Speed Of Sound In Air MDCAT Quiz with Answers
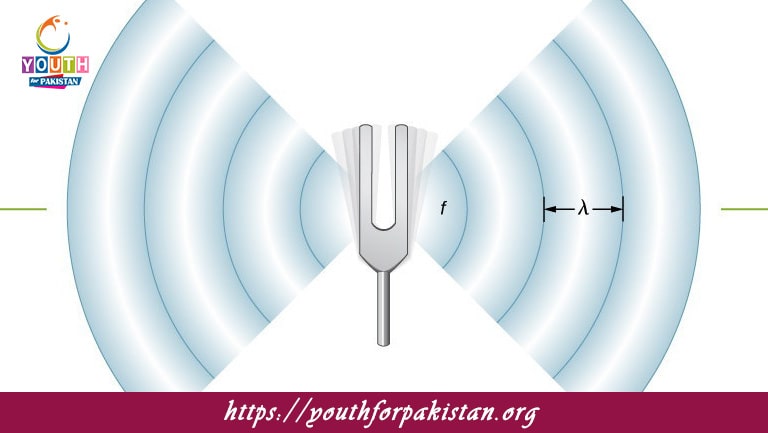
Speed Of Sound In Air MDCAT Quiz refers to the rate at which sound waves travel through the air. It is thus influenced by air temperature, pressure, and even its humidity. Usually, sound propagates faster through warmer air media and slower in cooler air. The speed of sound is therefore a very imperative concept in physics, holding crucial roles in the fields of acoustics, meteorology, and engineering. Therefore, MDCAT students need a thorough understanding regarding the speed of sound to accurately solve questions relevant to sound waves and wave propagation in air.
Factors Influencing Speed of Sound in Air
Temperature: Normally, the velocity of sound through air increases in correspondence with any increase in the temperature. So, at higher temperatures, particles of air media are relatively at higher mean speeds; therefore, they facilitate quick transmission of sounds. The general relation between velocity and temperature in degrees Celsius could be expressed by: v = 331 + 0.6 Tv = 331 + 0.6T v= velocity (speed) in m/s, T = temperature in centigrade Celsius.
Humidity: Increasing the humidity also causes an increase in the speed of sound. Since water vapor is less dense than dry air, moist air has less resistance to the movement of sound waves; thus, this causes sound to travel faster through humid air compared to dry air with the same temperature.
Air Pressure: Usually, the normal amount of pressure that air carries is not much of an influential factor for the speed of sound because pressure goes up both for density and temperature. The velocity of sound in air under abnormal conditions can show slight deviations because of drastic pressure changes when present at extremely high altitudes or under odd situations.
Medium: Although the focus here was all about the speed of sound through air, one would realize that the velocity is different through mediums. Liquids and solids make sound move quicker than a gas because liquids and solids have much more density and rigidity in comparison.
Speed of Sound at Standard Conditions
At 0°C (273 K), the speed of sound in dry air is approximately 331 m/s. For each 1°C rise in temperature, the speed of sound increases by 0.6 m/s. Thus, at 20°C, which is about room temperature, the speed of sound in air is about 343 m/s.
MDCAT Quiz: Speed of Sound in Air
In the MDCAT, one may find questions related to the speed of sound in air, including problems with temperature changes, humidity, and calculating sound speed at different conditions. For example, a question may ask one to calculate the speed of sound at a specific temperature or to use the temperature-speed relationship in finding the change in sound speed when the temperature changes.
- Test Name: Speed Of Sound In Air MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Speed of Sound in Air
Free flashcards on the speed of sound in air can be a very good resource for MDCAT students. The key concepts that can be included in these flashcards are the relationship between temperature and speed, the effects of humidity, and examples of calculations involving the speed of sound. Reviewing these flashcards regularly will help students reinforce their understanding of the properties of sound waves and improve their ability to solve related questions in the MDCAT Quiz.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.