Biological Enzymes MDCAT Quiz: Enzymes are essential biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body, making them a key topic for MDCAT preparation. Understanding the structure, function, and types of enzymes is fundamental for students studying biochemistry and physiology. Enhance your learning by practicing with an MDCAT Quiz focused on enzymes, helping you gain mastery over this essential concept for your exams.
Role and Function of Enzymes
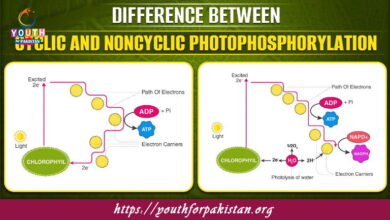
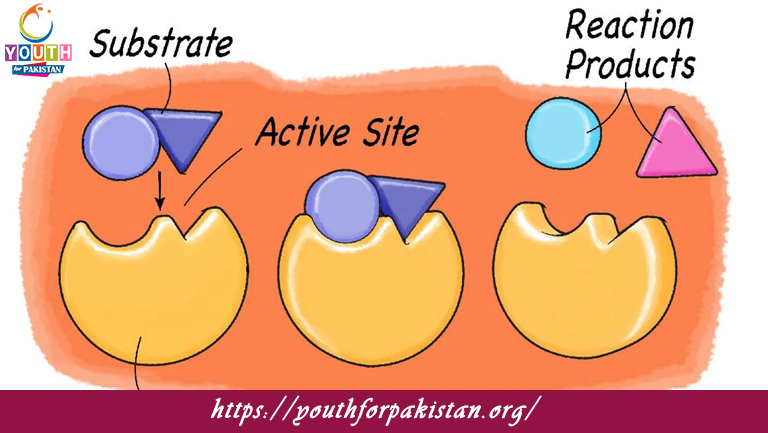
Enzymes are highly specialized proteins that lower the activation energy required for biochemical reactions. Each enzyme is specific to a particular substrate and catalyzes a particular reaction, such as digestion, metabolism, and DNA replication. Key factors like temperature, pH, and enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity. For example, amylase helps break down carbohydrates in the mouth, while lipase aids in fat digestion. A clear understanding of enzyme kinetics, including concepts like the lock-and-key model and induced fit model, is essential for MDCAT students.
MDCAT Quiz on Enzymes
Prepare effectively with an MDCAT Quiz that dives deep into the structure, function, and mechanisms of enzymes. The quiz covers important topics such as enzyme inhibition—both competitive and non-competitive—and coenzymes, the effects of various factors on enzyme activity. Regular practice with this quiz not only reinforces your understanding of enzymes but also teaches you how to handle MDCAT questions confidently.
Free Flashcards for Enzyme Study
Complement your preparation with Free Flashcards designed specifically to help you learn and memorize key concepts related to enzymes. These flashcards are great, with detailed definitions, examples of enzymes, and visual illustrations of enzyme-substrate interaction models—all of which make them an excellent resource for quick revision. The frequent use of these flashcards will strengthen your retention and improve your recall ability during the MDCAT exam.
The importance of mastering enzymes cannot be denied, especially for biochemistry and physiology in the MDCAT. So, use quizzes and flashcards to make sure you understand everything about enzymes, have better retention, and be confident when attempting associated questions in your exams.

The enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen is _______.
Catalase

_______ is an enzyme that helps break down collagen and other proteins found in connective tissues.
Collagenase

_______ is the enzyme responsible for converting pepsinogen into its active form, pepsin.
HCl (Hydrochloric acid)

The enzyme that converts citric acid into various intermediates in the citric acid cycle is _______.
Citrate synthase

_______ is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate in cells.
Hexokinase
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.