resistance becoming zero
If the resistance of a conductor is known at one temperature, its resistance at another temperature can be calculated using:
a) The temperature coefficient of resistance
b) The power formula
c) Ohm’s law
d) Kirchhoff’s laws
In a semiconductor, resistance decreases with temperature due to:
a) Increased charge carrier concentration
b) Decreased charge carrier concentration
c) Decreased electron mobility
d) Increased lattice vibrations
The resistance of an element with a high positive temperature coefficient will:
a) Show a significant increase in resistance with a slight rise in temperature
b) Show no change with temperature variations
c) Show a decrease in resistance with a rise in temperature
d) Become zero at high temperatures
The resistance of a thermistor at low temperatures is:
a) Higher
b) Lower
c) Constant
d) Undefined
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.