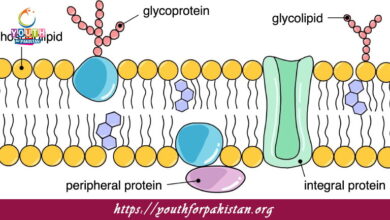
Water And Mineral Uptake By Roots Xylem And Phloem MDCAT MCQs

Welcome to the Water And Mineral Uptake By Roots Xylem And Phloem MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Water And Mineral Uptake By Roots, Xylem And Phloem Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Biology offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Water And Mineral Uptake By Roots, Xylem And Phloem MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Which structure in plant roots is primarily responsible for the absorption of water and minerals?
a) Root cap
b) Epidermis
c) Cortex
d) Xylem
In which part of the plant does water travel through the xylem?
a) Leaves
b) Roots
c) Stem
d) Flowers
What is the main function of the phloem in plants?
a) Water transport
b) Mineral transport
c) Nutrient transport
d) Food transport
Which process describes the movement of water from the soil into the plant root?
a) Osmosis
b) Diffusion
c) Active transport
d) Filtration
Which cells in the root are specifically adapted for the uptake of minerals?
a) Parenchyma cells
b) Sclerenchyma cells
c) Xylem cells
d) Root hair cells
What role does the root cap play in the absorption of water and minerals?
a) Protects the growing tip
b) Transports nutrients
c) Stores food
d) Absorbs water
How does the xylem contribute to the water transport in plants?
a) By storing water
b) By conducting water from roots to leaves
c) By absorbing nutrients
d) By transporting sugars
Which type of tissue in plants is involved in the transport of nutrients and sugars?
a) Xylem
b) Phloem
c) Epidermis
d) Cortex
What is the primary mechanism for the uptake of minerals from the soil into root cells?
a) Passive diffusion
b) Active transport
c) Bulk flow
d) Facilitated diffusion
Which plant structure is mainly responsible for water storage and regulation?
a) Xylem vessels
b) Root hairs
c) Guard cells
d) Phloem tubes
Where does the majority of water absorption occur in plant roots?
a) Root cap
b) Root hairs
c) Xylem
d) Cortex
What causes the movement of water through the plant’s xylem vessels?
a) Root pressure
b) Capillary action
c) Transpiration pull
d) Osmotic pressure
What is the primary function of root hairs in plants?
a) Absorbing sunlight
b) Storing nutrients
c) Enhancing water and mineral absorption
d) Producing seeds
Which of the following is NOT a component of the xylem?
a) Tracheids
b) Vessel elements
c) Parenchyma cells
d) Sieve tubes
What drives the movement of water from the roots to the leaves in plants?
a) Root pressure
b) Soil moisture
c) Transpiration
d) Gravitational pull
Which structure within the phloem is responsible for the transport of nutrients?
a) Xylem vessels
b) Companion cells
c) Sieve tubes
d) Root hairs
How does the plant regulate water loss through its leaves?
a) By opening and closing stomata
b) By increasing root pressure
c) By decreasing xylem activity
d) By storing excess water in roots
What is the function of companion cells in the phloem?
a) Support xylem vessels
b) Facilitate the loading and unloading of sugars
c) Absorb water
d) Provide structural support
Which part of the plant is responsible for the uptake of carbon dioxide?
a) Roots
b) Stems
c) Leaves
d) Flowers
What is the role of root pressure in water transport?
a) Pushes water upward through the xylem
b) Helps in nutrient absorption
c) Assists in the movement of sugars
d) Reduces water loss through transpiration
Which of the following structures is NOT involved in the transport of water?
a) Tracheids
b) Xylem vessels
c) Sieve tubes
d) Root hairs
Which of these processes involves the movement of water from the soil into plant roots?
a) Active transport
b) Osmosis
c) Transpiration
d) Photosynthesis
What is the primary driving force for the movement of water in plants during transpiration?
a) Root pressure
b) Capillary action
c) Cohesion and adhesion
d) Temperature gradient
How do plants primarily obtain their essential minerals?
a) From the atmosphere
b) Through the soil
c) From sunlight
d) Through the xylem
Which part of the plant is mainly involved in the transport of sugars and amino acids?
a) Xylem
b) Phloem
c) Epidermis
d) Cuticle
What mechanism allows water to travel through plant cell membranes?
a) Osmosis
b) Active transport
c) Diffusion
d) Filtration
Which cells are responsible for creating the pathway through which water moves in the xylem?
a) Sieve tube elements
b) Tracheids
c) Companion cells
d) Parenchyma cells
What is the primary role of the root cortex in water and mineral absorption?
a) Transport of nutrients
b) Protection of the vascular tissues
c) Storage of starch
d) Facilitating the movement of water and minerals to the xylem
What is the effect of high transpiration rates on the xylem?
a) Decreases water uptake
b) Increases root pressure
c) Enhances water transport to leaves
d) Reduces water loss
Which process primarily drives the upward movement of water in the xylem?
a) Capillary action
b) Root pressure
c) Transpiration
d) Soil moisture
How do root hairs contribute to water absorption in plants?
a) By increasing surface area for absorption
b) By storing water
c) By transporting sugars
d) By producing xylem cells
What role does the xylem play in maintaining plant structure?
a) It provides structural support through lignified tissues
b) It facilitates nutrient transport
c) It stores excess water
d) It helps in photosynthesis
What is the primary function of sieve tube elements in the phloem?
a) Transport of water
b) Storage of nutrients
c) Transport of sugars and other organic compounds
d) Absorption of minerals
How does the movement of water from soil to plant roots occur?
a) By active transport
b) By osmosis
c) By diffusion
d) By evaporation
Which process helps in the movement of minerals into plant roots?
a) Active transport
b) Passive diffusion
c) Osmosis
d) Facilitated diffusion
What is the role of guard cells in relation to water uptake?
a) They open and close stomata to regulate water loss
b) They absorb nutrients from the soil
c) They store excess water
d) They transport sugars
Which tissue type in plants primarily supports the vascular system?
a) Xylem
b) Phloem
c) Epidermal
d) Parenchyma
What type of movement is responsible for the ascent of water in plants?
a) Passive transport
b) Active transport
c) Bulk flow
d) Osmosis
How do plants typically increase water uptake during dry conditions?
a) By increasing the number of root hairs
b) By closing stomata
c) By decreasing transpiration
d) By increasing root pressure
Which part of the plant is crucial for transporting nutrients from the roots to other parts?
a) Xylem
b) Phloem
c) Epidermis
d) Guard cells
How do plants control water loss through their leaves?
a) By regulating transpiration rates
b) By increasing xylem activity
c) By storing water in vacuoles
d) By closing root pores
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.