Thermodynamics MDCAT Quiz with Answers
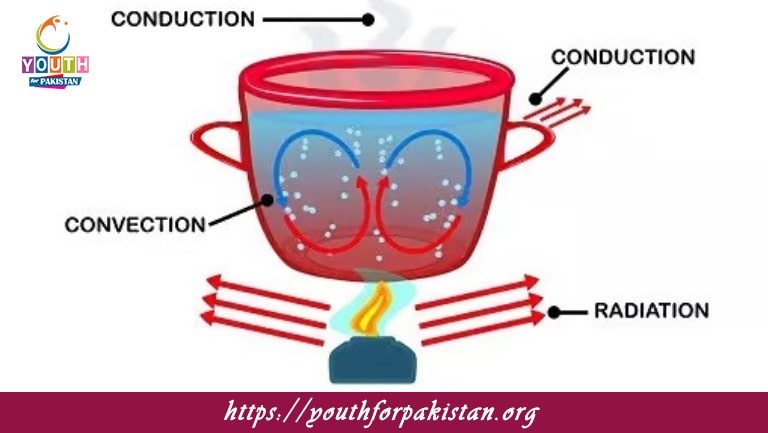
Thermodynamics MDCAT Quiz is that branch of science which tells us about the relations between heat, work, and energy. This topic is crucial for the students appearing in MDCAT because it is one of those subjects that tells about the critical understanding of the transformations of energy, systems, and processes. Our specialized MDCAT Quiz on thermodynamics contains everything from the most basic to complex applications. Thus, it ensures you understand this important subject properly.
MDCAT Thermodynamics Quiz to Succeed
Prepare to ace the MDCAT exam with our detailed thermodynamics quiz that delves into key areas such as the laws of thermodynamics, energy flow in systems, and behavior of gases. This quiz will challenge your understanding of concepts such as enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy, while helping you apply these principles to real-world scenarios. Whether it is understanding how heat engines work or calculating the efficiency of processes, our quiz is designed to reinforce your knowledge and boost your confidence for the exam.
- Test Name: Thermodynamics MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Thermodynamics Preparation
Our free flashcards for thermodynamics make studying efficient and engaging. These flashcards include concise definitions, formulas, and practical examples that are directly relevant to MDCAT exam topics. Quickly revise the key principles of thermodynamics, such as the laws governing energy transfer, thermodynamic cycles, and their applications in biological systems. These flashcards are an invaluable resource to strengthen your conceptual understanding and improve retention of important information.

The heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius is called:
Specific heat capacity

The law stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed is known as:
The first law of thermodynamics
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.