Cellular Structure Of Bacteria MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Cellular Structure Of Bacteria MDCAT Quiz: The cellular structure of bacteria is unique and highly specialized to make these microorganisms succeed in almost all kinds of environments. As prokaryotic cells, bacteria do not have membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus. Instead, the genetic material can be found in the region known as the nucleoid, which acts to regulate the functions of the cell. Knowledge of different structures found in bacterial cells is critical for MDCAT students in understanding the function and classification of these microorganisms. The MDCAT Quiz will test your knowledge concerning the different components of a bacterial cell and their roles within the cell in terms of keeping it alive and functional.
Key Structures of Bacterial Cells
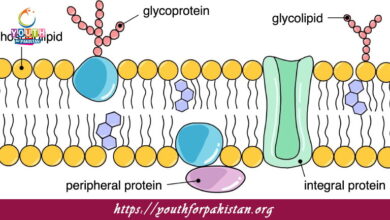
The various structures of a bacterial cell allow it to conduct necessary functions. The cell membrane encompasses the contents of the cell and regulates the entry and exit of materials. A cell wall, mostly composed of peptidoglycan, usually provides structural support and protection for most bacteria. The bacterial DNA is located in the nucleoid, and ribosomes inside the cell take part in the synthesis of proteins. Other than that, certain bacteria have other special structures like flagella, which help them to move, and pili, by which they attach to a surface. These are just a few features which will be highlighted during the MDCAT Quiz for better comprehension of their importance and function in bacterial cells.
Specialized Structures and Functions in Bacteria
In addition to the structures described, bacteria may have some other structures that enable them to survive in a given environment. For instance, some bacteria have capsules that provide protection against the immune system, while others produce endospores that, in effect, are dormant structures that help to survive adverse environmental conditions. Flagella are the protein filaments that give the bacteria motility through a liquid environment. Try a free Flashcard on bacterial structures that helps you quickly revise these features, ensuring you recall their importance and roles in bacterial survival and pathogenicity.
Quiz on the Cellular Structure of Bacteria
Taking a practice MDCAT Quiz on bacterial cellular structure will test your understanding of how each component contributes to the survival, reproduction, and interaction with the environment of the bacterium. The quiz will explore such aspects as the structure of the bacterial cell wall, the function of ribosomes, and that of flagella. In addition to this, using Free Flashcards will make you memorize key features of bacterial cells and your ability to recall them during your MDCAT exam.

The structure of a bacterial cell responsible for transporting substances is the _________.
Plasma membrane

Bacteria that possess a single layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall are called _________.
Gram-positive bacteria

The bacterial ribosome consists of a ________ ribosomal subunit and a ________ ribosomal subunit.
50S, 30S

The ________ is a protective barrier that helps bacteria resist desiccation and harsh conditions.
Capsule
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.