Cyclic and Noncyclic Phosphorylation MDCAT Quiz with Answers
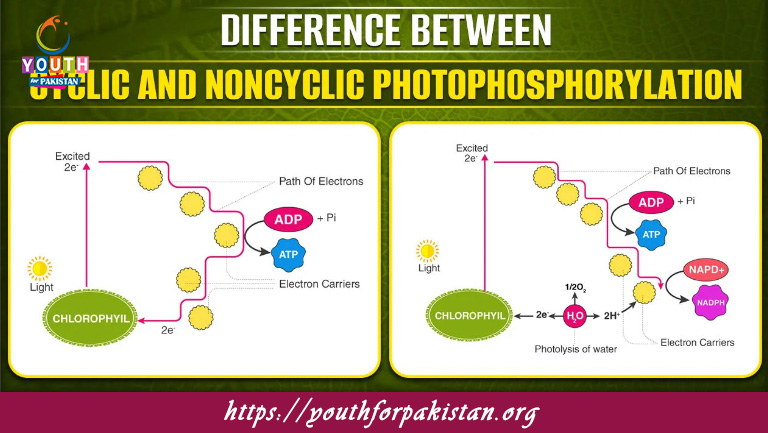
Cyclic and Noncyclic Phosphorylation MDCAT Quiz: Cyclic and non-cyclic phosphorylation are two events involved in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis that take place within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. While both of them result in the production of ATP, they differ in pathway, electron flow, and the extra molecules formed. These processes play a critical role in providing the energy and reducing power required for the light-independent phase (Calvin Cycle). It is very essential for MDCAT students to understand these mechanisms to enable them to tackle questions regarding photosynthesis and the production of energy.
Cyclic Phosphorylation
In cyclic phosphorylation, electrons excited by sunlight in photosystem I (PSI) are cycled back to the same photosystem. Only photosystem I is involved in this process, and neither NADPH nor oxygen is produced. The electrons pass through an electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis through photophosphorylation. Cyclic phosphorylation is especially important when the cell needs more ATP than NADPH or when NADP⁺ is scarce.
Noncyclic Phosphorylation
Noncyclic phosphorylation involves both photosystem II (PSII) and photosystem I (PSI) and is the primary pathway in the light-dependent reactions. Here, electrons excited in PSII are passed through an electron transport chain, generating ATP, and are then transferred to PSI. Electrons from PSI are used to reduce NADP⁺ into NADPH, a molecule essential for the Calvin Cycle. To replenish lost electrons in PSII, water is split in a process called photolysis, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
Test Your Knowledge with an MDCAT Quiz
Take the MDCAT Quiz on Cyclic and Noncyclic Phosphorylation to find out how well you understand the differences and importance of these processes. It will also include the role of photosystems, the production of ATP and NADPH, and the splitting of water during photolysis. You can improve your performance in answering questions from this section in MDCAT with frequent practice.
Free Flashcards for Quick Revision
Free Flashcards on Cyclic and Noncyclic Phosphorylation: a very concise summary of the main processes and distinctions between the pathways. They emphasize photosystems’ role, the products formed, and conditions favoring each type of phosphorylation and are an excellent tool for quick review and last-minute preparation for the MDCAT exam.
Mastering the concepts of Cyclic and Noncyclic Phosphorylation comes in handy while understanding the mechanisms of energy production in photosynthesis. Use our quizzes and flashcards to increase your knowledge and ace your MDCAT preparation!
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.