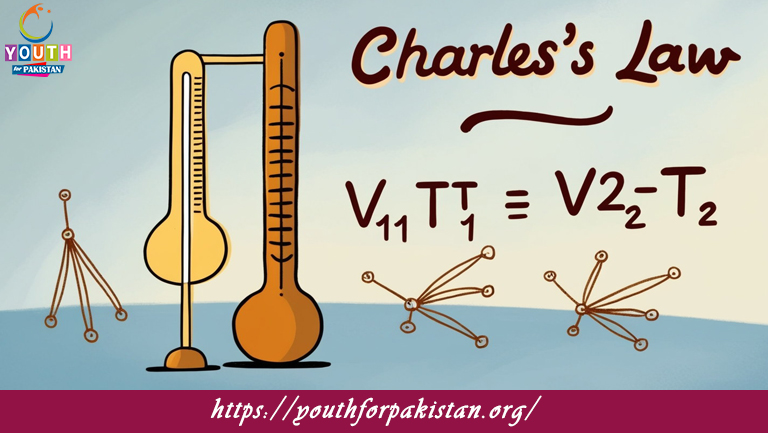
Charles’s Law MDCAT Quiz relates the temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure. It states that the volume of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature measured in Kelvin. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, so does its volume, provided the pressure remains constant. This law is fundamental for MDCAT students since it helps explain the behavior of gases when they are heated or cooled. The knowledge of Charles’s Law is necessary to solve the problems related to gas laws that frequently appear in the MDCAT Quiz.
MDCAT Quiz on Charles’s Law
The MDCAT Quiz on Charles’ Law has questions to check students’ ability in applying the law when solving problems relating to the relation between temperature and volume of a gas. The question paper involves a few questions about the calculation of final volume of gas with change in temperature and vice versa, keeping constant pressure. With regular practice on this quiz, students get enough problem-solving practice to equip them for answering similar questions appearing in the MDCAT exam.
0Get Your Username and Password for MDCAT Tests
Sign Up Now
Free Flashcard for Charles’s Law
Our Free Flashcard for Charles’s Law provides a succinct, clarifying explanation of the law and the formula with real-life examples. These flashcards are good for quick reference to the direct relationship between temperature and volume in a gas. Through the help of flashcards, the concepts of Charles’ Law could easily be committed to memory for students to easily apply during the MDCAT examination.

According to Charles's Law, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its __________.

Charles's Law is valid only when the __________ is constant.

As the temperature of a gas increases, the volume of the gas __________.

In Charles's Law, the temperature must be measured in __________.

The equation for Charles's Law is __________.

Charles's Law describes the relationship between __________ and temperature.

The temperature must always be in __________ for Charles's Law to be applied.

If the temperature of a gas is doubled, the volume will __________.

Charles's Law is also known as the law of __________.

As the temperature of a gas decreases, its volume __________.

The relationship in Charles's Law applies to __________ gases.

In Charles's Law, the volume of a gas is __________ related to temperature.

If the volume of a gas at 20°C is 2 liters, what will the volume be at 40°C?

Charles's Law is used to explain the behavior of __________.

The pressure of a gas in Charles's Law must be __________.

If the temperature of a gas is reduced, the volume will __________.

If the volume of a gas is 5 liters at 300 K, what would the volume be at 150 K?

The relationship between temperature and volume is __________.

For Charles's Law to hold true, the gas must be __________.

A balloon filled with air expands when heated due to __________.

If a gas occupies 10 liters at 200 K, what will be its volume at 400 K?

The equation for Charles's Law is used to calculate __________.

In Charles's Law, if the temperature is halved, the volume will __________.

The constant in the equation for Charles's Law is represented by __________.

Charles's Law applies only to gases that behave as __________ gases.

When a gas is heated in a flexible container, its volume will __________.

The temperature-volume relationship in Charles's Law is a __________ curve.

When the volume of a gas increases, its temperature is __________.

The volume of a gas at 273 K is 1 liter, what will be its volume at 546 K?

Charles's Law assumes that gas particles do not __________.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.
View Your Dashboard