Doppler Effect MDCAT Quiz with Answers
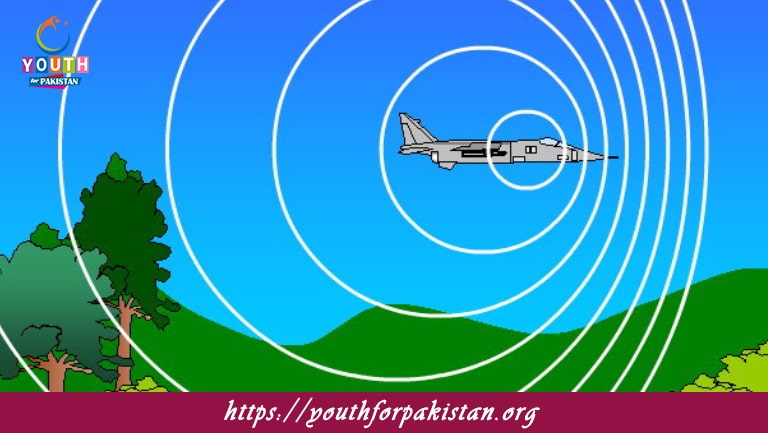

The Doppler Effect MDCAT Quiz is a change in the frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is most commonly observed in sound waves but applies to all types of waves, including light and electromagnetic waves. In the context of sound, the Doppler effect explains why the pitch of a sound changes when a moving sound source approaches or recedes from an observer. This principle is important for MDCAT students, particularly in the study of waves, sound, and relative motion.
Understanding the Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is a consequence of the motion of the source or the observer changing the relative position of the wave fronts. When the source of the wave is moving toward the observer, the wavefronts are compressed, hence shorter in wavelength and higher in frequency—higher pitch for sound. When the source moves away from the observer, the wave fronts are stretched out, resulting in a longer wavelength and a lower frequency—lower pitch.
Source Approach: When the source of sound waves is approaching the observer, the frequency of the waves appears to be higher, and the sound seems sharper or more intense.
Applications of the Doppler Effect
Sound and Music The most common experience in which the Doppler effect can be heard occurs when an ambulance or police car with a siren approaches and then passes by. When the vehicle approaches, the pitch of the siren sounds higher and when it recedes, the pitch sounds lower. This happens because the vehicle’s motion, relative to an observer, causes compression and stretching of the sound waves.
Radar and Medical Imaging: The principle of the Doppler effect is used in radar systems to measure the velocity of moving objects. In Doppler radar, the frequency shift of the reflected waves is used to measure the velocity of weather systems, vehicles, or even blood flow in medical imaging. Based on this principle, applications such as Doppler ultrasound have been developed for the monitoring of blood circulation.
Astronomy: The Doppler effect is essential in astronomy to find out how stars, galaxies, and other celestial bodies move. When a star or galaxy moves toward the Earth, the light from it shifts to the blue end of the spectrum—what is known as a blue shift—and when it moves away, the light shifts to the red end—known as a red shift. Astronomers can measure the velocity of these celestial bodies with respect to the Earth using this phenomenon.
Speed Detection in Automobiles: Police speed radar guns make use of the Doppler effect. The radar sends out electromagnetic waves, and by measuring the frequency shift of the reflected waves from a moving vehicle, the speed of that vehicle can be deduced.
Doppler Effect in Light Waves
Although the Doppler effect is mostly associated with sound waves, it surely does apply to electromagnetic waves like light. If the source of light is moving toward the observer, then the wavelength of the light is shortened—this is known as a blue shift—and if it is moving away, then the wavelength is stretched—this is known as a red shift. This is of particular importance in astrophysics, where the Doppler shift in the light from distant stars or galaxies enables scientists to measure the rate of expansion of the universe and to deduce the motion of celestial bodies.
Redshift and Blueshift: It is due to the Doppler shift of light waves, resulting in redshift (longer wavelengths, moving away) and blueshift (shorter wavelengths, moving toward). This concept is indispensable in understanding the Big Bang theory and the expansion of the universe, where the light coming from distant galaxies is redshifted, meaning they are moving away from us.
Key Factors Affecting the Doppler Effect
Speed of Source or Observer: The larger the relative velocity between the source and the observer, the stronger the Doppler effect. Increased speeds result in more significant frequency shifts.
Medium: The speed of sound is affected by the medium (air, water, or solid materials). The Doppler effect for sound waves depends on the speed of sound in the medium through which the waves propagate.
Direction of Motion: The effect will be greatest if the source and observer are either directly approaching or receding from each other. Motion at an angle decreases the magnitude of the frequency shift.
MDCAT Quiz: Doppler Effect
MDCAT students can expect to find questions about the Doppler effect, mainly in scenarios that involve sound waves, light waves, and relative motion. Students may be asked to calculate the observed frequency based on the relative motion of the source and observer or to explain the practical applications of the Doppler effect in various fields such as radar, astronomy, and medical imaging.
- Test Name: Doppler Effect MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Doppler Effect
The flashcards on the Doppler effect can help MDCAT students memorize quickly the important concepts, formulas, and applications of the principle. It may have flashcards containing practice problems for calculating the observed frequency and also real-life scenarios where the Doppler effect can be applied. Regular practice with these flashcards will enhance the student’s understanding of the Doppler effect, hence making them well-prepared for MDCAT Quiz questions.

How is the frequency affected when the source of sound moves towards the observer?
The frequency increases

How is the frequency affected when the source of sound moves away from the observer?
The frequency decreases

What happens to the observed frequency when the observer is moving towards a stationary source?
The frequency increases

What happens to the observed frequency when the observer is moving away from a stationary source?
The frequency decreases

What happens to the wavelength of sound when the source is moving towards the observer?
The wavelength decreases

In the Doppler effect, what happens when the source and observer move towards each other at the same speed?
The observed frequency doubles

What is the change in frequency called when the source moves towards the observer?
Positive Doppler shift

What is the change in frequency called when the source moves away from the observer?
Negative Doppler shift

What is the relationship between the speed of sound and the Doppler effect?
The speed of sound influences the observed frequency

In the Doppler effect, what happens to the frequency when the source and observer are moving in the same direction?
The observed frequency may increase or decrease

What happens to the frequency when the source moves faster than the observer?
The frequency decreases

What is the frequency shift for a stationary source and moving observer?
It depends on the speed of the observer

How does the Doppler effect explain the change in pitch of a passing car's horn?
The pitch becomes higher as the car approaches and lower as it moves away

How does the Doppler effect apply to light waves?
The frequency of light shifts towards the red or blue end of the spectrum

What is the "blueshift" in light waves?
The observed frequency increases due to the source moving towards the observer

In the Doppler effect, how does the velocity of the source affect the frequency shift?
The faster the source moves, the greater the shift in frequency

How does the Doppler effect influence sound waves in the atmosphere?
It causes a change in pitch as the source or observer moves

How does the Doppler effect apply to moving sound sources in air?
The frequency heard by the observer depends on the relative velocity

When both the source and observer are moving, how is the Doppler shift calculated?
By considering both velocities in the formula

How does the Doppler effect relate to the pitch of a moving car's horn?
The pitch increases as the car approaches and decreases as it moves away

In the Doppler effect, what happens when the source and observer move at the same speed?
No frequency shift occurs

What happens when a spaceship moves towards a distant observer?
The observer detects a frequency increase
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.