Amplitude MDCAT Quiz with Answers
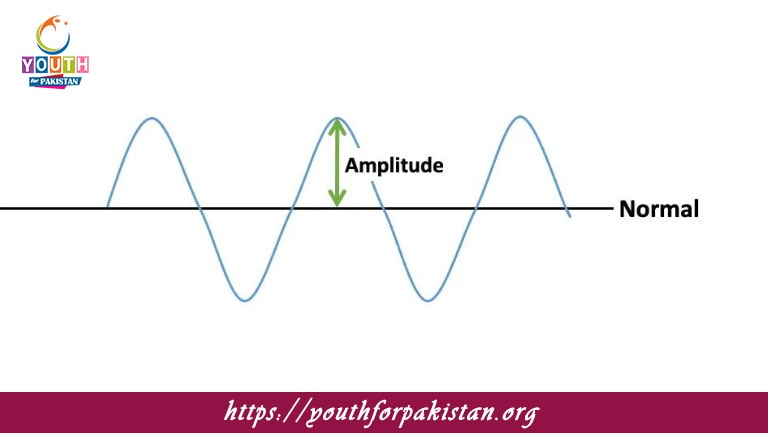
Amplitude MDCAT Quiz of a wave is defined as the maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position. For a transverse wave, it is the height of the crest or the depth of the trough of the wave, measured from the rest position, or equilibrium line. In the case of longitudinal waves, amplitude refers to the amount of compression and rarefaction in the wave, indicating how far the particles of the medium move from the equilibrium position. Amplitude is an important characteristic of waves, since it is directly connected to the energy carried by the wave. MDCAT students must learn about amplitude for both mechanical and electromagnetic waves because it influences the wave’s characteristics—intensity, energy, loudness (for sound waves), or brightness (for light waves).
Characteristics of Amplitude
Amplitude and Energy: The energy of a wave is directly proportional to the square of the amplitude. In other words, greater the amplitude, greater will be the energy carried by the wave. For instance, in sound waves, larger amplitudes mean the louder the sound, while for light waves, greater amplitudes mean brighter the light. It is an important relationship for explaining wave behavior in many different media.
Amplitude Measurement: The amplitude in a transverse wave is the distance from the equilibrium position to the crest peak or trough. In the case of a longitudinal wave, amplitude is described as the degree of compression or rarefaction; it represents the maximum displacement of particles in the medium, in the direction of wave propagation.
Effect of Amplitude on Wave Properties: Amplitude has a lot to say about the characteristics of the wave. A larger amplitude increases the intensity of the wave. For example, in mechanical waves like sound waves, amplitude refers to the loudness of the sound. In an electromagnetic wave, higher amplitude means higher intensity of light.
MDCAT Quiz: Amplitude Questions
The MDCAT Quiz may contain questions on the amplitude of a wave, asking students to calculate it given some parameters, such as the height of the crest or the depth of the trough. It may ask how amplitude is related to the energy of a wave, say, in discussing sound waves or light waves. The MDCAT students may also be required to describe how amplitude affects any one property of a wave, for example, intensity or loudness, and give real-life examples based on that description.
- Test Name: Amplitude MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Amplitude
Free flashcards focused on amplitude can be a helpful tool for MDCAT students. These flashcards can include diagrams of waves showing the amplitude, formulas for calculating energy in relation to amplitude, and practice problems that involve determining amplitude from wave characteristics. By reviewing these flashcards, students can reinforce their understanding of amplitude and improve their ability to solve wave-related problems efficiently in the MDCAT Quiz.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.