Electric Field And Its Intensity MDCAT Quiz with Answers
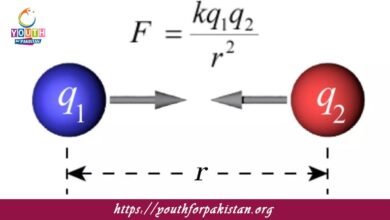
The Electric Field And Its Intensity MDCAT Quiz is one of the basic concepts of electromagnetism. It describes the influence a charged object exerts on its surroundings. The electric field is defined as the force per unit charge experienced by a small positive test charge placed in the field. The electric field is very important to MDCAT students since it gives a basis for the understanding of the interaction of charges, the exertion of forces in electric fields, and the distribution of potential energy.
Properties of Electric Fields
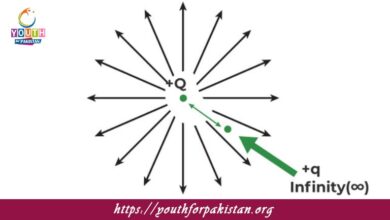
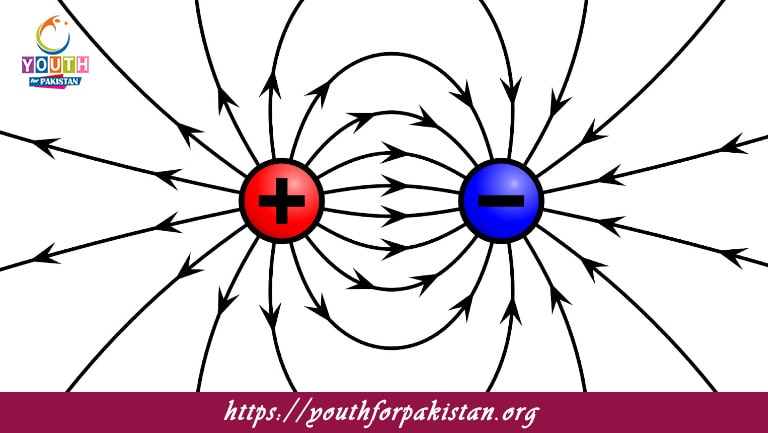
Field Lines: Electric field lines represent the path that a positive test charge would follow. They begin at positive charges and end at negative charges. The density of these lines indicates the strength of the electric field.
Superposition Principle: The total electric field due to multiple charges is the vector sum of the electric fields produced by each charge.
Electric Potential: The electric field is associated with the electric potential energy of a charge in the field. The field is the gradient (spatial derivative) of the potential.
Applications of Electric Field and Intensity
Capacitors: Electric fields play a crucial role in the operation of capacitors, which store energy in the form of an electric field between two plates.
Electric Forces in Biology: The electric field is very important in the functioning of biological systems, as in the cases of nerve signaling and the behavior of ions in cells.
Electrostatic Shielding: By understanding electric fields, one can design shielding systems like Faraday cages, which do not allow external electric fields to enter.
MDCAT Quiz: Electric Field and Intensity
The MDCAT Quiz on Electric Field and Intensity largely has problems to calculate an electric field due to point charges, examine in detail the behavior of field lines, and use the principle of superposition. The student may be asked questions that have to do with vector addition of electric fields or finding the net electric field at certain points in a system.
- Test Name: Electric Field And Its Intensity MDCAT Quiz
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 30
- Total Marks: 30
- Time: 30 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test, once you are finished, click the View Results button.
Free Flashcards for Electric Field and Intensity
Free flashcards for electric field and intensity are helpful to revise the concept rapidly and to practice it.
Diagrams of electric field lines around point charges, Conceptual questions on the nature of electric fields and forces. Using these flashcards, MDCAT students will be able to strengthen their problem-solving skills and better understand the concept of an electric field.
Experience the real exam environment with our expertly designed collection of over 25,000 MCQs MDCAT Mock Tests.