Lenz’s Law And Conservation Of Energy MDCAT MCQs
Welcome to the Lenz’s Law And Conservation Of Energy MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Lenz’s Law And Conservation Of Energy Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Physics offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Lenz’s Law And Conservation Of Energy MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Lenz’s Law states that the direction of the induced current is such that it:
a) Opposes the cause of its production
b) Aids the cause of its production
c) Is random
d) Is perpendicular to the magnetic field
According to the principle of conservation of energy, energy can:
a) Neither be created nor destroyed
b) Be created from nothing
c) Be destroyed completely
d) Be converted into mass
Lenz’s Law ensures that the induced EMF opposes the change in magnetic flux, which is consistent with:
a) Conservation of energy
b) Conservation of momentum
c) Conservation of charge
d) Conservation of mass
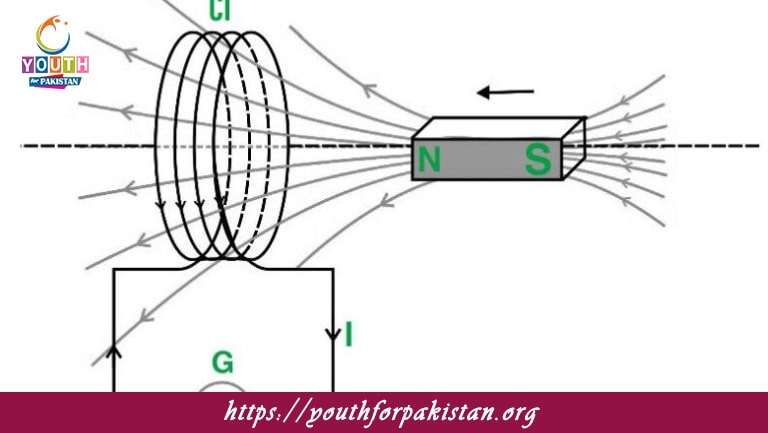
When a magnet is moved towards a coil, the induced current in the coil creates a magnetic field that:
a) Opposes the magnet’s motion
b) Supports the magnet’s motion
c) Is neutral
d) Increases the speed of the magnet
The negative sign in Faraday’s law of induction (E = -dΦ/dt) represents:
a) The direction of induced EMF as per Lenz’s Law
b) The magnitude of induced EMF
c) The energy dissipation
d) The phase difference between voltage and current
The opposing nature of induced current in Lenz’s Law indicates that the system will:
a) Conserve energy
b) Lose energy
c) Gain energy
d) Convert energy into mass
If the magnetic flux through a coil increases, the induced current will:
a) Flow in a direction to oppose the flux increase
b) Flow in a direction to increase the flux further
c) Not be generated
d) Be randomly directed
Lenz’s Law is a direct consequence of which fundamental principle?
a) Newton’s Third Law
b) Conservation of charge
c) Conservation of energy
d) Conservation of momentum
The induced EMF in a coil due to a changing magnetic field will:
a) Oppose the change in magnetic field
b) Support the change in magnetic field
c) Remain unaffected
d) Cause an increase in the magnetic field
Lenz’s Law helps in:
a) Determining the direction of induced current
b) Calculating the magnitude of current
c) Measuring the resistance of a circuit
d) Increasing the voltage across a resistor
In an electric generator, the induced EMF due to the movement of the coil in a magnetic field opposes the applied mechanical work. This is an application of:
a) Lenz’s Law and Conservation of Energy
b) Newton’s Second Law
c) Ohm’s Law
d) Kirchhoff’s Law
Lenz’s Law states that the induced current will flow in a direction that opposes:
a) The change in magnetic flux
b) The existing magnetic field
c) The electric field
d) The velocity of the charge carriers
According to Lenz’s Law, the direction of induced current in a closed loop due to a changing magnetic field is such that it creates:
a) A magnetic field opposing the original change
b) A magnetic field aiding the original change
c) A parallel electric field
d) No magnetic field
The conservation of energy in an electromagnetic system ensures that the total energy remains:
a) Constant
b) Increasing
c) Decreasing
d) Zero
When the magnetic flux through a coil changes, the induced EMF works to:
a) Oppose the flux change
b) Enhance the flux change
c) Have no effect
d) Increase the temperature of the coil
Lenz’s Law provides a physical interpretation of:
a) The conservation of energy in electromagnetic processes
b) The generation of magnetic fields
c) The movement of electric charges
d) The distribution of electric fields
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction respects the law of conservation of energy by ensuring that:
a) The induced EMF opposes the cause of induction
b) The induced current supports the change in flux
c) The energy is created in the circuit
d) The magnetic field is constant
The energy converted from mechanical to electrical form in a generator is consistent with:
