Characteristics Of Projectile Motion MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Characteristics Of Projectile Motion MDCAT Quiz wherein an object moves in a curved path under the influence of gravity with no propulsion after it has been launched. The characteristics that MDCAT students will acquaint themselves with in this respect include: independence of horizontal and vertical components of this motion, parabolic nature of the trajectory, and constant acceleration due to gravity. For MDCAT students, the mastering of these characteristics is of great importance to understand and solve physics problems related to motion and trajectories in the MDCAT Quiz.
Key Characteristics of Projectile Motion
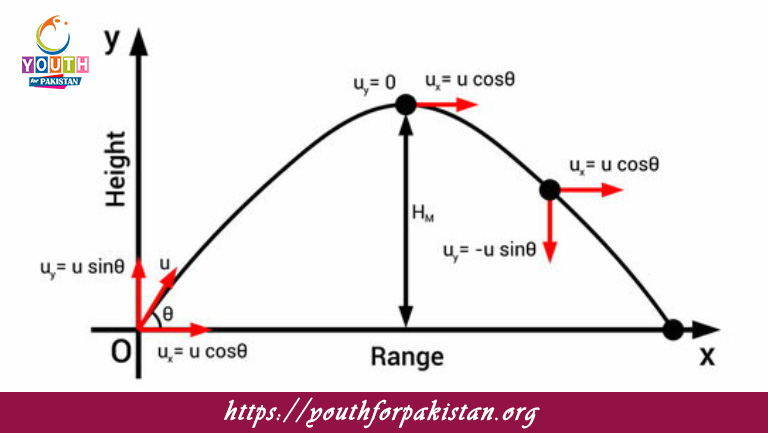
Projectile motion is governed by strict laws that dictate its motion. The horizontal motion, first of all, is at a constant velocity since no external forces—ignoring air resistance—act in that direction. In the vertical direction, though, the motion is affected by gravity; hence, it accelerates downward at a constant rate of 9.8m/s2. The trajectory of the projectile is parabolic, due to the combination of horizontal and vertical motions. At the highest point of its flight, the vertical velocity is momentarily zero before the object starts descending. These principles put MDCAT students in a position to calculate important parameters such as range, maximum height, and total time of flight using equations of motion.
MDCAT Quiz: Questions on Projectile Motion Characteristics
The MDCAT Quiz often includes questions dealing with the characteristics of projectile motion. For example, it may ask one to calculate the time of flight, maximum altitude, or horizontal range of an object. Another common question in this area involves determining the initial velocity components given a launch angle and speed. Such problems check the ability of the student to decompose the motion into horizontal and vertical components and correctly apply the kinematic equations. Practice is essential for mastering these concepts to improve problem-solving accuracy.
- Test Name: Characteristics Of Projectile Motion MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Projectile Motion Characteristics
Free flashcards can be a useful tool in helping MDCAT students memorize and review the characteristics of projectile motion. The flashcards may comprise key definitions and important equations. This will be done through regular review of flashcards, for students to retain critical information and hence apply it confidently while solving the MDCAT Quiz. This method incorporated into study routines will improve understanding and performance in physics topics related to motion and forces.
The acceleration acting on a projectile in the vertical direction is __________.
9.8 m/s29.8 , text{m/s}^29.8m/s2 downwards
A projectile launched at 30∘30^circ30∘ has the same range as one launched at __________.
60∘60^circ60∘
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.