Elastic Collision In One Dimension MDCAT Quiz with Answers
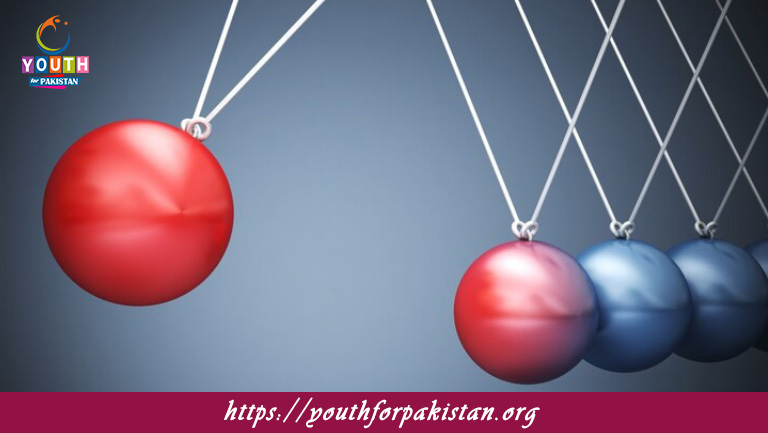

An Elastic Collision In One Dimension MDCAT Quiz is a specific type of collision where two objects move along a straight line before and after the interaction, and both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. This topic is highly relevant for MDCAT students, as it often appears in the physics section of the exam. Understanding how to apply the conservation laws in such collisions helps students analyze motion effectively and solve complex problems in the MDCAT Quiz.
Understanding Elastic Collisions in One Dimension
In a one-dimensional elastic collision, the objects involved move along a single axis, simplifying the calculations. The Law of Conservation of Momentum applies, stating that the total momentum of the system remains constant. MDCAT students must be able to use these equations to solve numerical problems systematically.
MDCAT Quiz: Elastic Collision in One Dimension Questions
The MDCAT Quiz frequently includes questions on elastic collisions in one dimension. These problems often require calculating the final velocities of the objects involved. For example, a question might provide the masses and initial velocities of two colliding objects and ask students to determine their velocities after the collision. Sometimes, students may also encounter conceptual questions, such as explaining why kinetic energy and momentum are conserved in elastic collisions. Practicing these types of problems helps students solidify their understanding of the underlying physics and perform better on the MDCAT exam.
- Test Name: Elastic Collision In One Dimension MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Elastic Collision in One Dimension
Free flashcards of one-dimensional elastic collisions can reinforce key concepts and equations for MDCAT preparation. These may include the formulas for the conservation of momentum and kinetic energy, together with step-by-step examples on how to solve typical collision problems. Going through these flashcards on a daily basis would help the student retain key principles and give them more confidence while solving collision-related problems in the MDCAT Quiz. Flashcards are good at increasing memory retention and boosting a student’s confidence in answering collision-related questions in the MDCAT Quiz.

The relative velocity of approach equals the relative velocity of __________ in elastic collisions.
separation

For elastic collisions in one dimension, the sum of initial and final kinetic energy is __________.
equal

If two objects with equal masses collide elastically in one dimension, they will __________ velocities.
exchange

The formula v1′=(m1−m2)v1+2m2v2m1+m2v_1' = frac{(m_1 - m_2)v_1 + 2m_2v_2}{m_1 + m_2}v1′=m1+m2(m1−m2)v1+2m2v2 calculates the final velocity of __________.
object 1

In an elastic collision, if one object is stationary before collision, its final velocity depends on __________.
the mass and velocity of the moving object

If two objects collide elastically in one dimension with equal masses, their final velocities __________.
are exchanged

Elastic collisions in one dimension can be analyzed using the equation for __________.
conservation of energy

The final velocities after a one-dimensional elastic collision depend on __________.
masses and initial velocities

In elastic collisions, the relative speed of separation is __________ the relative speed of approach.
equal to

For one-dimensional elastic collisions, the coefficient of restitution formula is __________.
e=1e = 1e=1

In an elastic collision in one dimension, when two identical objects collide, their velocities __________.
are swapped

The kinetic energy of each individual object in a one-dimensional elastic collision __________.
may change
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.