Charging And Discharging A Capacitor MDCAT MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Charging And Discharging A Capacitor MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Charging And Discharging A Capacitor Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Charging And Discharging A Capacitor MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Charging And Discharging A Capacitor MDCAT MCQs Test Preparations
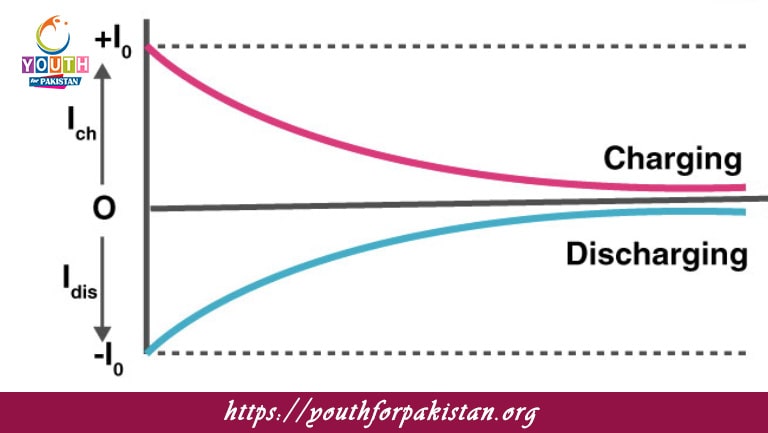
The voltage across a charging capacitor increases:
A) Exponentially
B) Linearly
C) Inversely
D) Logarithmically
The current through a discharging capacitor decreases:
A) Exponentially
B) Linearly
C) Constantly
D) Logarithmically
The voltage across a discharging capacitor after a long time is:
A) Maximum
B) Minimum
C) Zero
D) Equal to the supply voltage
In a capacitor charging circuit, the time constant is:
A) The time required for the voltage to reach 63.2% of the maximum value
B) The time required for the current to become zero
C) The time required for the capacitor to be fully charged
D) The time required for the capacitor to be completely discharged
The current through a capacitor during charging is:
A) Maximum at the start and decreases over time
B) Constant
C) Zero at the start and increases over time
D) Zero throughout
The time required for a capacitor to charge to approximately 99% of its full charge is:
A) 1 time constant
B) 2 time constants
C) 5 time constants
D) 10 time constants
The time constant of an RC circuit determines:
A) The speed of charging and discharging
B) The maximum voltage of the capacitor
C) The resistance of the circuit
D) The capacitance of the capacitor
When a capacitor is fully charged, the current through it is:
A) Zero
B) Maximum
C) Half of the maximum value
D) Constant
During discharging, the rate of decrease of the capacitor’s voltage is:
A) Exponential
B) Linear
C) Constant
D) Logarithmic
During charging, the rate of change of voltage across a capacitor is:
A) Decreasing
B) Constant
C) Increasing
D) Zero
The capacitor’s voltage after one time constant
τ during charging is:
A) 37% of the maximum voltage
B) 63% of the maximum voltage
C) 50% of the maximum voltage
D) 90% of the maximum voltage
The time constant of an RC circuit determines how:
A) Fast the capacitor charges or discharges
B) High the voltage can be
C) Large the capacitance is
D) Strong the current is
For a capacitor discharging through a resistor, the charge on the capacitor decreases:
A) Exponentially
B) Linearly
C) Constantly
D) Logarithmically
At the end of one time constant
τ during discharging, the capacitor’s voltage is:
A) 37% of its initial value
B) 63% of its initial value
C) 50% of its initial value
D) 90% of its initial value
In a charging capacitor circuit, the rate of change of current is:
A) Exponential
B) Linear
C) Constant
D) Logarithmic
The discharge current of a capacitor through a resistor decreases:
A) Exponentially
B) Linearly
C) Constantly
D) Logarithmically
When a capacitor is connected in series with a resistor and a battery, the capacitor:
A) Charges up to the supply voltage
B) Charges to 37% of the supply voltage
C) Does not charge
D) Discharges immediately
The capacitor’s current during charging is initially:
A) Maximum
B) Zero
C) Constant
D) Minimal
After how many time constants is a capacitor considered fully discharged?
A) 1 time constant
B) 2 time constants
C) 5 time constants
D) 10 time constants
The charging current of a capacitor through a resistor decreases:
A) Exponentially
B) Linearly
C) Constantly
D) Logarithmically
The time constant of a capacitor-resistor circuit is:
A) Directly proportional to both resistance and capacitance
B) Inversely proportional to resistance and capacitance
C) Directly proportional to resistance only
D) Inversely proportional to capacitance only
The rate at which a capacitor charges up depends on:
A) The resistance and capacitance in the circuit
B) The voltage of the capacitor
C) The initial charge of the capacitor
D) The current through the capacitor
After discharging for 5 time constants, the capacitor’s charge is:
A) Almost zero
B) 50% of its initial charge
C) 37% of its initial charge
D) The same as its initial charge
The voltage across a capacitor while discharging:
A) Decreases exponentially
B) Increases exponentially
C) Remains constant
D) Decreases linearly
In a series RC circuit, if the capacitance is doubled, the time constant will:
A) Double
B) Halve
C) Remain unchanged
D) Increase by a factor of four
During discharging, the time constant affects:
A) The rate at which the capacitor discharges
B) The maximum voltage of the capacitor
C) The resistance of the capacitor
D) The capacitance of the capacitor
When a capacitor discharges through a resistor, the voltage drops:
A) Exponentially
B) Linearly
C) Constantly
D) Logarithmically
The charging current of a capacitor is initially:
A) Maximum
B) Zero
C) Constant
D) Minimal
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.