Alternating Current Generator MDCAT Quiz with Answers
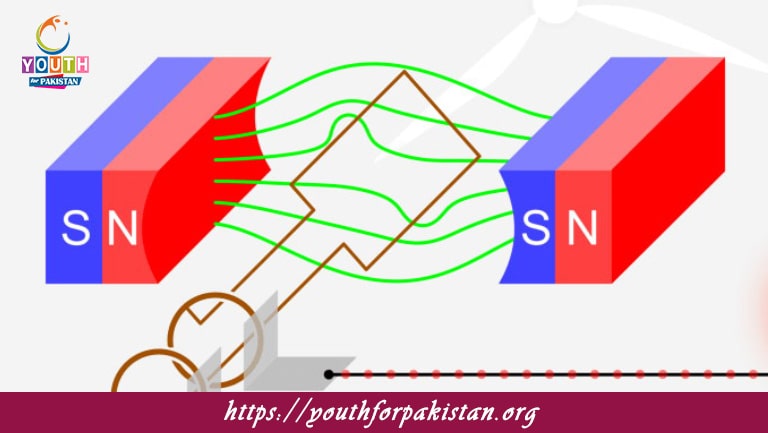
Alternating Current Generator MDCAT Quiz Generator, commonly called an alternator, is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The AC generator generates an electromotive force (emf) in the coil of wire when it is rotated within the magnetic field by applying Faraday’s Law. Hence, changing the direction of the induced current with the rotation of the coil produces an alternating current. In other words, the frequency of the alternating current depends upon the speed of rotation and the number of coils used in the generator. In the MDCAT paper, an AC generator can be understood while attempting problems related to electromagnetic induction, conversion of energy, and power generation systems.
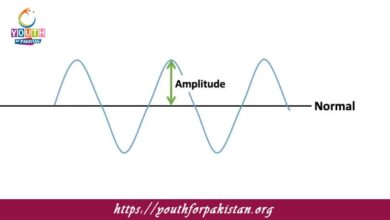
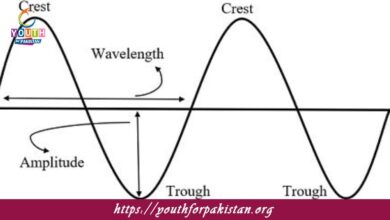
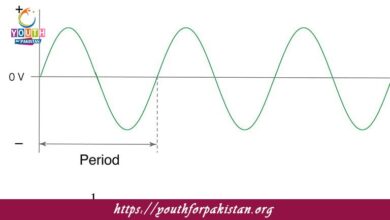
Alternating Current Generator MDCAT Quiz
An MDCAT Quiz on AC Generators will help you solidify your understanding of how mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. These quizzes deal with such topics as induced emf calculations, the relationship between coil rotation and current frequency, and the role of the magnetic field in generating AC. Practice regularly with these quizzes to improve your skills in solving problems and prepare well for related questions on the MDCAT exam.
- Test Name: Alternating Current Generator MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Efficient Revision
Free Flashcards on Alternating Current Generators provide concise definitions, formulas, and important concepts such as the calculation of induced emf in a rotating coil, the relationship between current, voltage, and frequency, and how an AC generator works in real-world power plants. Flashcards are an excellent revision tool to quickly recall key information and prepare for the MDCAT exam.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.