First Law Of Thermodynamics MDCAT MCQs with Answers
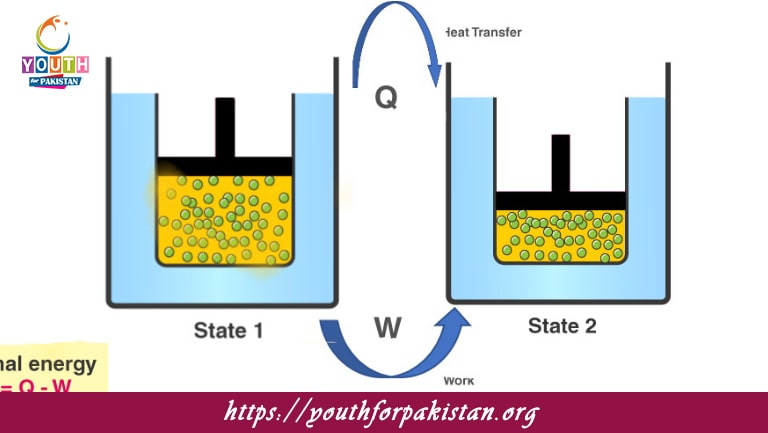
Welcome to the First Law Of Thermodynamics MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared First Law Of Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding First Law Of Thermodynamics MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
First Law Of Thermodynamics MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
The First Law of Thermodynamics is also known as:
A) Law of Conservation of Momentum
B) Law of Conservation of Energy
C) Law of Conservation of Mass
D) Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, the total energy of an isolated system is:
A) Constant
B) Variable
C) Increasing
D) Decreasing
The internal energy of a system increases when:
A) Work is done on the system
B) Work is done by the system
C) Heat is removed from the system
D) The system expands without heat exchange
Which of the following processes involves no change in internal energy?
A) Isothermal
B) Adiabatic
C) Isobaric
D) Isochoric
If a gas absorbs 500 J of heat and does 200 J of work, what is the change in internal energy?
A) 300 J
B) 700 J
C) 200 J
D) 500 J
In a cyclic process, the net work done by the system is equal to:
A) The net heat absorbed
B) The net heat released
C) Zero
D) The change in internal energy
During an isochoric process, the work done by the gas is:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Zero
D) Equal to the heat absorbed
If a system does 100 J of work and 200 J of heat is added, what is the change in internal energy?
A) 100 J
B) 200 J
C) 300 J
D) 400 J
Which of the following is an example of the First Law of Thermodynamics?
A) Heat engines
B) Refrigerators
C) Heat pumps
D) All of the above
In an adiabatic process, the heat exchanged is:
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Maximum
The work done by a system during an isobaric process depends on:
A) The change in pressure
B) The change in volume
C) The change in temperature
D) The change in internal energy
When a gas is compressed in an adiabatic process, its:
A) Temperature increases
B) Temperature decreases
C) Internal energy remains constant
D) Pressure remains constant
The heat energy absorbed or released in an isothermal process is:
A) Equal to the change in internal energy
B) Equal to the work done by the system
C) Equal to the work done on the system
D) Zero
During an isobaric process, the pressure of the gas:
A) Remains constant
B) Increases
C) Decreases
D) Fluctuates
The First Law of Thermodynamics is violated in:
A) Isothermal processes
B) Cyclic processes
C) Perpetual motion machines of the first kind
D) Adiabatic processes
The First Law of Thermodynamics can be applied to:
A) Open systems
B) Closed systems
C) Isolated systems
D) All of the above
If no work is done by the system, the change in internal energy is equal to:
A) The heat added to the system
B) The heat removed from the system
C) Zero
D) The change in pressure
Which process follows the First Law of Thermodynamics?
A) Heating water
B) Melting ice
C) Boiling water
D) All of the above
In an isothermal process, the internal energy of the system:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains constant
D) Fluctuates
If a system loses 100 J of heat and 50 J of work is done on the system, what is the change in internal energy?
A) -50 J
B) -100 J
C) 150 J
D) -150 J
The work done by a gas in an adiabatic process is:
A) Equal to the heat absorbed
B) Equal to the change in internal energy
C) Equal to the change in temperature
D) Zero
In an isochoric process, the change in internal energy is:
A) Equal to the heat absorbed
B) Equal to the work done by the system
C) Zero
D) Equal to the change in temperature
During an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, the work done by the gas is:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Zero
D) Infinite
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the First Law of Thermodynamics?
A) It states that energy can be created or destroyed
B) It is a special case of the Second Law of Thermodynamics
C) It is applicable to all thermodynamic processes
D) It is valid only for reversible processes
The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on:
A) Pressure
B) Volume
C) Temperature
D) The type of gas
Which quantity is conserved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics?
A) Mass
B) Momentum
C) Energy
D) Volume
In an isolated system, the sum of heat and work is:
A) Constant
B) Variable
C) Increasing
D) Decreasing
Which of the following is a correct interpretation of the First Law of Thermodynamics?
A) Energy is always conserved
B) Work done on the system is always positive
C) Heat added to the system is always positive
D) The internal energy of a system is always zero
If a system performs 250 J of work and the change in internal energy is 500 J, what is the heat added to the system?
A) 250 J
B) 500 J
C) 750 J
D) 1000 J
During an adiabatic expansion, the internal energy of the gas:
A) Remains constant
B) Increases
C) Decreases
D) Becomes zero
In a closed system, if heat is added, the internal energy:
A) Decreases
B) Remains constant
C) Increases
D) Becomes zero
The First Law of Thermodynamics does not apply to:
A) Biological systems
B) Isolated systems
C) Closed systems
D) Perpetual motion machines of the first kind
For an ideal gas, the work done during an isothermal process is directly proportional to:
A) Temperature
B) Volume
C) Pressure
D) Internal energy
If a gas absorbs 600 J of heat and does 200 J of work, what is the change in internal energy?
A) 800 J
B) 400 J
C) 200 J
D) 600 J
Which of the following processes follows the First Law of Thermodynamics?
A) Free expansion
B) Heating
C) Cooling
D) All of the above
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.