Atomic Spectra MDCAT Quiz with Answers
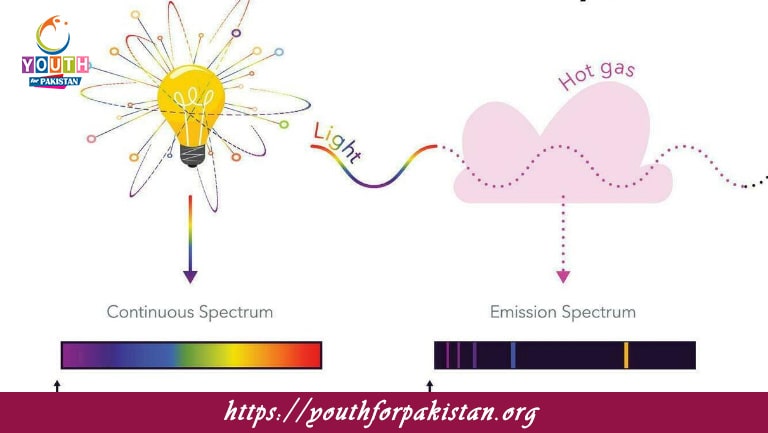
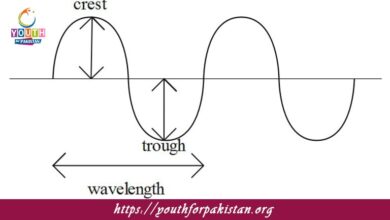
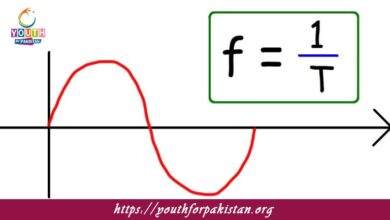
Atomic Spectra MDCAT Quiz the unique set of wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed by atoms as the electrons change energy levels within an atom. Every element has a unique atomic spectrum, which serves as a “fingerprint” for that element. This spectrum is seen with the help of a spectrometer and comprises certain lines corresponding to the differences in energy between the allowed energy levels of the atom. Atomic spectra played an important role in the early development of quantum mechanics, specifically in understanding the behavior of electrons in atoms. Bohr’s model of the atom explained these spectra by assuming electrons exist in definite orbits around the nucleus and light is either emitted or absorbed as the electrons jump from one orbit to another. For MDCAT students, the concept of atomic spectra is very important for solving problems relating to atomic structure and light interactions.
Test Your Knowledge with an MDCAT Quiz
An MDCAT Quiz on Atomic Spectra will strengthen your understanding of the principles behind emission and absorption spectra. These quizzes include subjects such as Bohr’s Model, the calculation of wavelengths using the Rydberg formula, and differences between continuous, line, and band spectra. Regular practice will ensure that you are well-prepared to handle questions on the atomic spectra that come up in the MDCAT exam—questions that frequently test knowledge about atomic structure and light behavior.
- Test Name: Atomic Spectra MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Quick Revision
The free flashcards on Atomic Spectra will quickly summarize important concepts like Bohr’s energy levels, the Rydberg equation, and applications of atomic spectra in the identification of elements. Flashcards are good for a quick review of important formulas and definitions, helping you retain critical information for the MDCAT exam.

The energy of a photon emitted or absorbed during an atomic transition is proportional to:
The difference in energy levels

In atomic spectra, the wavelengths of emitted photons depend on:
The energy difference between levels

The wavelength of the emitted radiation is inversely proportional to:
The energy difference between levels

The wavelength of light emitted in an atomic transition is determined by:
The energy difference between levels

The energy difference between two levels in an atom is proportional to:
The frequency of the emitted photon

The transition of an electron from the n = 3 to n = 2 energy level in hydrogen produces light in the:
Balmer series

The frequency of the emitted radiation during an atomic transition depends on:
The energy difference between the two levels

The wavelength of light emitted during a transition in an atom can be calculated using:
The Rydberg formula

The lines in an atomic emission spectrum correspond to:
Transitions of electrons between discrete energy levels
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.