Carnivorous Plants/Parasitic Nutrition MDCAT Quiz with Answers

Carnivorous Plants/Parasitic Nutrition MDCAT Quiz; Carnivorous plants and parasitic nutrition are fascinating biological phenomena that highlight the diverse adaptations of plants in response to nutrient limitations. These plants, unlike most, are capable of deriving some or all of their nutrients from animals or other plants. If you’re preparing for the MDCAT exam, understanding these unique nutritional strategies can be crucial. This MDCAT Quiz will test your knowledge on various aspects of carnivorous plants, their habitats, and the mechanisms they use to trap and digest prey.
Understanding Carnivorous Plants
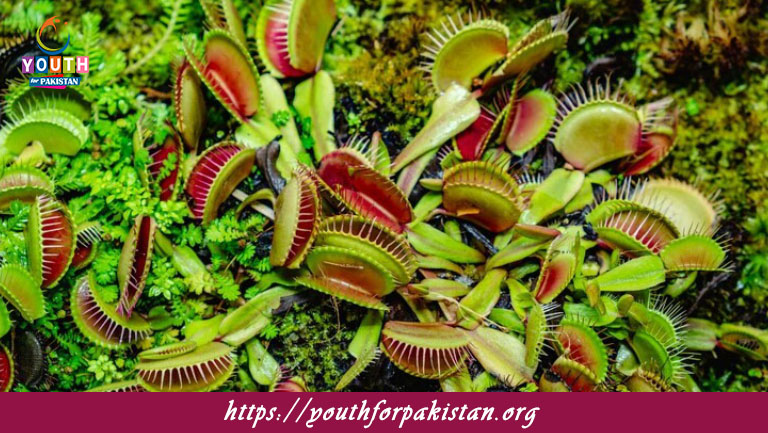
Such plants have evolved to entrap and digest prey, mostly insects, as a supplementary means of obtaining nutrients. This is particularly significant in soils low in nutrients, such as bogs and swamps. The species like Venus flytrap, pitcher plants, and sundews use highly adapted structures to entice, trap, and digest their prey. Such adaptations are not just vital for their survival but also open more horizons toward understanding the subject of evolutionary biology. This quiz will allow students to understand the various types of carnivorous plants and the scientific principles that underlie these unique feeding strategies.
Parasitic Nutrition in Plants
Some parasitic plants, such as mistletoe and dodder, have evolved to directly access the host’s nutrient products. These plants are categorized into hemiparasites or holoparasites, depending on their level of reliance on the host for food. Hemiparasites are photosynthetic; hence they partially depend on the host for water and minerals but holoparasites entirely depend on their host for survival. A Free Flashcard resource can help you memorize important characteristics of these plants enhancing your understanding for the MDCAT exam.
Quiz on MDCAT and Plant Nutrition
To master topics like parasitic nutrition and carnivorous plants, taking a MDCAT Quiz can help reinforce concepts and improve recall. The quiz will cover various questions about the anatomy and physiology of these plants, their ecological roles, and their interaction with other organisms. The flashcards available on this topic also provide an interactive way to review essential facts quickly, ensuring you’re well-prepared for exam day.

The movement of insects into the pitcher plant’s trap is aided by ________.
Nectar secreted by the plant

The opening of a pitcher plant’s trap is covered by ________ to prevent the escape of trapped insects.
A lid or cover

The evolutionary adaptation of pitcher plants enables them to grow in soil that is ________.
Nutrient-poor
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.