Carboxylic Acids Classification MDCAT Quiz with Answers
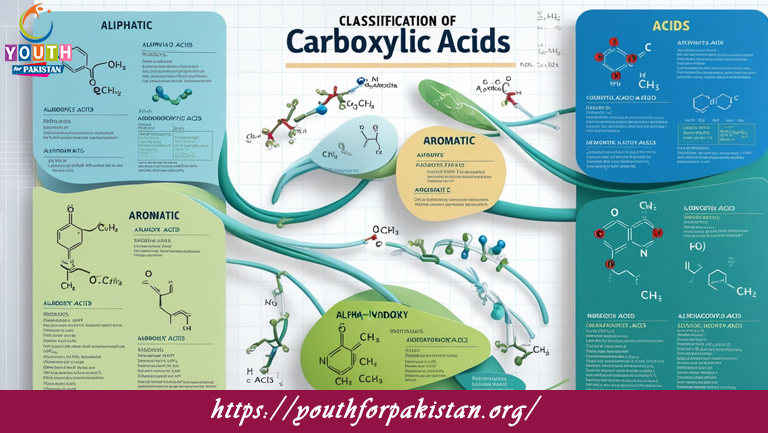
Carboxylic Acids Classification MDCAT Quiz is very important for organic chemistry, especially for MDCAT students. There are a few factors on which carboxylic acids can be classified, like the number of carboxyl groups, the structure of the carbon chain, and the presence or absence of other functional groups. This helps students understand the diverse nature of carboxylic acids and their reactivity in different chemical reactions.
Classification Based on the Number of Carboxyl Groups
Monocarboxylic Acids: These are carboxylic acids that have one carboxyl group (-COOH) in their carbon structure. Examples include acetic acid (CH₃COOH), formic acid (HCOOH), and propanoic acid (C₂H₅COOH). Monocarboxylic acids are very typical and well-studied in organic chemistry.
Dicarboxylic Acids: These acids have two carboxyl groups attached within the structure. They are sometimes referred to as diacids. Common examples are oxalic acid (ethanedioic acid, C₂H₂(CO₂H)₂), succinic acid (butanedioic acid, C₄H₆O₄), and malonic acid (propanedioic acid, C₃H₄O₄). Very interestingly, dicarboxylic acids participate in special kinds of reactions known as decarboxylation and condensation.
Tricarboxylic Acids: These acids have three carboxyl groups. Citric acid (C₆H₈O₇) is the common tricarboxylic acid found in fruits like lemons. Tricarboxylic acids are vital in metabolic processes, as in the Krebs cycle.
Hydroxy Acids: These are carboxylic acids that also contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the carbon chain. For example, lactic acid (2-hydroxypropanoic acid) and citric acid (2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylic acid) are hydroxy acids.
Amino Acids: These are carboxylic acids that also contain an amino group (-NH₂) in their structure. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Examples include glycine (aminoethanoic acid) and glutamic acid.
Halogenated Carboxylic Acids: These acids contain one or more halogen atoms (such as chlorine, bromine, or fluorine) attached to the carbon chain. For example, chloroacetic acid (ClCH₂COOH) contains a chlorine atom.
Special Classes of Carboxylic Acids:
Fatty Acids: These are the long-chain monocarboxylic acids containing typically 12-18 carbon atoms, found in animal and vegetable fats and oils. Example: stearic acid (C₁₈H₃₆O₂) and oleic acid (C₁₈H₃₄O₂). They are important in nutrition and used in soap-making and production of biodiesel.
Dicarboxylic Acid Derivatives: These are dicarboxylic acids that have been modified to contain other functional groups such as ester, anhydride, and amide groups. For example, phthalic acid (benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid) is used for manufacturing plasticizers and dyes.
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Carboxylic Acid Classification
This MDCAT Quiz on classification of carboxylic acids will enable one to determine whether he/she fully understands the many ways in which carboxylic acids can be classified based on structure alone, as well as their functional group. Questions may ask for the name, identification, or classification of given carboxylic acids.
Free Flashcard: Key Insights on Carboxylic Acid Classification
Our free flashcard set on the classification of carboxylic acids allows for a quick reference guide through all the different classes of carboxylic acids, such as aliphatic, aromatic, and polycarboxylic acids. These flashcards are an excellent tool for reinforcing your knowledge and ensuring you’re well-prepared for the MDCAT exam.

Glutaric acid, containing five carbon atoms and two carboxyl groups, is a __________.
Dicarboxylic acid

A carboxylic acid with no additional functional groups is called a __________ acid.
Simple carboxylic acid

Carboxylic acids that have hydroxyl groups along with the carboxyl group are called __________.
Hydroxy acids

A carboxylic acid with only one carboxyl group and no other functional groups is a __________.
Simple carboxylic acid

Carboxylic acids having an aromatic ring attached to a -COOH group are called __________.
Aromatic acids

Carboxylic acids that have the carboxyl group attached to an alkyl chain are called __________.
Aliphatic acids
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.