a) Lenz’s Law
b) Faraday’s Law
c) Ampere’s Law
d) Coulomb’s Law
In a transformer, the conservation of energy is maintained because:
a) The input power equals the output power, accounting for losses
b) The input power is less than the output power
c) The input power is greater than the output power
d) There is no energy conversion
When a conductor moves through a magnetic field, the work done in moving the conductor is converted into:
a) Electrical energy
b) Kinetic energy
c) Thermal energy
d) Potential energy
The opposing EMF generated in an inductive circuit is due to:
a) Lenz’s Law
b) Ohm’s Law
c) Coulomb’s Law
d) Gauss’s Law
Lenz’s Law can be used to predict the:
a) Direction of induced current
b) Magnitude of magnetic flux
c) Electric field strength
d) Number of charge carriers
Lenz’s Law and the principle of conservation of energy are demonstrated in:
a) Eddy currents
b) Superconductors
c) Insulators
d) Capacitors
When a magnetic field through a loop increases, the induced current flows in a direction that:
a) Produces a magnetic field opposing the increase
b) Supports the increase
c) Increases the loop’s area
d) Causes the magnetic field to remain constant
The work done against the induced EMF in a moving conductor is converted into:
a) Electrical energy
b) Thermal energy
c) Kinetic energy
d) Chemical energy
In an electric motor, Lenz’s Law ensures that:
a) The rotor moves in the direction opposite to the magnetic force
b) The rotor speed is directly proportional to the current
c) The system conserves energy
d) The motor generates more energy than it consumes
In an electromagnetic system, Lenz’s Law provides:
a) A method to calculate the energy conversion efficiency
b) A technique to generate excess energy
c) A way to store electrical energy
d) A means to eliminate energy loss
The opposition of the induced current to the applied magnetic field change in a coil demonstrates:
a) Lenz’s Law and energy conservation
b) Kirchhoff’s Laws
c) Maxwell’s Equations
d) The photoelectric effect
In a superconducting loop, an induced current due to a changing magnetic field will:
a) Persist indefinitely
b) Dissipate quickly
c) Generate heat
d) Increase the loop’s resistance
In a generator, Lenz’s Law causes:
a) A drag force opposing the motion
b) An accelerating force
c) An increase in mechanical energy
d) A decrease in resistance
The principle of conservation of energy in an electromagnetic system states that:
a) The total energy remains constant
b) Energy is created
c) Energy is destroyed
d) Magnetic energy is always zero
Lenz’s Law is crucial in understanding the functioning of:
a) Induction cooktops
b) Light-emitting diodes
c) Solar cells
d) Chemical batteries
The opposing force experienced when moving a conductor through a magnetic field is due to:
a) Lenz’s Law
b) Coulomb’s Law
c) Ampere’s Law
d) Faraday’s Law
Lenz’s Law helps in maintaining:
a) The conservation of energy
b) The generation of energy
c) The destruction of energy
d) The conservation of momentum
The principle that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but only transformed is demonstrated by:
a) Lenz’s Law
b) Ohm’s Law
c) Coulomb’s Law
d) Pascal’s Law
In electromagnetic braking, the braking force is due to:
a) Lenz’s Law
b) Newton’s First Law
c) Archimedes’ Principle
d) Bernoulli’s Principle
The existence of Lenz’s Law ensures that an induced current always opposes:
a) The change that produced it
b) The direction of the magnetic field
c) The electric field
d) The temperature gradient
In a circuit, the work done against the induced EMF is stored as:
a) Magnetic energy
b) Thermal energy
c) Potential energy
d) Kinetic energy
The conservation of energy in an electromagnetic system prevents:
a) Perpetual motion machines
b) Efficient energy transfer
c) Energy conversion
d) Magnetic flux change
The direction of induced current as per Lenz’s Law ensures:
a) Energy is not created out of nothing
b) Energy is maximized
c) Energy is dissipated
d) Energy is amplified
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.





