Capacitor MDCAT Quiz with Answers
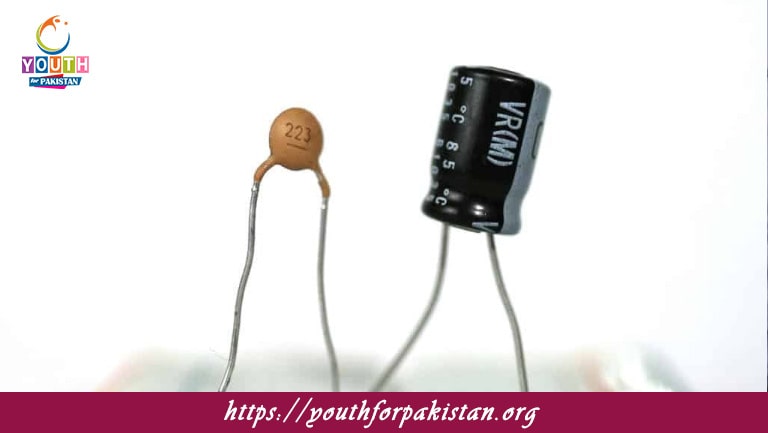

A Capacitor MDCAT Quiz is a two-terminal electronic component with the ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. It basically contains two conductive plates separated by an insulating material, known as a dielectric. Capacitors are extremely important components in many types of electronic devices and systems; therefore, understanding their principle of working and behavior is necessary for MDCAT students going to appear in physics examinations.
Definition and Working Principle
A capacitor is said to store energy when a voltage difference is applied across its plates. The bigger the voltage, the larger the electric field between the plates; this results in opposite charges accumulating on each plate. How much charge a capacitor can store depends on its capacitance, defined as the amount of charge stored per unit voltage:
Types of Capacitors
Fixed Capacitors: These are capacitors with fixed values of capacitance, often chosen for particular uses in energy storage and signal filtering.
Variable Capacitors: These make it possible to mechanically or electronically alter capacitance; common in applications related to tuning circuits.
Electrolytic Capacitors: These are polarized capacitors with high capacitance values, often used in power supply filters.
Supercapacitors: These have very high values of capacitance and are used in energy storage applications in modern electronics.
Applications of Capacitors
Energy Storage: Capacitors store energy and release it when needed. They are applied in many areas, including power supply systems, cameras (flash capacitors), and backup systems.
Filtering: Capacitors smooth voltage fluctuations in power supplies by filtering out noise and reducing ripple in DC circuits.
Tuning Circuits: Capacitors are used in tuning circuits in radio receivers and transmitters for the selection of specific frequencies.
Signal Processing: Capacitors can be used in amplifiers and filters for the modification of signal frequency in communication systems.
MDCAT Quiz: Capacitor
The MDCAT Quiz on Capacitors often includes questions about the calculation of capacitance, energy storage, and the behavior of capacitors in different configurations. Students may be asked to find the capacitance of a capacitor with a given dielectric or to find how much energy is stored in a capacitor with a given voltage and capacitance value.
- Test Name: Capacitor MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Capacitors
Free flashcards for capacitors provide an excellent way to review key concepts,
These flashcards will help MDCAT students solidify their knowledge and perform better on electrostatics and electronics-based questions.

The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depends on:
Area of the plates and distance between them

The total capacitance of capacitors connected in series is:
Less than the capacitance of the smallest capacitor

The capacitance of a capacitor with a dielectric is:
Greater than the capacitance without a dielectric

When a charged capacitor is connected to a resistor, the charge on the capacitor:
Decays exponentially

The capacitance of a capacitor with a dielectric constant k is:
k times the capacitance without the dielectric
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.