Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium oscillate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. These waves repeat at regular intervals, forming a periodic pattern of oscillations. The energy of a transverse periodic wave is transferred through the medium in the form of oscillations, but the individual particles of the medium only move up and down (or side to side), not along the direction the wave travels. In MDCAT, this forms an important concept, especially in topics related to wave motion, wave speed, and energy transfer.
Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz
Particle Motion: In a transverse periodic wave, the displacement of particles is perpendicular to the wave’s propagation direction. For instance, if the rope or string is used as a medium, then the particles move up and down, but the wave itself moves horizontally. The motion of the particles occurs in a repeating, periodic manner.
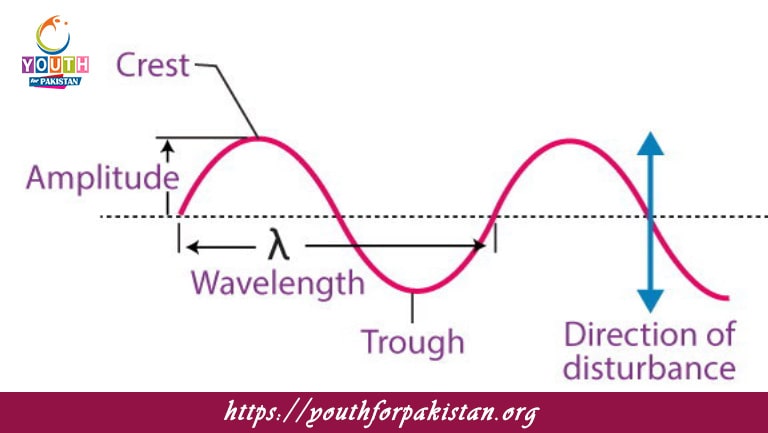
CRESTS AND TROUGHS: The wave consists of crests and troughs. The crests are the high points, while the troughs are the low points. The distance between two successive crests or two successive troughs is called the wavelength of the wave. This pattern repeats regularly, giving the wave its periodic nature.
Amplitude: The amplitude of a transverse periodic wave is defined as the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position. The greater the amplitude, the more energy the wave carries. Thus, for a sound wave, high amplitude corresponds to loud sounds.
Examples of Transverse Periodic Waves
Waves on a String: When a string is vibrated, for example in musical instruments, it creates a transverse periodic wave. Particles of the string move up and down periodically, transferring energy along the string. Such waves are described by their amplitude, wavelength, and frequency.
Water Waves. The waves on the surface of water are transverse periodic waves. The water particles move up and down in a regular, oscillating pattern as the wave propagates horizontally across the surface.
Electromagnetic Waves: Light waves and other forms of electromagnetic radiation (such as radio waves, microwaves, etc.) are transverse waves, where electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave travel. These waves do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum.
Seismic Waves: Some seismic waves (specifically S-waves or shear waves) are transverse periodic waves. These waves travel through the Earth and cause the ground to move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
Interference: When two transverse waves meet, they can interfere with each other. If the waves are in phase—meaning the crests align with the crests and troughs with the troughs—then they will undergo constructive interference, resulting in a wave having a larger amplitude. If they are out of phase—meaning crests align with troughs—then they will undergo destructive interference, which can cancel out the waves.
Reflection: A transverse wave can be reflected from a boundary, for example, a wall or a fixed end of the string. The reflection may be inverted or non-inverted depending on the conditions at the boundary.
Diffraction: When a transverse wave goes through a narrow opening or encounters an obstacle, it can bend around the obstacle, creating a pattern of wave propagation. This is called diffraction.
MDCAT Quiz: Transverse Periodic Waves Questions
In the MDCAT Quiz, expect questions on what is known regarding the properties of transverse periodic waves. That may include any question about relations among amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and speed of waves. Similarly, some questions may want students to describe an interference scenario or solve an application problem. Understanding the properties of transverse periodic waves better will help the student answer that type of question in the MDCAT Quiz.
- Test Name: Transverse Periodic Waves MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Transverse Periodic Waves
Free flashcards on transverse periodic waves are an effective way for MDCAT students to master this concept. The flashcards may have waveforms diagrams and definitions of such important terms as amplitude, wavelength, and frequency; they should also give problems that will help reinforce the mathematical relationships of transverse waves. Going through these flashcards on a daily basis will make the student much more prepared for the questions related to waves that appear in the MDCAT Quiz.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.