Transverse Waves MDCAT Quiz is a type of wave in which the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. In other words, as the wave travels through the medium, the individual particles vibrate up and down or side to side, while the wave itself moves in the forward direction. Transverse waves are common in many natural phenomena, such as light waves, water waves, and waves on a string. MDCAT students have to understand characteristics and behavior associated with transverse waves since most of the phenomena related to waves are frequently asked in physics.
Characteristics of Transverse Waves
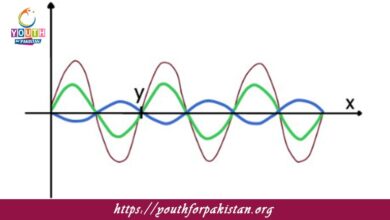
Particle Motion: In a transverse wave, the particles of the medium oscillate at right angles (perpendicular) to the direction in which the wave is traveling. For example, in a water wave, the water particles move up and down, while the wave itself moves horizontally.
Crests and Troughs: High points of the wave are called crests, and the low points are known as troughs. These points help in defining the amplitude and shape of the wave. The distance between two successive crests (or two successive troughs) is called the wavelength.
Amplitude: The amplitude of a transverse wave is the maximum displacement of the particles from their equilibrium position. It is measured from the midpoint (rest position) to the crest or trough. Larger amplitudes correspond to waves with higher energy.
MDCAT Quiz: Transverse Waves Questions
In the MDCAT Quiz, a student may be asked to describe some of the characteristics of transverse waves, including finding the amplitude, wavelength, and frequency from a diagram or problem. More importantly, questions may come about the behavior of transverse waves in different media or calculations related to wave speed. In other words, an understanding of these major attributes of transverse waves relative to other wave phenomena is critical for success in this exam.
- Test Name: Transverse Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
0Get Your Username and Password for MDCAT Tests
Sign Up Now
Free Flashcards for Transverse Waves
Free flashcards on transverse waves help MDCAT students consolidate their understanding of this type of wave. Flashcards may include visual aids like diagrams of transverse waves showing crests, troughs, amplitude, and wavelength, along with formulas for calculating wave properties. Going through these flashcards regularly will make the students revise what they know and will let them be better prepared for questions on waves in the MDCAT Quiz.

What is the characteristic motion of particles in a transverse wave?
The particles move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation

Which of the following is an example of a transverse wave?

In a transverse wave, where is the displacement of particles at the crest?
Maximum upward displacement

In a transverse wave, where is the displacement of particles at the trough?
Maximum downward displacement

What is the direction of particle motion in a transverse wave?
Perpendicular to the direction of wave travel

How does the amplitude of a transverse wave affect its energy?
Greater amplitude results in more energy

Which of the following is not a transverse wave?

What does the crest of a transverse wave represent?
The maximum displacement of particles in the upward direction

What is the distance between two consecutive crests in a transverse wave?

How is the amplitude of a transverse wave defined?
The maximum displacement of particles from the equilibrium position

What happens to the energy of a transverse wave when the amplitude is increased?

In which type of medium do transverse waves typically travel?

What is the shape of a transverse wave?
It forms a sinusoidal curve

What is the effect of increasing the frequency of a transverse wave?
The wave becomes more energetic

How are transverse waves different from longitudinal waves?
In transverse waves, particles move perpendicular to the wave direction

What is the phase difference between two points on a transverse wave that are one wavelength apart?

How does the frequency of a transverse wave relate to its wavelength?
Higher frequency results in a shorter wavelength

What kind of wave can transfer energy without transferring matter?

In a transverse wave, where is the velocity of the particles zero?
At the equilibrium position

Which of the following is true about the speed of a transverse wave?
The speed is constant for a given medium

What is the relationship between the wavelength and frequency of a transverse wave?
Wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency

What type of wave is a water wave?

In a transverse wave, what happens when two waves meet in phase?
They undergo constructive interference

What is the relationship between the velocity, frequency, and wavelength of a transverse wave?
Velocity = Frequency × Wavelength

What does the amplitude of a transverse wave determine?

In a transverse wave, the direction of vibration is
Perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer

What is the motion of particles in a transverse wave in relation to the direction of the wave?
The motion is perpendicular to the wave's direction

How is a transverse wave created in a stretched string?
By disturbing the string vertically

What happens to a transverse wave when it passes from one medium to another?
It may change speed and direction

Which of the following waves is not an example of a transverse wave?
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.
View Your Dashboard